Postdoc position in Regulation of Gene Transcription by RNA
... A post-doctoral position is available at the Central-European Institute of Technology (CEITEC), Brno, Czech Republic, in the newly established group of Dalibor Blazek (lab pages at: http://www.ceitec.cz/en/inherited-diseases-ii-transcriptional-regulation/rg38? langselect=1 ). The project focuses on ...
... A post-doctoral position is available at the Central-European Institute of Technology (CEITEC), Brno, Czech Republic, in the newly established group of Dalibor Blazek (lab pages at: http://www.ceitec.cz/en/inherited-diseases-ii-transcriptional-regulation/rg38? langselect=1 ). The project focuses on ...
Bio 313 worksheet 14 - Iowa State University
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
... For the following state whether it is a characteristic of Prokaryotes, Eukaryotes, or both 1. Transcription occurs in the nucleus and translation in the cytoplasm 2. Able to utilize post-transcriptional control 3. Transcription unit contains promoter, RNA coding region, and terminator 4. Transcripti ...
Key concepts_Regulation of transcription in Bacteria
... involves the linkage of translation and transcription that occurs in bacteria. Transcription factors are usually allosteric proteins, in which one or another con-formational state with specific DNA-binding capabilities is favored by the absence or presence of a small effector molecule. Bacterial tra ...
... involves the linkage of translation and transcription that occurs in bacteria. Transcription factors are usually allosteric proteins, in which one or another con-formational state with specific DNA-binding capabilities is favored by the absence or presence of a small effector molecule. Bacterial tra ...
RNA Transcription
... The genetic code translates the 4-letter alphabet of mRNA into the 20-word language of protein. What is the minimum number of nucleotides needed to specify 20 amino acids? Is it two, three, four…? If mRNA were read in units of two nucleotides, it could specify only 16 (42) amino acids –too few! Erg ...
... The genetic code translates the 4-letter alphabet of mRNA into the 20-word language of protein. What is the minimum number of nucleotides needed to specify 20 amino acids? Is it two, three, four…? If mRNA were read in units of two nucleotides, it could specify only 16 (42) amino acids –too few! Erg ...
D7-Transcription and Translation
... In order to translate DNA (RNA) you must first crack the genetic “code”! The genetic code is a triplet code in which a group of three bases (codon) of a DNA molecule code for a particular amino acid. ...
... In order to translate DNA (RNA) you must first crack the genetic “code”! The genetic code is a triplet code in which a group of three bases (codon) of a DNA molecule code for a particular amino acid. ...
Eukaryotic gene expression: major considerations
... Cyan: alternating b-turns; Pink: extended regions. ...
... Cyan: alternating b-turns; Pink: extended regions. ...
Three types of RNA polymerase in eukaryotic nuclei
... Cyan: alternating β-turns; Pink: extended regions. ...
... Cyan: alternating β-turns; Pink: extended regions. ...
DNA/RNA.lecture
... 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. transfer RNAs (tRNA) b. ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) D. How is it made? 1. Musical analogy 2. similar a. DNA b. the information c. RNA 3. RNA polymerase a. 3’ end b. promoter termination signal c. transcription unit d. synthetic process 4. Steps: a. ...
... 2. Other 2 types of RNA - protein-producing machinery a. transfer RNAs (tRNA) b. ribosomal RNAs (rRNA) D. How is it made? 1. Musical analogy 2. similar a. DNA b. the information c. RNA 3. RNA polymerase a. 3’ end b. promoter termination signal c. transcription unit d. synthetic process 4. Steps: a. ...
Transcription: Synthesizing RNA from DNA
... RNA Polymerase complex builds single-stranded mRNA 5 to 3 the is complementary to the template strand of DNA (except T’s are U’s) Does not require a PRIMER to start building (as in replication). Therefore elongation starts as soon as RNA polymerase complex moves to gene and binds to promoter. ...
... RNA Polymerase complex builds single-stranded mRNA 5 to 3 the is complementary to the template strand of DNA (except T’s are U’s) Does not require a PRIMER to start building (as in replication). Therefore elongation starts as soon as RNA polymerase complex moves to gene and binds to promoter. ...
Powerpoint file
... elongation and termination. 4. The nucleotide at the 5’ end of an RNA strand retains all three of its phosphate groups; all subsequent nucleotides release pyrophosphate (PPi) when added to the chain and retain only their a phosphate (red). 5. The released PPi is subsequently hydrolyzed by pyrophosph ...
... elongation and termination. 4. The nucleotide at the 5’ end of an RNA strand retains all three of its phosphate groups; all subsequent nucleotides release pyrophosphate (PPi) when added to the chain and retain only their a phosphate (red). 5. The released PPi is subsequently hydrolyzed by pyrophosph ...
