DNA Transcription & Protein Translation
... 3. Each set of 3 mRNA bases (codons) will pair with a complimentary tRNA base triplet (called an anticodon). 4. Each tRNA is specific to an amino acid, as tRNA's are added to the sequence, amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, eventually forming a protein that is later released by the tR ...
... 3. Each set of 3 mRNA bases (codons) will pair with a complimentary tRNA base triplet (called an anticodon). 4. Each tRNA is specific to an amino acid, as tRNA's are added to the sequence, amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, eventually forming a protein that is later released by the tR ...
BINF6201/8201 Basics of Molecular Biology
... Higher level structures of DNA Ø In eukaryotic cells, DNA molecules are highly compacted by wrapping around the histone protein core, forming nucleosomes. Ø The histone core is made up of 2 copies of each of the four histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Ø Nucleosomes are further coiled to form ...
... Higher level structures of DNA Ø In eukaryotic cells, DNA molecules are highly compacted by wrapping around the histone protein core, forming nucleosomes. Ø The histone core is made up of 2 copies of each of the four histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Ø Nucleosomes are further coiled to form ...
Reverse Transcriptase - IISME Community Site
... 1) Single strand of DNA is created from the viral Reverse Transcriptase. 2) Mutations often occur during the reverse transcription process and thus casing drug resistance in the treatment of the cancer patient. Slide 5 Antiviral drug is also commonly known as reverse transcriptase inhibitor. ...
... 1) Single strand of DNA is created from the viral Reverse Transcriptase. 2) Mutations often occur during the reverse transcription process and thus casing drug resistance in the treatment of the cancer patient. Slide 5 Antiviral drug is also commonly known as reverse transcriptase inhibitor. ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
Information Flow 2
... acids. There are many tRNAs. Each has an anticodon that is complementary to one of the the codons. tRNA gly carries tRNA-gly Glycine and has the anticodon CCC. The anticodon CCC base-pairs with the codon GGG and positions the amino acid for polymer formation. ...
... acids. There are many tRNAs. Each has an anticodon that is complementary to one of the the codons. tRNA gly carries tRNA-gly Glycine and has the anticodon CCC. The anticodon CCC base-pairs with the codon GGG and positions the amino acid for polymer formation. ...
Zoology 145 course
... • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes all RNA molecules. • In contrast, eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in their nuclei. – RNA polymerase II is used for mRNA synthesis. ...
... • Bacteria have a single type of RNA polymerase that synthesizes all RNA molecules. • In contrast, eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases (I, II, and III) in their nuclei. – RNA polymerase II is used for mRNA synthesis. ...
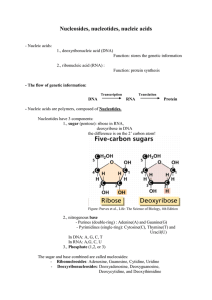
Nucleosides, nucleotides, nucleic acids
... The nucleotides are connected by a 3’-5’ phosphodiester bond to form a strand. Figure: structure of a single-stranded RNA molecule. There is a 3’ and a 5’ end of the ...
... The nucleotides are connected by a 3’-5’ phosphodiester bond to form a strand. Figure: structure of a single-stranded RNA molecule. There is a 3’ and a 5’ end of the ...
To begin with, all the DNA polymerases either the five types in
... is one mismatch for 10 billions to 100 billions. As we know, our DNA is 6 billion base. There is no one polymerase copies all this 6 billion. We have many bubbles and every polymerase works in a bubble. The area between a bubble and another is nearly 10000 or 100000 base. A polymerase may be given a ...
... is one mismatch for 10 billions to 100 billions. As we know, our DNA is 6 billion base. There is no one polymerase copies all this 6 billion. We have many bubbles and every polymerase works in a bubble. The area between a bubble and another is nearly 10000 or 100000 base. A polymerase may be given a ...
CENTRAL DOGMA AND GENE REGULATION
... sequences) and introns (insertion sequences) 2. The pre-mRNA is edited; the intron are removed. 3. A cap is added at the start site and a poly A++ tail is added at to the termination site. 4. The resulting mRNA is called “transcript”. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes (rER) and re ...
