... trp operon and the lac operon. The trp operon is a repressible operon because the repressor coded by a regulator gene must bind with a corepressor (i.e., tryptophan) before the complex can bind to the operator and stop protein synthesis.In the lac operon, a repressor protein ordinarily binds the ope ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
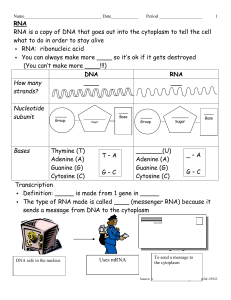
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
... RNA is a copy of DNA that goes out into the cytoplasm to tell the cell what to do in order to stay alive RNA: ribonucleic acid You can always make more ____ so it’s ok if it gets destroyed (You can’t make more ____!!!) DNA RNA How many ____ ___ strands? Nucleotide subunit ...
Practice Quiz
... 10. ______________ are a specialization of the plasma membrane that increases surface area. 11. During DNA replication, cytosine always binds to _________ with _________ hydrogen bonds. 12. RNA is different from NDA in that RNA is single-stranded, possesses ribose sugar, and ________ instead of thym ...
... 10. ______________ are a specialization of the plasma membrane that increases surface area. 11. During DNA replication, cytosine always binds to _________ with _________ hydrogen bonds. 12. RNA is different from NDA in that RNA is single-stranded, possesses ribose sugar, and ________ instead of thym ...
RNA Viruses
... • NS at 5’ end - S at 3’ • In vitro only synthesize NS proteins; stop signal leads to polyprotein • In vivo get shorter mRNA only after minus strand synthesis that codes for S polyprotein • Internal transcription site on minus strand • Minus is template for mRNA and for genome • S message is more ab ...
... • NS at 5’ end - S at 3’ • In vitro only synthesize NS proteins; stop signal leads to polyprotein • In vivo get shorter mRNA only after minus strand synthesis that codes for S polyprotein • Internal transcription site on minus strand • Minus is template for mRNA and for genome • S message is more ab ...
Document
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
... having evolved one from another through gene duplication. Paralogs are separated by a gene duplication event. • Each specific gene family member (e.g. a specific gene in human) is an ortholog of the same family member in another species (e.g. mouse). Both evolved from an ancestral globin gene. Ortho ...
Transcription and the Central Dogma
... – “Consensus” sequence meaning the DNA sequence from many genes averages out to this. – The closer these 2 regions actually are to the consensus sequences, the “stronger” the promoter, meaning the more likely RNA polymerase binding and transcription will occur. ...
... – “Consensus” sequence meaning the DNA sequence from many genes averages out to this. – The closer these 2 regions actually are to the consensus sequences, the “stronger” the promoter, meaning the more likely RNA polymerase binding and transcription will occur. ...
READ: Protein Synthesis File
... within the DNA to direct the conformational changes as well as the binding of helicases and transcription factors. Other non-coding DNA sequences called enhancers are not necessary for transcription, but their presence upstream or downstream from a gene can affect the rate of transcription. Protein ...
... within the DNA to direct the conformational changes as well as the binding of helicases and transcription factors. Other non-coding DNA sequences called enhancers are not necessary for transcription, but their presence upstream or downstream from a gene can affect the rate of transcription. Protein ...
Topic 13: ORGANIZATION OF DNA INTO GENES AND THE
... synthesis); not so in eukaryotes because (1) some regions of the newly formed mRNA must be excised and (2) the 3’ and 5’ ends must be modified to facilitate transport out of the nucleus as well as to make the message more stable. (1) eukaryotic gene structure- genes actually consists of bundles of r ...
... synthesis); not so in eukaryotes because (1) some regions of the newly formed mRNA must be excised and (2) the 3’ and 5’ ends must be modified to facilitate transport out of the nucleus as well as to make the message more stable. (1) eukaryotic gene structure- genes actually consists of bundles of r ...
Lecture 7
... • Bidirectional- from distinct starting pointproceeds in both directions • Semi- conservative- each of the 2 DNA helix’s generated contains 1 new strand and 1 old strand ...
... • Bidirectional- from distinct starting pointproceeds in both directions • Semi- conservative- each of the 2 DNA helix’s generated contains 1 new strand and 1 old strand ...
10-DNA-TranslationControl
... The lac operon is also regulated by an activator The activator is a protein called CAP It binds to the CAP-binding site and gives the RNA polymerase more access to the promoter However, a “low glucose” signal molecule has to bind to CAP before CAP can bind to the DNA ...
... The lac operon is also regulated by an activator The activator is a protein called CAP It binds to the CAP-binding site and gives the RNA polymerase more access to the promoter However, a “low glucose” signal molecule has to bind to CAP before CAP can bind to the DNA ...
Ch 13 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transfers each amino acid to the ribosome according to mRNA. ...
