Slide 1
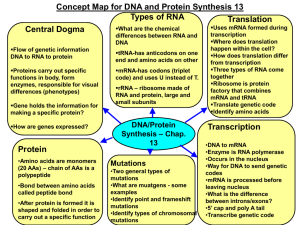
... (20 AAs) – chain of AAs is a polypeptide •Bond between amino acids called peptide bond •After protein is formed it is shaped and folded in order to carry out a specific function ...
... (20 AAs) – chain of AAs is a polypeptide •Bond between amino acids called peptide bond •After protein is formed it is shaped and folded in order to carry out a specific function ...
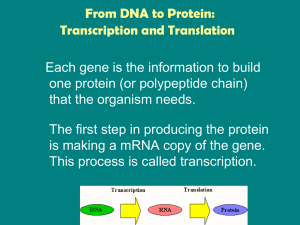
The Central Dogma of Biology states that DNA codes for RNA, and
... BEFORE WE EXAMINE THE STEPS! ...
... BEFORE WE EXAMINE THE STEPS! ...
HANDOUT: CH 17 pt 1 Study
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
... CHAPTER 17 STUDY QUESTIONS, part 1: From Gene to Protein (p. 325-344) 1) Summarize the one gene – one polypeptide hypothesis. ...
Protein Synthesis Notes: Transcription and Translation
... Codon: group of ___________ nucleotides on the messenger RNA that specifies one amino acid. 3. _______________ (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the mRNA. 4. This tRNA has an ________________ that matches the codon on the mRNA strand. _____________________: group of 3 unpaired nucleotides on a t ...
... Codon: group of ___________ nucleotides on the messenger RNA that specifies one amino acid. 3. _______________ (transfer RNA) carries amino acids to the mRNA. 4. This tRNA has an ________________ that matches the codon on the mRNA strand. _____________________: group of 3 unpaired nucleotides on a t ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Shaped like a “hair pin” or a T Responsible for bringing the amino acids for translation Contains “anti-codons” that match up with mRNA temporarily ...
... Shaped like a “hair pin” or a T Responsible for bringing the amino acids for translation Contains “anti-codons” that match up with mRNA temporarily ...
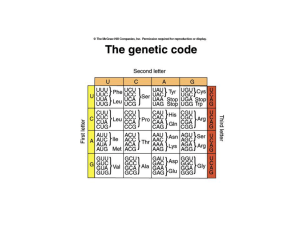
Features of the genetic code
... • A capping enzyme adds a G to the first nucleotide in the transcript in the unusual 5’-5’ direction (phosphate to phosphate bond). Then a methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be cr ...
... • A capping enzyme adds a G to the first nucleotide in the transcript in the unusual 5’-5’ direction (phosphate to phosphate bond). Then a methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be cr ...
Promoter-proximal Elements
... Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or eve ...
... Both enhancers and silencers affect transcription rate. Each has unique DNA sequence for the binding of regulatory proteins. Enhancer sequences contain multiple binding sites for trans-acting regulatory proteins. Enhancers could be located upstream from the promoter, downstream from the gene, or eve ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Kent City School District
... Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
... Elongation adds new RNA bases, including Uracil, down the exposed DNA bases Termination occurs when RNA polymerase hits the “stop” signal and detaches the new single strand of RNA ...
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired with adenine instead of thymine. • Transcription occurs on an ongoing basis as proteins needed, replication only occurs prior ...
... • Only a gene is copied, not the whole chromosome. • RNA nucleotides are added instead of DNA nucleotides. – Uracil is paired with adenine instead of thymine. • Transcription occurs on an ongoing basis as proteins needed, replication only occurs prior ...
Molecular Genetics (Unit 6 and Unit 6.2) Study Guide Each of the
... o Leading strand, lagging strand/Okazaki fragments, Origins of Replication, replication fork o Enzymes involved/job of each enzyme Helicase, telomerase, primase, polymerase(more than one), ligase, topoisomerase, hydrolase, nuclease o Recognize/complete complementary strands of DNA/RNA if given a s ...
... o Leading strand, lagging strand/Okazaki fragments, Origins of Replication, replication fork o Enzymes involved/job of each enzyme Helicase, telomerase, primase, polymerase(more than one), ligase, topoisomerase, hydrolase, nuclease o Recognize/complete complementary strands of DNA/RNA if given a s ...
The Molecular Genetics of Gene Expression
... Transcription Initiation • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 20-200 bp long—is the initial binding site of RNA polymerase and transcription initiation factors ...
... Transcription Initiation • Promoter = nucleotide sequence 20-200 bp long—is the initial binding site of RNA polymerase and transcription initiation factors ...
