No Slide Title
... • Transcription is terminated by signals within the DNA sequence at the end of the gene • Hairpin formation in RNA destabilizes the DNA/RNA hybrid and releases RNA transcript • In some cases, termination depends on the rho () termination factor ...
... • Transcription is terminated by signals within the DNA sequence at the end of the gene • Hairpin formation in RNA destabilizes the DNA/RNA hybrid and releases RNA transcript • In some cases, termination depends on the rho () termination factor ...
20141203103493
... DNA wraps around Nucleosome-unit of DNA wrapped around histones Supercoiling-Chromatinchromosomes Heterochromatin-remains condensed Euchromatin-loose during interphase Cellular differentiation-making cells different; accomplished by turning genes “on” or “off”differential gene expression ...
... DNA wraps around Nucleosome-unit of DNA wrapped around histones Supercoiling-Chromatinchromosomes Heterochromatin-remains condensed Euchromatin-loose during interphase Cellular differentiation-making cells different; accomplished by turning genes “on” or “off”differential gene expression ...
USMLE Step 1 Web Prep — Transcription and RNA Processing: Part
... Gene expression is cell-type dependent. ...
... Gene expression is cell-type dependent. ...
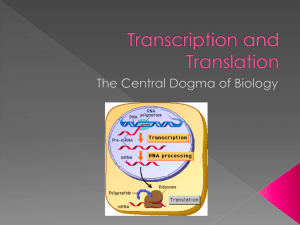
Transcription
... site; those extending in the opposite direction are upstream. The σ70 subunit binds to specific sequences near the −10 and −35 positions in the promoter. The α subunits lie close to the DNA in the upstream direction. The β and β′ subunits associate with the start site ...
... site; those extending in the opposite direction are upstream. The σ70 subunit binds to specific sequences near the −10 and −35 positions in the promoter. The α subunits lie close to the DNA in the upstream direction. The β and β′ subunits associate with the start site ...
Transcript Maps
... • transcription-control region Collective term for all the cis-acting DNA regulatory sequences that regulate transcription of a particular gene. ...
... • transcription-control region Collective term for all the cis-acting DNA regulatory sequences that regulate transcription of a particular gene. ...
Molecular Genetics Review - Biology 12U Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids
... Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: The Molecular Basis of Life material of heredity - components or RNA and DNA *5 people in the book who are important for DNA history : Watson and Crick; Franklin; Chargaff; Meishner; and Griffith. structure of nucleic acids organiztion of genetic material in prokaryotes a ...
... Chapter 7: Nucleic Acids: The Molecular Basis of Life material of heredity - components or RNA and DNA *5 people in the book who are important for DNA history : Watson and Crick; Franklin; Chargaff; Meishner; and Griffith. structure of nucleic acids organiztion of genetic material in prokaryotes a ...
Transcription and Translation computer lab test review
... During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Name the RNA codon that is used to start translation. Which three codons will sto ...
... During transcription, RNA is developed from a strand of DNA. List the base pairs used to make RNA. What is the name of the DNA strand used in transcription? Where does transcription occur? Where does translation occur? Name the RNA codon that is used to start translation. Which three codons will sto ...
Transcription and Translation
... I.e. difference in enzymes (make different amounts of molecules) I.e. difference in antibodies (some get sick more often or from different things) ...
... I.e. difference in enzymes (make different amounts of molecules) I.e. difference in antibodies (some get sick more often or from different things) ...
Ch. 17: From Gene to Protein
... 3) RNA splicing: exons (expressed sequences) kept introns (intervening sequences) are spliced out forming a spliceosome ...
... 3) RNA splicing: exons (expressed sequences) kept introns (intervening sequences) are spliced out forming a spliceosome ...
MS Word file
... A variety of different consensus sequences may be found in the regulatory promoters. Main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is in assembly of ...
... A variety of different consensus sequences may be found in the regulatory promoters. Main difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is in assembly of ...
Pre-writing Activity for 3.05…DNA Replication For this assignment
... Pages 1 to 3 of the lesson go over the history of discovering DNA, structure of DNA, DNA replication, and DNA vs RNA. Please be sure that you take notes on these topics, as you will see this information on DBAs, module exams, and semester exams. ...
... Pages 1 to 3 of the lesson go over the history of discovering DNA, structure of DNA, DNA replication, and DNA vs RNA. Please be sure that you take notes on these topics, as you will see this information on DBAs, module exams, and semester exams. ...
Slide 1
... Bacterial transcription initiation • RNA polymerase initiates transcription of most genes at a unique DNA position lying upstream of the coding sequence • The base pair where transcription initiates is termed the transcription-initiation site or start site • By convention, the transcription-initiat ...