... Transfers each amino acid to the ribosome according to mRNA. ...
Document
... Short-term - genes are quickly turned on or off in response to the environment and demands of the cell. Long-term - genes for development and differentiation. ...
... Short-term - genes are quickly turned on or off in response to the environment and demands of the cell. Long-term - genes for development and differentiation. ...
chapter13
... Temporal regulation: some genes seem to be inducible only at certain periods in the life of the organism. ...
... Temporal regulation: some genes seem to be inducible only at certain periods in the life of the organism. ...
Protein Synthesis
... RNA is needed to produce proteins. It is so similar to DNA that it serves as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. Three different types of RNA are involved in the making of a protein. 1. mRNA (messenger RNA): mRNA creates a complementary strand from DNA and carries it out of the nucleus into the cyt ...
... RNA is needed to produce proteins. It is so similar to DNA that it serves as a temporary copy of a DNA sequence. Three different types of RNA are involved in the making of a protein. 1. mRNA (messenger RNA): mRNA creates a complementary strand from DNA and carries it out of the nucleus into the cyt ...
Protein Synthesis - SCF Faculty Site Homepage
... • A “window” in the DNA is opened – ultimately, a gene. • RNA Nucleotides are added (from 5’ to 3’) in accordance with the DNA parent template (which is read from 3’ to 5’). ...
... • A “window” in the DNA is opened – ultimately, a gene. • RNA Nucleotides are added (from 5’ to 3’) in accordance with the DNA parent template (which is read from 3’ to 5’). ...
Controlling the genes
... • TFIID binds to the ‘TATA’ box - a short region of DNA located about 25 bases upstream of the gene start site • TFIIA and TFIIB bind to TFIID causing local unraveling of the DNA • TFIIE, TFIIH, TFIIF, and RNA Pol II bind next • Addition of phosphate groups to the RNA Pol II allows transcription to ...
... • TFIID binds to the ‘TATA’ box - a short region of DNA located about 25 bases upstream of the gene start site • TFIIA and TFIIB bind to TFIID causing local unraveling of the DNA • TFIIE, TFIIH, TFIIF, and RNA Pol II bind next • Addition of phosphate groups to the RNA Pol II allows transcription to ...
RNA Transcription
... temporarily unwound (by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase as we shall see) to create a transcription bubble. The bubble has two strands known as the template and the non-template strand. RNA is copied from the template strand. The region of strand separation moves down the DNA with continual unwindi ...
... temporarily unwound (by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase as we shall see) to create a transcription bubble. The bubble has two strands known as the template and the non-template strand. RNA is copied from the template strand. The region of strand separation moves down the DNA with continual unwindi ...
ppt from class - Pingry School
... arsenate, halogenated compounds • Extract nitrogen and phosphate from waste water Potential food source ...
... arsenate, halogenated compounds • Extract nitrogen and phosphate from waste water Potential food source ...
Information Flow
... peels off can form a “hairpin loop.” The hairpin structure is recognized by RNA polymerase and this causes it to dissociate from the DNA. ...
... peels off can form a “hairpin loop.” The hairpin structure is recognized by RNA polymerase and this causes it to dissociate from the DNA. ...
Here are the answers
... Create a flow chart to describe the formation of a protein. Describe the activities of DNA and the three types of RNA. Accept all reasonable ...
... Create a flow chart to describe the formation of a protein. Describe the activities of DNA and the three types of RNA. Accept all reasonable ...
3rd quarter Assessment
... dominant trait and make it Capital • Use the same letter and make it lower case • All codominance and Incomplete Dominance crosses end in the 2 codominant traits creating ...
... dominant trait and make it Capital • Use the same letter and make it lower case • All codominance and Incomplete Dominance crosses end in the 2 codominant traits creating ...
The DNA Song
... one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” ...
... one of 4 bases: cytosine, guanine, thymine, and adenine. These nucleotides link together by covalent (strong) bonds between the sugars and phosphate groups to form strands. Two of the strands link together at the bases with hydrogen (weak) bonds. During DNA replication, an enzyme, helicase, “unzips” ...
Regulation of gene expression
... even when they are bound to DNA thousands of nucleotide pairs away from the promoter, this feature allows a single promoter to be controlled by an almost unlimited number of regulatory sequences scattered along the DNA • the DNA, at this time, loops out to allow all proteins to come into contact, re ...
... even when they are bound to DNA thousands of nucleotide pairs away from the promoter, this feature allows a single promoter to be controlled by an almost unlimited number of regulatory sequences scattered along the DNA • the DNA, at this time, loops out to allow all proteins to come into contact, re ...
RNA
... • according to base-pairing rules the mRNA base triplets are called codons • shared by the simplest bacteria after the most complex plants and animals ...
... • according to base-pairing rules the mRNA base triplets are called codons • shared by the simplest bacteria after the most complex plants and animals ...