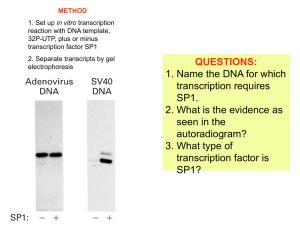
Chapter 17 - Denton ISD
... what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in ...
... what is spliced; this is called ___________________. Exon shuffling during cross-over may also be useful in ...
Lecture #7 Date ______
... of RNA polymerase to an initiation sequence (TATA box) Elongation~ RNA polymerase continues unwinding DNA and adding nucleotides to the 3’ end Termination~ RNA polymerase reaches terminator sequence ...
... of RNA polymerase to an initiation sequence (TATA box) Elongation~ RNA polymerase continues unwinding DNA and adding nucleotides to the 3’ end Termination~ RNA polymerase reaches terminator sequence ...
pptx - WVU School of Medicine
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
... DNA sequences “upstream” of transcription initiation site. • different σ factors recognize different promoters (σ70 = most genes; σ32 = heat shock proteins; σ28 = flagella & chemotaxis genes). • 2 DNA sequences (-35 & -10) found in most prokaryotic promoters – “upstream” of transcription start site ...
Slide 1
... Rho-dependent termination sites are present in some -phage and E. coli genes • The Rho factor is a hexameric protein around which a 70- to 80-base segment of the growing RNA transcript wraps • Rho then moves along the RNA in the 3 direction until it eventually unwinds the RNA-DNA hybrid at the ac ...
... Rho-dependent termination sites are present in some -phage and E. coli genes • The Rho factor is a hexameric protein around which a 70- to 80-base segment of the growing RNA transcript wraps • Rho then moves along the RNA in the 3 direction until it eventually unwinds the RNA-DNA hybrid at the ac ...
PG1005 Lecture 17 Gene Transcription
... TBP-TATA binding protein TAF-TBP associated factors N.B. Binding of TBP leads to a pronounced bend in the DNA. 2) TFIIB binds at consensus sites around the TATA box and directs entry of the polymerase 3)TFIIH binds and exercises 2 key functions 1. Helicase activity 2. Kinase activity ...
... TBP-TATA binding protein TAF-TBP associated factors N.B. Binding of TBP leads to a pronounced bend in the DNA. 2) TFIIB binds at consensus sites around the TATA box and directs entry of the polymerase 3)TFIIH binds and exercises 2 key functions 1. Helicase activity 2. Kinase activity ...
DNA Function II - Complete Vocab with
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
... General Transcription Factors: Other enzymes/proteins that are required for RNA Polymerase to function Transcription Activators: Proteins that bind to enhancers to stimulate transcription Transcription Repressors: Proteins that bind to enhancers to shut down transcription Enhancer: A sequence of DNA ...
Gene Expression
... • Conditions tightly controlled – Lactose must be high, but no other sugar present – [Lactose] and [glucose] ...
... • Conditions tightly controlled – Lactose must be high, but no other sugar present – [Lactose] and [glucose] ...
RNA polymerases
... This could be a protein or some functional RNA The difference between various cells in a specific organism is due to difference in gene expression ...
... This could be a protein or some functional RNA The difference between various cells in a specific organism is due to difference in gene expression ...
Seminar questions Transcription/Translation
... a) What is the role of TPB (TATA-box binding protein) in eukaryotic transcription? Describe its structure and how it induces conformational changes in the DNA double-helix. Why is this an important step of transcription initiation? b) The trigger loop and the bridge helix are two important parts of ...
... a) What is the role of TPB (TATA-box binding protein) in eukaryotic transcription? Describe its structure and how it induces conformational changes in the DNA double-helix. Why is this an important step of transcription initiation? b) The trigger loop and the bridge helix are two important parts of ...
Transcription factors - Raleigh Charter High School
... activators to enhance transcription. • Activator - transcription factor which binds to an enhancer and stimulates transcription of gene. help position of the initiation complex on the promoter. • TATA Box - the DNA sequence which indicates where the DNA can be read and decoded. • RNA Polymerase - en ...
... activators to enhance transcription. • Activator - transcription factor which binds to an enhancer and stimulates transcription of gene. help position of the initiation complex on the promoter. • TATA Box - the DNA sequence which indicates where the DNA can be read and decoded. • RNA Polymerase - en ...
Lecture 4: DNA transcription
... Poly(A)polymerase and cleavage & polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) attach poly(A) generated from ATP ...
... Poly(A)polymerase and cleavage & polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF) attach poly(A) generated from ATP ...
Chapter 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 8.7 Study Guide Key terms: Ribonucleic acid
... 2. What happens to the information on a DNA molecule during transcription? 3. What are repressor proteins and where do they bind? 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm (with or without) a complete set of both introns and exons. (please circle the appropriate response) 5. When are intro ...
