DNA and RNA review
... What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles do enzymes play in DNA replication and maintenance? Describe the structure of RNA. What is/are the function(s) of RNA? What is a nucleotide? Of what does an RNA nucleotide consist? What are the nitrogen (nitr ...
... What is produced in DNA replication? Why is DNA replication necessary? What important roles do enzymes play in DNA replication and maintenance? Describe the structure of RNA. What is/are the function(s) of RNA? What is a nucleotide? Of what does an RNA nucleotide consist? What are the nitrogen (nitr ...
Gene Regulation
... • Sometimes genes are off completely and never transcribed again; some are just turned up or down – Eukaryotic genes typically turned up and down a little compared to huge increases for prokaryotes. • Genes that are “on” all the time = Constitutive • Many genes can be regulated “coordinately” – Euka ...
... • Sometimes genes are off completely and never transcribed again; some are just turned up or down – Eukaryotic genes typically turned up and down a little compared to huge increases for prokaryotes. • Genes that are “on” all the time = Constitutive • Many genes can be regulated “coordinately” – Euka ...
Sten_Ilmjärv_Different Aspects of Gene Regulation
... very little of DNA actually encodes proteins and therefore the genes may be separated by vast sequences of junk DNA. As well as there are non-coding sequences between different genes, there can be such areas within the gene as well. These areas are called introns, which can actually be many times lo ...
... very little of DNA actually encodes proteins and therefore the genes may be separated by vast sequences of junk DNA. As well as there are non-coding sequences between different genes, there can be such areas within the gene as well. These areas are called introns, which can actually be many times lo ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein
... Peptide bonds link amino acids together There are 20 essential amino acids found in all living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
... Peptide bonds link amino acids together There are 20 essential amino acids found in all living things. Some have modifications. o o o • Amino acids form 1 , 2 & 3 protein structures – Structures are essential to protein function ...
Do Now: - South Orange
... mRNA is transcribed Ribosome positions start codon to bind to anti-codon on tRNA Ribosome moves along mRNA, binding new tRNA and aa’s. Peptide bond binds aa’s as the chain builds and tRNA’s move along the chain Process continues until there is a stop codon in mRNA ...
... mRNA is transcribed Ribosome positions start codon to bind to anti-codon on tRNA Ribosome moves along mRNA, binding new tRNA and aa’s. Peptide bond binds aa’s as the chain builds and tRNA’s move along the chain Process continues until there is a stop codon in mRNA ...
Proteins – where do they come from?
... they need to make their own proteins. Or we eat animals that ate the plants (Whopper, please!) ...
... they need to make their own proteins. Or we eat animals that ate the plants (Whopper, please!) ...
Gene Regulation
... • Sometimes genes are off completely and never transcribed again; some are just turned up or down – Eukaryotic genes typically turned up and down a little compared to huge increases for prokaryotes. • Genes that are “on” all the time = Constitutive • Many genes can be regulated “coordinately” – Euka ...
... • Sometimes genes are off completely and never transcribed again; some are just turned up or down – Eukaryotic genes typically turned up and down a little compared to huge increases for prokaryotes. • Genes that are “on” all the time = Constitutive • Many genes can be regulated “coordinately” – Euka ...
File
... TRANSLATION – STEP 2 (CODONS) The ribosome reads mRNA three bases at a time. Three nitrogen bases (called a codon or a triplet; EX ...
... TRANSLATION – STEP 2 (CODONS) The ribosome reads mRNA three bases at a time. Three nitrogen bases (called a codon or a triplet; EX ...
Proteins
... TRANSLATION – STEP 2 (CODONS) The ribosome reads mRNA three bases at a time. Three nitrogen bases (called a codon or a triplet; EX ...
... TRANSLATION – STEP 2 (CODONS) The ribosome reads mRNA three bases at a time. Three nitrogen bases (called a codon or a triplet; EX ...
Protein Synthesis
... them those names! Be ready to share. Don’t tell them the answer to the second question until you watch the animation. ...
... them those names! Be ready to share. Don’t tell them the answer to the second question until you watch the animation. ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... acts as the start codon, it also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three codons act as stop codons and do not code for an amino acid. In these cases, the researchers would not have found radioactivity trapped on filters. Collaborative Questions 1. Discuss RNA processing in eukaryotes. A ...
... acts as the start codon, it also codes for the amino acid methionine. The other three codons act as stop codons and do not code for an amino acid. In these cases, the researchers would not have found radioactivity trapped on filters. Collaborative Questions 1. Discuss RNA processing in eukaryotes. A ...
Solutions for Practice Problems for Molecular Biology, Session 3
... after base pair 11 (shown in bold). What effect will this insertion mutation have on the mRNA transcript and resulting protein? The mRNA will be longer by one nucleotide, but because the insertion is prior to the start codon, the protein is unchanged. g) A different mutation results in the substitut ...
... after base pair 11 (shown in bold). What effect will this insertion mutation have on the mRNA transcript and resulting protein? The mRNA will be longer by one nucleotide, but because the insertion is prior to the start codon, the protein is unchanged. g) A different mutation results in the substitut ...
File
... Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription. Splicing of mRNA increases the number of different proteins an organism can produce. Gene expression is regulated by proteins that bind to specific base sequences in DNA. The environment of a cell and of an organism has an impact on gene expression. ...
... Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription. Splicing of mRNA increases the number of different proteins an organism can produce. Gene expression is regulated by proteins that bind to specific base sequences in DNA. The environment of a cell and of an organism has an impact on gene expression. ...
WELCOME TO BIOLOGY 2002 - University of Indianapolis
... Figure 17.6 The stages of transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination (Layer 1) ...