... Bacterial transcription initiation • RNA polymerase initiates transcription of most genes at a unique DNA position lying upstream of the coding sequence • The base pair where transcription initiates is termed the transcription-initiation site or start site • By convention, the transcription-initiat ...
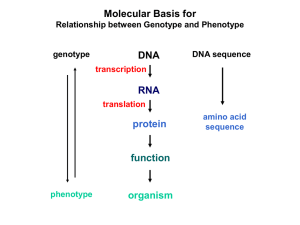
1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule
... 1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule. Include in your explanation the words and phrases: base-pairing rule, complementary nucleotides, cytoplasm, DNA, gene, messenger RNA, nucleotide, nucleus, RNA polymerase, amino acid, anti-codon, codon, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, nucleotide, ...
... 1. Explain how a gene directs the synthesis of an mRNA molecule. Include in your explanation the words and phrases: base-pairing rule, complementary nucleotides, cytoplasm, DNA, gene, messenger RNA, nucleotide, nucleus, RNA polymerase, amino acid, anti-codon, codon, cytoplasm, DNA, mRNA, nucleotide, ...
Chapter 6
... make them begin catalysis and end catalysis. What are these differences? 3. Which is more accurate, DNA replication or RNA transcription? 4. Explain the proteins and mechanisms involved in the initiation of transcription 5. What determines how many copies of a transcript (mRNA) are made? 6. How are ...
... make them begin catalysis and end catalysis. What are these differences? 3. Which is more accurate, DNA replication or RNA transcription? 4. Explain the proteins and mechanisms involved in the initiation of transcription 5. What determines how many copies of a transcript (mRNA) are made? 6. How are ...
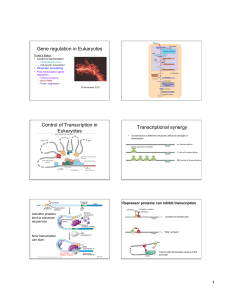
Gene regulation in Eukaryotes Control of Transcription in
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
... ~1.5% of the human genome, but ~90% of the genome appears to be transcribed… ...
Dr. Anton Meinhart Department of Biomolecular
... Macromolecular Machines in eukaryotic RNA 3’-end Processing Concomitant with eukaryotic transcription, RNA undergoes extensive modification. Nuclear processes, such as capping, splicing and cleavage / polyadenylation are necessary for producing a mature RNA. These RNA processing events take place in ...
... Macromolecular Machines in eukaryotic RNA 3’-end Processing Concomitant with eukaryotic transcription, RNA undergoes extensive modification. Nuclear processes, such as capping, splicing and cleavage / polyadenylation are necessary for producing a mature RNA. These RNA processing events take place in ...
word
... 5’ capping: 7-methylguanosine is added to the 5’ end of nascent mRNA that associates with the phosphorylated CTD of RNA polymerase II ...
... 5’ capping: 7-methylguanosine is added to the 5’ end of nascent mRNA that associates with the phosphorylated CTD of RNA polymerase II ...
04/03
... Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or eve ...
... Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or eve ...
分子生物學小考(一) 範圍ch3~ch7
... that sense and respond to changes in surroundings. These two-component systems may involve which of the following? I. Protein phosphorylation (A) I only ...
... that sense and respond to changes in surroundings. These two-component systems may involve which of the following? I. Protein phosphorylation (A) I only ...
RNA-Unit 6 cont.
... 61 code for amino acids (20 possibilities) 1 codes to start = AUG = methionine ...
... 61 code for amino acids (20 possibilities) 1 codes to start = AUG = methionine ...
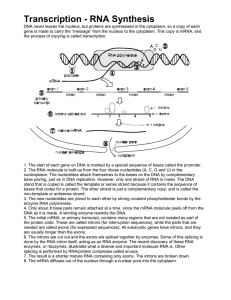
Transcription
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
8.4 Transcription - Issaquah Connect
... 8.4 Transcription The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a g ...
... 8.4 Transcription The transcription process is similar to replication. • Transcription and replication both involve complex enzymes and complementary base pairing. • The two processes have different end results. – Replication copies all the DNA; transcription copies one gene growing RNA strands a g ...
RNA Synthesis and Splicing
... -> cyclic peptide of 8 amino acids -> binds tightly to RNA polymerase II -> blocks elongation of RNA synthesis ...
... -> cyclic peptide of 8 amino acids -> binds tightly to RNA polymerase II -> blocks elongation of RNA synthesis ...
Previously in Bio308
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
... How does RNA polymerase work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? How does a ribosome work and what does it make? How does it know where to start and stop? If the DNA in every cell in your body is the ...
Gene to Protein
... nucleotides through the coding region Termination – Ends at the termination sequence. mRNA is now complete ...
... nucleotides through the coding region Termination – Ends at the termination sequence. mRNA is now complete ...