... sequences) and introns (insertion sequences) 2. The pre-mRNA is edited; the intron are removed. 3. A cap is added at the start site and a poly A++ tail is added at to the termination site. 4. The resulting mRNA is called “transcript”. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes (rER) and re ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... together, while chaperone proteins stabilize partially folded regions. ...
... together, while chaperone proteins stabilize partially folded regions. ...
MS Word File
... Eukaryotes TATA Box and CAAT box TATA box=AT rich sequence similar to –10; CAAT box=GGCCATTCT within 100 bases of start site ...
... Eukaryotes TATA Box and CAAT box TATA box=AT rich sequence similar to –10; CAAT box=GGCCATTCT within 100 bases of start site ...
Capacity Matrix Name: Date Started: Date Completed: Class/Course
... Identify the key molecules involved in replication Identify the key cellular structures involved in replication Describe the steps in the replication process Illustrate replication Identify the key molecules involved in transcription Identify the key cellular structures involved in ...
... Identify the key molecules involved in replication Identify the key cellular structures involved in replication Describe the steps in the replication process Illustrate replication Identify the key molecules involved in transcription Identify the key cellular structures involved in ...
Protein Synthesis Continued
... Each codon “codes” for a specific amino acid Using the chart on p. 303 decode the mRNA sequence from the previous slide. – UCGCACGGUU – Serine – Histidine - Glycine ...
... Each codon “codes” for a specific amino acid Using the chart on p. 303 decode the mRNA sequence from the previous slide. – UCGCACGGUU – Serine – Histidine - Glycine ...
GBE 335 MOLECULAR GENETICS
... recombination, control of gene expression, RNA and protein synthesis, viruses, plasmids, transposable genetic elements, recombinant DNA technology. ...
... recombination, control of gene expression, RNA and protein synthesis, viruses, plasmids, transposable genetic elements, recombinant DNA technology. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... steps after RNA polymerase binding • Some promoters require activators to stimulate the transition from closed to open complex. • Activators that stimulate this kind of promoter work by triggering a conformation change in either RNA polymerase or DNA. • This mechanism is an example of allostery. • O ...
... steps after RNA polymerase binding • Some promoters require activators to stimulate the transition from closed to open complex. • Activators that stimulate this kind of promoter work by triggering a conformation change in either RNA polymerase or DNA. • This mechanism is an example of allostery. • O ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
Bio07_TR__U04_CH12.QXD
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
Section 12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
Cell Signaling - Lectures For UG-5
... phosphorylation of the LRP coreceptor by GSK3 and another and another kinase, and thus allows subsequent binding of Axin. 2. This disrupts the Axin-APC-GSK3B-catenin complex, preventing phosphorylation of B-catenin by GSK3 which leads accumulation of B-catenin in the cell. 3. After translocation to ...
... phosphorylation of the LRP coreceptor by GSK3 and another and another kinase, and thus allows subsequent binding of Axin. 2. This disrupts the Axin-APC-GSK3B-catenin complex, preventing phosphorylation of B-catenin by GSK3 which leads accumulation of B-catenin in the cell. 3. After translocation to ...
Reading Study Guide B
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
... Describe the DNA transcription process by completing each sentence. During transcription, DNA is used to make _______________________________________. Only _________________________________________________________ are transcribed. Many copies of RNA can be made from _________________________________ ...
CS374 - Stanford University
... enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
... enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
05. Protein synthesis
... region (high in A and T, takes less energy to break these bonds) As in DNA replication, the DNA is "unzipped" by the enzyme helicase, leaving the single nucleotide chain open to be copied. When DNA is unwound it exposes the template strand The part of DNA not being used to make mRNA is called the co ...
... region (high in A and T, takes less energy to break these bonds) As in DNA replication, the DNA is "unzipped" by the enzyme helicase, leaving the single nucleotide chain open to be copied. When DNA is unwound it exposes the template strand The part of DNA not being used to make mRNA is called the co ...
worksheet 12-3
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...
... Transcription (page 301) 5. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about transcription. a. During transcription, DNA polymerase binds to RNA and separates the DNA strands. b. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA as a template to assemble nucleotides into a strand of RNA. c. RNA polymerase ...