... Figure 17.6 The stages of transcription: initiation, elongation, and termination (Layer 1) ...
doc NTC Mar 31
... So if lactose is not present in the culture medium then the Laci gene is transcribed and is able to bind into the laci repressor protein, which is able to bind to the operator which is a DNA sequence upstream of the promoter of the Lac Operon. Therefore the RNA polymerase has a physical block, so ...
... So if lactose is not present in the culture medium then the Laci gene is transcribed and is able to bind into the laci repressor protein, which is able to bind to the operator which is a DNA sequence upstream of the promoter of the Lac Operon. Therefore the RNA polymerase has a physical block, so ...
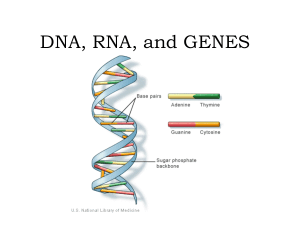
DNA, RNA, and GENES
... the amino acids bond. • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
... the amino acids bond. • Ribosomal RNA makes up ribosomes, where proteins are built. • Transfer RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to build the proteins. ...
Biology 105: Biology Science for Life with Physiology, 3rd Ed., Belk
... 20 organism resulting from incorporation of foreign organism’s DNA 21the key that matches mRNA codons to the amino acids for which they code 22 the entire suite of genes present in an organism; Human Genome Project mapped out our 20-25, 000 genes 23 enzymes that unwind & separate the 2 DNA strands b ...
... 20 organism resulting from incorporation of foreign organism’s DNA 21the key that matches mRNA codons to the amino acids for which they code 22 the entire suite of genes present in an organism; Human Genome Project mapped out our 20-25, 000 genes 23 enzymes that unwind & separate the 2 DNA strands b ...
Protein
... 2nd phase of Mitosis The kinetochore fibers move the Chromosomes to the equator (middle) – Each chromatid is attached to the fibers at the centromere. ...
... 2nd phase of Mitosis The kinetochore fibers move the Chromosomes to the equator (middle) – Each chromatid is attached to the fibers at the centromere. ...
this lecture as PDF here
... complementary nucleotide RNA strand. One significant difference between RNA and DNA sequence is the presence of U, or uracil in RNA instead of the T, or thymine of DNA. In the case of protein-encoding DNA, transcription is the first step that ultimately leads to the translation of the genetic code, ...
... complementary nucleotide RNA strand. One significant difference between RNA and DNA sequence is the presence of U, or uracil in RNA instead of the T, or thymine of DNA. In the case of protein-encoding DNA, transcription is the first step that ultimately leads to the translation of the genetic code, ...
4.2.08 105 lecture
... The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary amino acid sequence) of the protein to be made. The aquaporin protein has a specific structure due to the primary amino acid sequence and the specific structure of a protein gives each protein a specif ...
... The coding region is the genetic information in the DNA that tells the specific structure (primary amino acid sequence) of the protein to be made. The aquaporin protein has a specific structure due to the primary amino acid sequence and the specific structure of a protein gives each protein a specif ...
Chapter 17 Notes : From Gene to Protien
... is used in mRNA synth. 3 Steps of transcription : Initiation Elongation Termination Promoter also indicates which strand is template. In prokaryotes : RNA polymerase automatically binds to promoter region and begins working In eukaryotes : Transcription factors bind to the promoter region to c ...
... is used in mRNA synth. 3 Steps of transcription : Initiation Elongation Termination Promoter also indicates which strand is template. In prokaryotes : RNA polymerase automatically binds to promoter region and begins working In eukaryotes : Transcription factors bind to the promoter region to c ...
Document
... transferrin receptor mRNA would be high, even in the presence of high amounts of iron, because the IRP would always remain bound to the IRE and stabilize the transferrin receptor mRNA. Such a person would not have any problem taking up iron into his/her cells. In fact, this person would take up a lo ...
... transferrin receptor mRNA would be high, even in the presence of high amounts of iron, because the IRP would always remain bound to the IRE and stabilize the transferrin receptor mRNA. Such a person would not have any problem taking up iron into his/her cells. In fact, this person would take up a lo ...
C1. The common points of control are as follows: 1. DNA
... transferrin receptor mRNA would be high, even in the presence of high amounts of iron, because the IRP would always remain bound to the IRE and stabilize the transferrin receptor mRNA. Such a person would not have any problem taking up iron into his/her cells. In fact, this person would take up a lo ...
... transferrin receptor mRNA would be high, even in the presence of high amounts of iron, because the IRP would always remain bound to the IRE and stabilize the transferrin receptor mRNA. Such a person would not have any problem taking up iron into his/her cells. In fact, this person would take up a lo ...
200 THINGS TO KNOW AP Biology TEST
... CAM plants are desert succulents ( cactus) stomata close during day open at night to avoid dessication) ( C3 and C4 plants stomata opened up during day) 91. C4 uses 5ATP per molecule C3 only use 3ATP per molecule ( more efficient) 92. C4 sugarcane, corn 93. Telomere: region of repetitive DNA at the ...
... CAM plants are desert succulents ( cactus) stomata close during day open at night to avoid dessication) ( C3 and C4 plants stomata opened up during day) 91. C4 uses 5ATP per molecule C3 only use 3ATP per molecule ( more efficient) 92. C4 sugarcane, corn 93. Telomere: region of repetitive DNA at the ...
DNA/RNA
... 9 Directs order of linking amino acids in protein construction 9 Order of nucleotides determine order of amino acids for ...
... 9 Directs order of linking amino acids in protein construction 9 Order of nucleotides determine order of amino acids for ...