
A comparative analysis of two methods for the... of electric-field-induced perturbations to molecular vibration
... the normal coordinate m1l2(R-Re), where m is the reduced nuclear mass and R is the internuclear separation. The second and third terms in Eq. (3) are referred to as the electrical harmonicity and anharmonicity, respectively. The wave function tPo can be found as a perturbed harmonic oscillator wave ...
... the normal coordinate m1l2(R-Re), where m is the reduced nuclear mass and R is the internuclear separation. The second and third terms in Eq. (3) are referred to as the electrical harmonicity and anharmonicity, respectively. The wave function tPo can be found as a perturbed harmonic oscillator wave ...
Random Laser - Department of Physics
... photons to be emitted. Similarly, lower excitation energy tends to reduce the photon emission. If the electron energy is less than the energy difference between the ground state and the first excited state (which is the band gap), then no electron absorption occurs, resulting in no CL. CL can be obs ...
... photons to be emitted. Similarly, lower excitation energy tends to reduce the photon emission. If the electron energy is less than the energy difference between the ground state and the first excited state (which is the band gap), then no electron absorption occurs, resulting in no CL. CL can be obs ...
A1983PW59500001
... man in Paris. It was he who dug out my paper and suggested to Tejiro Yonezawa and me 1 2 that we apply my method to amino acids. . Only then did the ‘Del Re method’ start its career. A curious one indeed, as I could see when reviewing the method in 1980.~In spite of its simplicity, and in spite of b ...
... man in Paris. It was he who dug out my paper and suggested to Tejiro Yonezawa and me 1 2 that we apply my method to amino acids. . Only then did the ‘Del Re method’ start its career. A curious one indeed, as I could see when reviewing the method in 1980.~In spite of its simplicity, and in spite of b ...
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... • Bohr argued that the electrons in a atom also couldn’t lose energy continuously, but must do so in quantum “jumps” • Bohr assumed that the electrons move about in a certain circular orbit • Each orbit have a specific amount of energy • The electrons could move about in that orbit without radiatin ...
... • Bohr argued that the electrons in a atom also couldn’t lose energy continuously, but must do so in quantum “jumps” • Bohr assumed that the electrons move about in a certain circular orbit • Each orbit have a specific amount of energy • The electrons could move about in that orbit without radiatin ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - An introduction
... Spin-orbit coupling/ splitting: final state effect for orbitals with orbital angular momentum l> 0. A magnetic interaction between an electron’s spin and its orbital angular momentum. Example Ti. Upon photoemission an electron from the p orbital is removed - remaining electron can adopt one of two c ...
... Spin-orbit coupling/ splitting: final state effect for orbitals with orbital angular momentum l> 0. A magnetic interaction between an electron’s spin and its orbital angular momentum. Example Ti. Upon photoemission an electron from the p orbital is removed - remaining electron can adopt one of two c ...
Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding
... Ans2. Lyman series: When excited electrons in hydrogen atoms fall from higher energy levels to first energy level, the series of lines observed are called Lyman series. They are observed in ultraviolet region. Lyman = R(1/12 - 1/n2), n = 2, 3, 4, 5, ......... Balmer series: When excited electrons in ...
... Ans2. Lyman series: When excited electrons in hydrogen atoms fall from higher energy levels to first energy level, the series of lines observed are called Lyman series. They are observed in ultraviolet region. Lyman = R(1/12 - 1/n2), n = 2, 3, 4, 5, ......... Balmer series: When excited electrons in ...
Lesson 2
... many of these approximate ways of computing V(R), and tested most of them out so you can get an idea of their accuracy. • Software is not perfect, but more packaged and easy to use than most CFD software. If you ask for the same basis set and level of approximation with the same geometry R in differ ...
... many of these approximate ways of computing V(R), and tested most of them out so you can get an idea of their accuracy. • Software is not perfect, but more packaged and easy to use than most CFD software. If you ask for the same basis set and level of approximation with the same geometry R in differ ...