401Lecture5sp2013post
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
... Each probe specific for sequences separated by known distances in linear Fig. 6-35 Lodish et al. 2013 DNA What result would you expect if DNA exists in loops? Would you expect loops to be present at all stages of cell cycle? ...
Exercises 5 - Attempto Controlled English.
... 7. Introns are sections of DNA that will be spliced out after transcription. 8. The genes of eukaryotic organisms often contain non-coding regions called introns which are removed from the messenger RNA in a process known as splicing. 9. Transcription is the process through which a DNA sequence is ...
... 7. Introns are sections of DNA that will be spliced out after transcription. 8. The genes of eukaryotic organisms often contain non-coding regions called introns which are removed from the messenger RNA in a process known as splicing. 9. Transcription is the process through which a DNA sequence is ...
Steps in gene expression: comparison of
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
... Six steps at which eukaryotic gene expression can be controlled. In prokaryotic cells, genes do not have introns (no step 2) and transcription and translation are not separated in space and time (no step 3). ...
Unit 7 Study Guide ANSWERS 2014
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
... 10. What determines the specificity of a protein? The order of the nitrogenous bases in the DNA 11. In a eukaryotic cell, where does mRNA processing take place? During Transcription 12. What are the two processes that link the gene to the protein? Transcription and Translation 13. Proteins are made ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
... 1) DNA sequences are translated into RNA messages by RNA polymerases. 2) The initiation of RNA synthesis is controlled by specific DNA promoter sequences. 3) The synthesis of RNA is governed by initiation, elongation, and termination steps. 4) Eukaryotic mRNA is extensively processed ...
... 1) DNA sequences are translated into RNA messages by RNA polymerases. 2) The initiation of RNA synthesis is controlled by specific DNA promoter sequences. 3) The synthesis of RNA is governed by initiation, elongation, and termination steps. 4) Eukaryotic mRNA is extensively processed ...
Gene Expression Vocabulary
... 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a protein 6. RNA polymerase: an enzyme that begins transcription 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that ac ...
... 3. Gene expression: the process of information from DNA to proteins 4. Transcription: the information in DNA is transferred to mRNA 5. Translation: the information in mRNA is used to make a protein 6. RNA polymerase: an enzyme that begins transcription 7. Promoter: a specific sequence of DNA that ac ...
Genes
... T his is the simplest eukaryotic promoter. Most have additional sequences upstream and downstream that interact to determine what genes will be transcribed and when . ...
... T his is the simplest eukaryotic promoter. Most have additional sequences upstream and downstream that interact to determine what genes will be transcribed and when . ...
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2006 Roger D Kornberg Molecular
... with DNA, RNA inhibitors and protein complexes ...
... with DNA, RNA inhibitors and protein complexes ...
DNA Replication, RNA Molecules and Transcription
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
... A transcription reaction requires a DNA molecule to serve as template for transcription with a promoter (and, in vivo, transcription factors) to indicate where to begin transcribing and which strand to transcribe. Transcription reactions also require an RNA polymerase that recognizes the promoter on ...
Regulation of Gene Expression
... • Genes that are involved in the same metabolic pathway are often found in the same operon – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA ...
... • Genes that are involved in the same metabolic pathway are often found in the same operon – All under the control of the same promoter region – Thus these genes are transcribed all together into one continuous mRNA strand: polycistronic mRNA • Proteins are then synthesized from that mRNA ...
2007b
... 1. Describe the properties of the general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II, I and III. What is TBP and what general transcription factors have TBP as a component? What enzymatic activities do some of the transcription factors possess and how do they facilitate transcription? Describe TAFs ...
... 1. Describe the properties of the general transcription factors of RNA polymerase II, I and III. What is TBP and what general transcription factors have TBP as a component? What enzymatic activities do some of the transcription factors possess and how do they facilitate transcription? Describe TAFs ...
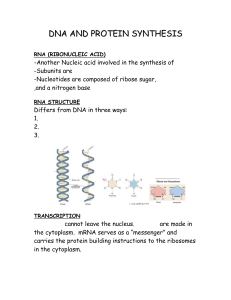
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
... the cytoplasm. mRNA serves as a “messenger” and carries the protein building instructions to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. ...
Title - Iowa State University
... d. regulation of individual genes by combination with other genes e. regulation of individual genes by combination with general factors 19. What is(are) function(s) of DNA Polymerase III? a. covalent addition of the deoxy-nucleotides to 3’ end of a new DNA strand b. covalent addition of the deoxy-nu ...
... d. regulation of individual genes by combination with other genes e. regulation of individual genes by combination with general factors 19. What is(are) function(s) of DNA Polymerase III? a. covalent addition of the deoxy-nucleotides to 3’ end of a new DNA strand b. covalent addition of the deoxy-nu ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand b ...
... 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme that assembles a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template is RNA polymerase. 6. The region of DNA where the production of an RNA strand b ...