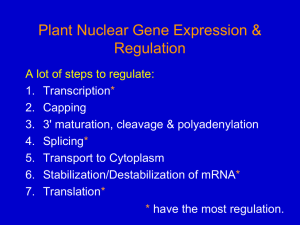
Nuclear gene expression 1
... with ß and ß’ subunits of E. coli RNAP. 2. Largest subunit is phosphorylated on its COOH-terminal domain (CTD) – Phosphor. needed for transition from initiation elongation – CTD also interacts with other proteins ...
... with ß and ß’ subunits of E. coli RNAP. 2. Largest subunit is phosphorylated on its COOH-terminal domain (CTD) – Phosphor. needed for transition from initiation elongation – CTD also interacts with other proteins ...
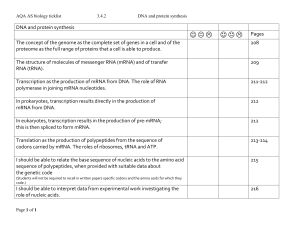
doc 3.4.2 protein synthesis checklist
... Transcription as the production of mRNA from DNA. The role of RNA polymerase in joining mRNA nucleotides. ...
... Transcription as the production of mRNA from DNA. The role of RNA polymerase in joining mRNA nucleotides. ...
A CAAT–Box Binding Factor Gene That Regulates Seed Development
... •Transcription is initiated at regions of DNA called promoters. Specific sequences of nucleotide bases at a promoter are recognized by both transcription factors and RNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA. The mRNA strand produced is complementary to the transcribed strand (the antisense st ...
... •Transcription is initiated at regions of DNA called promoters. Specific sequences of nucleotide bases at a promoter are recognized by both transcription factors and RNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes RNA. The mRNA strand produced is complementary to the transcribed strand (the antisense st ...
power point presentation
... The data collected through different approach can be used as reference to each other for possible final confidential result. ...
... The data collected through different approach can be used as reference to each other for possible final confidential result. ...
Transcription
... – additions or losses of nucleotide pairs in a gene; alters the ‘reading frame’ of ...
... – additions or losses of nucleotide pairs in a gene; alters the ‘reading frame’ of ...
How do we get proteins? - Sebastian Charter Junior High
... 2. mRNA is read by the ribosome 3. Every 3 bases = codon ...
... 2. mRNA is read by the ribosome 3. Every 3 bases = codon ...
Study Guide MBMB 451A Fall 2002
... 4. Define basal versus activated transcription. 5. Describe the different ways in which the activity of transcription factors can be regulated in the cell. 6. Describe the properties of the transcription factors TFIID, IIA, IIB, IIE, IIF, and IIH. What are TAFs and are they important for basal tran ...
... 4. Define basal versus activated transcription. 5. Describe the different ways in which the activity of transcription factors can be regulated in the cell. 6. Describe the properties of the transcription factors TFIID, IIA, IIB, IIE, IIF, and IIH. What are TAFs and are they important for basal tran ...
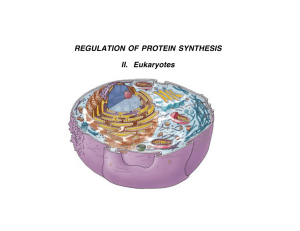
Regulating Protein Synthesis
... Regulation of protein synthesis is necessary in all cells, but much more complex in eukaryotes, because both the cells and the organism they form are more complex. Uncoiling of chromatin: DNA, histone ...
... Regulation of protein synthesis is necessary in all cells, but much more complex in eukaryotes, because both the cells and the organism they form are more complex. Uncoiling of chromatin: DNA, histone ...
Proteins
... pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins ...
... pries DNA apart and hooks RNA nucleotides together from the DNA code Promoter region on DNA: where RNA polymerase attaches and where initiation of RNA begins ...
Transcription
... C. Bacterial mRNA undergo extensive post-translational modifications. D. Chromatin plays a large role in regulation of transcription in eukaryotic cells. ...
... C. Bacterial mRNA undergo extensive post-translational modifications. D. Chromatin plays a large role in regulation of transcription in eukaryotic cells. ...
RNA Transcription/Translation STUDY GUIDE
... 4. What are the 4 nitrogen bases found in RNA? How do they pair up? ...
... 4. What are the 4 nitrogen bases found in RNA? How do they pair up? ...
Gene_expression
... Regulation of transcription • Regulation of transcription controls when transcription occurs and how much RNA is created. Transcription of a gene by RNA polymerase can be regulated by at least five ...
... Regulation of transcription • Regulation of transcription controls when transcription occurs and how much RNA is created. Transcription of a gene by RNA polymerase can be regulated by at least five ...