Motor unit and Electromyogram (EMG )
... application of a large magnetic field. It is a state of matter that is proposed to exist in special, two-dimensional semiconductors with spin-orbit coupling. In addition, as the quantum spin Hall state does not break any discrete symmetries such as time-reversal or parity, its effect on graphene has ...
... application of a large magnetic field. It is a state of matter that is proposed to exist in special, two-dimensional semiconductors with spin-orbit coupling. In addition, as the quantum spin Hall state does not break any discrete symmetries such as time-reversal or parity, its effect on graphene has ...
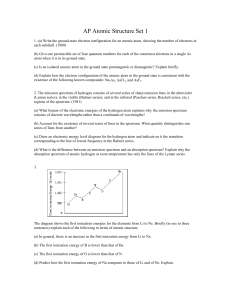
AP Atomic Structure Set 1
... (b) Give one permissible set of four quantum numbers for each of the outermost electrons in a single As atom when it is in its ground state. (c) Is an isolated arsenic atom in the ground state paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Explain briefly. (d) Explain how the electron configuration of the arsenic ato ...
... (b) Give one permissible set of four quantum numbers for each of the outermost electrons in a single As atom when it is in its ground state. (c) Is an isolated arsenic atom in the ground state paramagnetic or diamagnetic? Explain briefly. (d) Explain how the electron configuration of the arsenic ato ...
Physical Chemistry II – Exam 1 SOLUTIONS
... 5.) (16 points) The idea of quantization is one of the key elements of quantum theory. Explain the concept of quantization. Then, using one example system, describe at least one property of the system that exhibits quantization. Make sure to include in your discussion an equation that illustrates qu ...
... 5.) (16 points) The idea of quantization is one of the key elements of quantum theory. Explain the concept of quantization. Then, using one example system, describe at least one property of the system that exhibits quantization. Make sure to include in your discussion an equation that illustrates qu ...
Problem Set 11
... (a) Write down the generic expression for the energy. (b) Write down the wave function for the ground-state. Pay attention to the ranges of the potential. (c) Assume that the particle in the box is an electron, and the size of the box is L = 1 nm. How much energy (in eV) is needed to make the electr ...
... (a) Write down the generic expression for the energy. (b) Write down the wave function for the ground-state. Pay attention to the ranges of the potential. (c) Assume that the particle in the box is an electron, and the size of the box is L = 1 nm. How much energy (in eV) is needed to make the electr ...
2.5 FERMI`S GOLDEN RULE
... 1) ! Ek varies slowly with frequency and there is a continuum of final states. (By slow what we are saying is that the observation point t is relatively long). 2) The matrix element Vk! is invariant across the final states. These assumptions allow those variables to be factored out of integral ...
... 1) ! Ek varies slowly with frequency and there is a continuum of final states. (By slow what we are saying is that the observation point t is relatively long). 2) The matrix element Vk! is invariant across the final states. These assumptions allow those variables to be factored out of integral ...
L 35 Modern Physics [1]
... according to classical ideas, should very quickly radiate away all of its energy If this were so, then we would observe that atoms emit light over a continuous range of wavelengths (colors) NOT SO! ...
... according to classical ideas, should very quickly radiate away all of its energy If this were so, then we would observe that atoms emit light over a continuous range of wavelengths (colors) NOT SO! ...
5.2.12.C 2011 Physical Science: All students will understand that
... Forms of Energy: Knowing the characteristics of familiar forms of energy, including potential and kinetic energy, is useful in coming to the understanding that, for the most part, the natural world can be explained and is predictable. (5.2.C) Essential Questions 1. How do we know that things have en ...
... Forms of Energy: Knowing the characteristics of familiar forms of energy, including potential and kinetic energy, is useful in coming to the understanding that, for the most part, the natural world can be explained and is predictable. (5.2.C) Essential Questions 1. How do we know that things have en ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.
















![L 35 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001036078_1-1a4f17b9367db590f7dcb987ef21bbe6-300x300.png)




