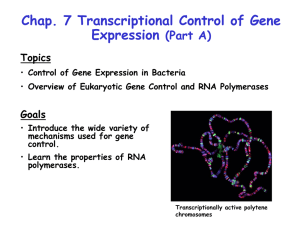
Control of Gene Expression
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
Chapter 7A
... Regulatory Elements in Eukaryotic Genes The regulation of transcription of many eukaryotic genes is highly complex. Genes can be expressed differently in various tissues, during different stages of development, and under different environmental conditions. The complexity of expression of the Pax6 g ...
... Regulatory Elements in Eukaryotic Genes The regulation of transcription of many eukaryotic genes is highly complex. Genes can be expressed differently in various tissues, during different stages of development, and under different environmental conditions. The complexity of expression of the Pax6 g ...
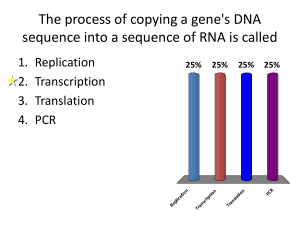
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly synthesized strand 2. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence 3. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming 4. Both RNA a ...
... Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and transcription? 1. Nucleotides are added to the 3' end of the newly synthesized strand 2. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence 3. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming 4. Both RNA a ...
Protein Synthesis - Helena High School
... 4. What is the goal of transcription? 5. Where does transcription take place in eukaryotic cells? 6. What RNA molecule copies the DNA code to serve as a template to make proteins? 7. If a section of DNA has the following order of bases, what would the complementary mRNA be? DNA segment: ...
... 4. What is the goal of transcription? 5. Where does transcription take place in eukaryotic cells? 6. What RNA molecule copies the DNA code to serve as a template to make proteins? 7. If a section of DNA has the following order of bases, what would the complementary mRNA be? DNA segment: ...
Gene Regulation - Two Rivers High School
... cell, but death of the organism itself. O Gene regulation allows such organisms to do things that will allow them to fit into hostile and extreme environments and to adapt to changes. (antibiotics) ...
... cell, but death of the organism itself. O Gene regulation allows such organisms to do things that will allow them to fit into hostile and extreme environments and to adapt to changes. (antibiotics) ...
Transcription Worksheet and Answer Key
... What occurs first, transcription or translation? _________________________ ...
... What occurs first, transcription or translation? _________________________ ...
Molecular Basis for Relationship between Genotype and Phenotype
... sequence of amino acids in a protein.” Mutant alleles of trpA gene differed in the position of the mutation at the DNA level, which corresponded to position of amino acid substitution in the gene product. Colinearity of mutations and altered amino acids in a subunit of tryptophan synthetase from E. ...
... sequence of amino acids in a protein.” Mutant alleles of trpA gene differed in the position of the mutation at the DNA level, which corresponded to position of amino acid substitution in the gene product. Colinearity of mutations and altered amino acids in a subunit of tryptophan synthetase from E. ...
Word of the Day
... Transcription(in the nucleus) RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies it into RNA. A’s connect with U’s and G’s connect with C’s. The starting point of transcription is known as the Promoter, the end is known as the terminal signal. After transcription the mRNA moves into the cytosol for protein synth ...
... Transcription(in the nucleus) RNA polymerase unzips DNA and copies it into RNA. A’s connect with U’s and G’s connect with C’s. The starting point of transcription is known as the Promoter, the end is known as the terminal signal. After transcription the mRNA moves into the cytosol for protein synth ...
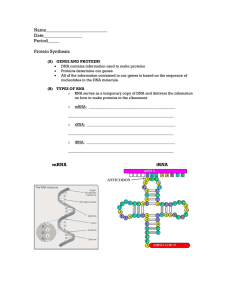
Name___________________________ Date_________________ Period_____
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
... All of the information contained in our genes is based on the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA molecule. (B) TYPES OF RNA o RNA serves as a temporary copy of DNA and delivers the infomation on how to make proteins to the ribosomes o ...
Lecture TandT
... • Genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA. • RNA polymerase is the enzyme for the job. ...
... • Genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA. • RNA polymerase is the enzyme for the job. ...
BIO 103 - Genes
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
... template strand: used to make RNA coding strand: complementary to the template strand RNA polymerase: puts nucleotides together to make RNA strand ...
Nucleic Acids - faculty at Chemeketa
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
... What will be the composition of the DNA strand complementary to –AGCCA– ? a. b. c. d. ...
Transcription Biology Review
... up amino acids – Helix-turn-Helix (Homeodomain) – Helix-loop-helix – Zinc Finger ...
... up amino acids – Helix-turn-Helix (Homeodomain) – Helix-loop-helix – Zinc Finger ...
