Systematic improvement of the correlation energy of solids
... correlation functional fail systematically to treat certain classes of problems, such as, e.g., the weakly interacting systems. The adiabatic connection fluctuation and dissipation (ACFDT) theorem represents a promising way to systematically improve the precision of DFT. Until now, this approach has ...
... correlation functional fail systematically to treat certain classes of problems, such as, e.g., the weakly interacting systems. The adiabatic connection fluctuation and dissipation (ACFDT) theorem represents a promising way to systematically improve the precision of DFT. Until now, this approach has ...
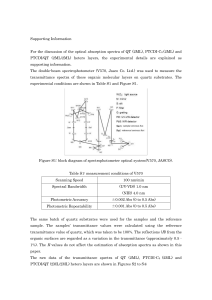
Supporting Information For the discussion of the optical absorption
... A very weak peak was observed around 2.45 eV. Forker et al. assigned this peak to the S0-S1 (HOMO-LUMO) transition. A strong absorption peak was reported [17, 18] under in-situ measurement. However, the transmittance spectrum of our deposited QT 2ML ...
... A very weak peak was observed around 2.45 eV. Forker et al. assigned this peak to the S0-S1 (HOMO-LUMO) transition. A strong absorption peak was reported [17, 18] under in-situ measurement. However, the transmittance spectrum of our deposited QT 2ML ...
PHYSICS 4E QUIZ 4 SPRING QUARTER 2010 PROF. HIRSCH
... (c) Show that your result in (b) agrees with the prediction of the Bohr atom for this n and Z. Alternatively, if you didn't find n and Z in (a), use the fact that your result in (b) should agree with the Bohr atom prediction to deduce the values of n and Z. Problem 3 (10 pts) (a) Sodium has atomic n ...
... (c) Show that your result in (b) agrees with the prediction of the Bohr atom for this n and Z. Alternatively, if you didn't find n and Z in (a), use the fact that your result in (b) should agree with the Bohr atom prediction to deduce the values of n and Z. Problem 3 (10 pts) (a) Sodium has atomic n ...
Hwk Set #14 - Publisher`s solutions
... The red-orange colors in the neon emission spectrum are due to transitions from excited 3p states to the lower energy but still excited 3s states. This occurs because the ground states are collisionally excited by the electrical discharge. The absorption spectrum of a gas consists of only those spec ...
... The red-orange colors in the neon emission spectrum are due to transitions from excited 3p states to the lower energy but still excited 3s states. This occurs because the ground states are collisionally excited by the electrical discharge. The absorption spectrum of a gas consists of only those spec ...
Ab initio molecular dynamics: ground and excited states
... the state, as well as explicitly on the atomic positions • In order to find the force on any particular atom, we would therefore have use the chain rule to write ...
... the state, as well as explicitly on the atomic positions • In order to find the force on any particular atom, we would therefore have use the chain rule to write ...
Quantum Mechanics Physics
... Laboratory • Problem: How much energy is contained in the quanta between the different levels of excited electron energy orbitals? And what are the frequencies and wavelengths of the energy? • Hypothesis: The amount of energy given off is calculated by the colors of the quanta of light given off whe ...
... Laboratory • Problem: How much energy is contained in the quanta between the different levels of excited electron energy orbitals? And what are the frequencies and wavelengths of the energy? • Hypothesis: The amount of energy given off is calculated by the colors of the quanta of light given off whe ...
Interaction with the radiation field
... Motivation: We want to calculate the transition probability Pm->n (the probability that a particle which started out in the state |m> will be found, at time t, in state |m>) ...
... Motivation: We want to calculate the transition probability Pm->n (the probability that a particle which started out in the state |m> will be found, at time t, in state |m>) ...
Balmer Series
... to several line series, which are sequences of lines corresponding to electron transitions, each ending or beginning with the same atomic state in hydrogen. Thus, for example, the Balmer Series involves transitions starting (for absorption) or ending (for emission) with the first excited state (n=2) ...
... to several line series, which are sequences of lines corresponding to electron transitions, each ending or beginning with the same atomic state in hydrogen. Thus, for example, the Balmer Series involves transitions starting (for absorption) or ending (for emission) with the first excited state (n=2) ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.