... 2. What happens to the information on a DNA molecule during transcription? 3. What are repressor proteins and where do they bind? 4. mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters the cytoplasm (with or without) a complete set of both introns and exons. (please circle the appropriate response) 5. When are intro ...
Genetic Controls in Eukaryotes
... o Bind to promoter (TATA box); RNA Pol II can bind o “General” transcription factors leads to slow transcription. - General = essential to initiation of transcription of all protein o “Specific” transcription factors leads to faster transcription = Specific to transcription of particular protein. ...
... o Bind to promoter (TATA box); RNA Pol II can bind o “General” transcription factors leads to slow transcription. - General = essential to initiation of transcription of all protein o “Specific” transcription factors leads to faster transcription = Specific to transcription of particular protein. ...
CS 262—Lecture 1 Notes • 4-‐5 HWs, 3 late days • (Optional
... • DNA must be read from 5’ to 3’ end • RNA usually single-‐stranded o Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in DNA, recruits RNA polymerase o RNA ...
... • DNA must be read from 5’ to 3’ end • RNA usually single-‐stranded o Uracil replaces Thymine in RNA • Gene transcription: Transcription factors recognize binding sites in DNA, recruits RNA polymerase o RNA ...
The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology states that
... RNAP will bind to the wrong site of the DNA and transcribe the wrong gene ...
... RNAP will bind to the wrong site of the DNA and transcribe the wrong gene ...
Study Guide: The Cell
... 23. Make sure that you know how to read the codons on an mRNA strand to translate it into the correct sequence of amino acids. 24. Make sure that you know how to use the amino acid circular table. 25. Make sure that you are comfortable with the Chapter 13 vocabulary and definitions!!! ...
... 23. Make sure that you know how to read the codons on an mRNA strand to translate it into the correct sequence of amino acids. 24. Make sure that you know how to use the amino acid circular table. 25. Make sure that you are comfortable with the Chapter 13 vocabulary and definitions!!! ...
CH. 11 : Transcriptional Control of Gene Expression
... General Transcription Factors: initiation factors that place polymerase molecules at transcription start sites and help template strand enter active site Example in Polymerase II: TFIIA, TFIIB, etc. ...
... General Transcription Factors: initiation factors that place polymerase molecules at transcription start sites and help template strand enter active site Example in Polymerase II: TFIIA, TFIIB, etc. ...
Lecture 7
... A) Identify regions of the genome to be transcribed in ge neral. B) Activate transcription and processing at the correct time. C) Inactivate transcription of those mRNAs where there is enough protein D) Coordinate expression with other events in the cell cycle. E) Ability to change phenotype F) Cont ...
... A) Identify regions of the genome to be transcribed in ge neral. B) Activate transcription and processing at the correct time. C) Inactivate transcription of those mRNAs where there is enough protein D) Coordinate expression with other events in the cell cycle. E) Ability to change phenotype F) Cont ...
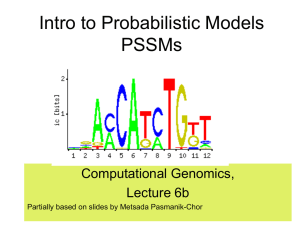
CG7b-PSSM
... A large number of biological units with common functions tend to exhibit similarities at the sequence level. These include very short “motives”, such as gene splice sites, DNA regulatory binding sites, recognized by transcription factors (proteins that bind to the promoter and control gene expressio ...
... A large number of biological units with common functions tend to exhibit similarities at the sequence level. These include very short “motives”, such as gene splice sites, DNA regulatory binding sites, recognized by transcription factors (proteins that bind to the promoter and control gene expressio ...
Protein Synthesis Study Guide 1. What is the “central dogma” of
... 6. Explain the process of translation. How do the different types of RNA work together? 7. What is a codon? 8. How does a ribosome know where to start and stop translation? 9. What is an anticodon? Where are anticodons located? 10. What type of bond links amino acids together? 11. What is mRNA proce ...
... 6. Explain the process of translation. How do the different types of RNA work together? 7. What is a codon? 8. How does a ribosome know where to start and stop translation? 9. What is an anticodon? Where are anticodons located? 10. What type of bond links amino acids together? 11. What is mRNA proce ...
outline File - selu moodle
... Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most com ...
... Wobble effect at third position Near universal 15.3 Prokaryotic Transcription Begins at a promoter transcribes the transcription unit ends at the terminator Promoter – sequence within DNA Elongation uses RNA polymerase to add ribonucleotides that are complementary to the template strand Most com ...
Transcription Factors
... – act at numerous sites on many chromosomes – Influence transcription by interacting with other proteins or segments of DNA • “Upstream” = being 5’ to the start site – Negative numbers of bases ...
... – act at numerous sites on many chromosomes – Influence transcription by interacting with other proteins or segments of DNA • “Upstream” = being 5’ to the start site – Negative numbers of bases ...