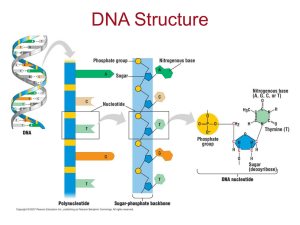
DNA
... 1. Made of a single strand of nucleotides 2. Each nucleotide consists of a. five carbon sugar (ribose) b. phosphate group c. nitrogenous base (adenine, URACIL, guanine, cytosine) B. Transcription (DNA & mRNA) 1. Occurs in the nucleus 2. RNA polymerase a. Binds to the DNA at the promoter site b. “unz ...
... 1. Made of a single strand of nucleotides 2. Each nucleotide consists of a. five carbon sugar (ribose) b. phosphate group c. nitrogenous base (adenine, URACIL, guanine, cytosine) B. Transcription (DNA & mRNA) 1. Occurs in the nucleus 2. RNA polymerase a. Binds to the DNA at the promoter site b. “unz ...
第一次课件第八章
... • GC boxes bound by DNA binding protein SP1 • SP1 recruits TFIID by binding TAFII110 • Partially reconstituted complex (TBP and 3 TAFs) in addition to other GTFs, Pol II leads to high levels of transcription ...
... • GC boxes bound by DNA binding protein SP1 • SP1 recruits TFIID by binding TAFII110 • Partially reconstituted complex (TBP and 3 TAFs) in addition to other GTFs, Pol II leads to high levels of transcription ...
Gene expression
... • nucleotide sequence encoded by a gene that remains present within the final mature RNA product of that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. • This is the expressed genetic material… the light is turned on. ...
... • nucleotide sequence encoded by a gene that remains present within the final mature RNA product of that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. • This is the expressed genetic material… the light is turned on. ...
Genetic Code and Transcription
... RNA Polymerase moves down DNA Transcription bubble moves with polymerase ...
... RNA Polymerase moves down DNA Transcription bubble moves with polymerase ...
Chemists Discover How Cells Create Stability During
... modeling RNA-DNA interactions. What we’ve discovered is that genes exist in a threedimensional helix for a number of very good reasons and the topological lock depends on this three-dimensional relationship for its success.” Their findings appear in the current issue of the Journal of Biological Che ...
... modeling RNA-DNA interactions. What we’ve discovered is that genes exist in a threedimensional helix for a number of very good reasons and the topological lock depends on this three-dimensional relationship for its success.” Their findings appear in the current issue of the Journal of Biological Che ...
Molecular Genetics
... • Promoter is where the RNA polymerase will bond • Contains TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site where transcription is initiated. • Transcription Factors attach first • RNA Polymerase then bonds to complete assembly ...
... • Promoter is where the RNA polymerase will bond • Contains TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site where transcription is initiated. • Transcription Factors attach first • RNA Polymerase then bonds to complete assembly ...
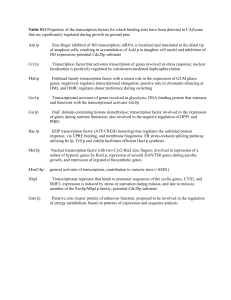
Table S11 Properties of the transcription factors for which binding
... bZIP transcription factor (ATF/CREB1 homolog) that regulates the unfolded protein response, via UPRE binding, and membrane biogenesis; ER stress-induced splicing pathway utilizing Ire1p, Trl1p and Ada5p facilitates efficient Hac1p synthesis ...
... bZIP transcription factor (ATF/CREB1 homolog) that regulates the unfolded protein response, via UPRE binding, and membrane biogenesis; ER stress-induced splicing pathway utilizing Ire1p, Trl1p and Ada5p facilitates efficient Hac1p synthesis ...
From Gene to Protein
... to the Synthesis of Proteins • If Genes (bits of information on DNA) contain knowledge of how to assemble a polypeptide, then there must be a process by which information on the DNA is conveyed to the protein making machinery of the cell ...
... to the Synthesis of Proteins • If Genes (bits of information on DNA) contain knowledge of how to assemble a polypeptide, then there must be a process by which information on the DNA is conveyed to the protein making machinery of the cell ...
18. Gene Expression
... Three main phases: Initiation Elongation Termination Initiation: • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 5’ to the transcription start site o binding site of RNA polymerase initiation factor (sigma subunit, σ) o Promoter recognition by RNA polymerase is a prerequisite for transcription initiation o Many pr ...
... Three main phases: Initiation Elongation Termination Initiation: • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 5’ to the transcription start site o binding site of RNA polymerase initiation factor (sigma subunit, σ) o Promoter recognition by RNA polymerase is a prerequisite for transcription initiation o Many pr ...