RNA polymerase II is the key enzyme in the process of
... corresponding functions (right column). Fill in the answer sheet by providing the correct number associated with each letter. A. TFIIH B. C. D. E. F. ...
... corresponding functions (right column). Fill in the answer sheet by providing the correct number associated with each letter. A. TFIIH B. C. D. E. F. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. ...
... 3.Transfer RNA (tRNA)—transfers each amino acid and anticodon to the appropriate place on the mRNA strand. ...
Exam 1 Review KEY
... 23.) What is a polyribosome? Why would a cell contain polyribosomes? Many ribosomes on one mRNA. The cell is trying to produce many of one kind of protein. 24.) By coupling a reaction, an ___exergonic_______ reaction allows an ___endergonic______ reaction to become spontaneous. This is caused by th ...
... 23.) What is a polyribosome? Why would a cell contain polyribosomes? Many ribosomes on one mRNA. The cell is trying to produce many of one kind of protein. 24.) By coupling a reaction, an ___exergonic_______ reaction allows an ___endergonic______ reaction to become spontaneous. This is caused by th ...
A Zero-Knowledge Based Introduction to Biology
... enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
... enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
Chapter 17 Guided Notes
... The idea of a catalytic role for snRNA arose from the discovery of ribozymes, ___________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________. ...
... The idea of a catalytic role for snRNA arose from the discovery of ribozymes, ___________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________. ...
REVIEW for EXAM4-May 12th
... To reiterate, the sequence of events in Central Dogma as follow: first transcription > posttranscription> translation > post-translation. Transcriptional control is the most important step in this process because it is the first step and determines whether the gene will be transcribed in the first p ...
... To reiterate, the sequence of events in Central Dogma as follow: first transcription > posttranscription> translation > post-translation. Transcriptional control is the most important step in this process because it is the first step and determines whether the gene will be transcribed in the first p ...
File
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
... a. Before translation occurs, messenger RNA is transcribed from DNA in the nucleus. b. Translation occurs in the nucleus. c. It is the job of transfer RNA to bring the proper amino acid into the ribosome to be attached to the growing peptide chain. d. When the ribosome reaches a stop codon, it relea ...
Control of Eukaryotic Gene Expression (Learning Objectives)
... histones in control of gene expression. Define the term epigenetics. 3. Identify the main mechanism for turning on gene expression. Explain why control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells is like a “dimmer switch”, an “ON” switch that can be fine tuned. 4. Identify the major switch and all the fi ...
... histones in control of gene expression. Define the term epigenetics. 3. Identify the main mechanism for turning on gene expression. Explain why control of gene expression in eukaryotic cells is like a “dimmer switch”, an “ON” switch that can be fine tuned. 4. Identify the major switch and all the fi ...
12.3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries copies of messages encoded on DNA to the rest of the cell. • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) makes up part of the ribosome ...
... • Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries copies of messages encoded on DNA to the rest of the cell. • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) makes up part of the ribosome ...
No Slide Title
... 3) Once bound, RNA polymerase “melts” the DNA 4) rNTPs bind template 5) RNA polymerase catalyzes phosphodiester bonds, melts and unwinds template 6) sigma falls off after ~10 bases are added ...
... 3) Once bound, RNA polymerase “melts” the DNA 4) rNTPs bind template 5) RNA polymerase catalyzes phosphodiester bonds, melts and unwinds template 6) sigma falls off after ~10 bases are added ...
TRANSCRIPTION AND PROCESSING OF RNA
... (translational open reading frames (ORF) or cistrons). In prokaryotes polycistronic mRNAs are common. In eukaryotes, monocistronic mRNAs are the general rule, but some transcription units encode more than one polypeptide as a consequence of alternative transcriptional start sites and/or alternative ...
... (translational open reading frames (ORF) or cistrons). In prokaryotes polycistronic mRNAs are common. In eukaryotes, monocistronic mRNAs are the general rule, but some transcription units encode more than one polypeptide as a consequence of alternative transcriptional start sites and/or alternative ...
Transcription and Translation: Protein synthesis
... Mutations lead to mistakes in the proteins being made. Mutations can happen during DNA replication and change the “blueprint of the cell” Or During transcription or translation so a wrong protein or no protein is made ...
... Mutations lead to mistakes in the proteins being made. Mutations can happen during DNA replication and change the “blueprint of the cell” Or During transcription or translation so a wrong protein or no protein is made ...
AP Details for Protein Synthesis
... – TATA box binding site – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors – Enhancer region – binding site for activators (activate genes) – Silence region – Binding site for repressors (turns genes off) ...
... – TATA box binding site – binding site for RNA polymerase & transcription factors – Enhancer region – binding site for activators (activate genes) – Silence region – Binding site for repressors (turns genes off) ...
Protein Synthesis - Overview
... ribosome contains two sites for tRNA: an A (acceptor) site and a P (peptide) site. tRNA (Met- AUG) enters the P site. the rest of the tRNA enter at the A site and form peptide bonds between the amino acids as the chain forms. ...
... ribosome contains two sites for tRNA: an A (acceptor) site and a P (peptide) site. tRNA (Met- AUG) enters the P site. the rest of the tRNA enter at the A site and form peptide bonds between the amino acids as the chain forms. ...
Replication/Transcription/Translation
... Transcription 1. Helicase unzips DNA 2. RNA Polymerase attaches to promoter ...
... Transcription 1. Helicase unzips DNA 2. RNA Polymerase attaches to promoter ...
Name
... be made during transcription: DNA strand: TAC – GCA - TGG – AAA – GGG – CGG – ACT mRNA strand: ____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ Next, use the decoder chart below to write the corresponding amino acids that would be coded for by the mRNA that you created: Amino acids: ______ - ___ ...
... be made during transcription: DNA strand: TAC – GCA - TGG – AAA – GGG – CGG – ACT mRNA strand: ____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ - _____ Next, use the decoder chart below to write the corresponding amino acids that would be coded for by the mRNA that you created: Amino acids: ______ - ___ ...
RNA and Translation notes
... •Transcription and translation are coupled in prokaryotes: translation occurs while the mRNA is being made. ...
... •Transcription and translation are coupled in prokaryotes: translation occurs while the mRNA is being made. ...
Learning Guide:
... 5. Explain what would happen to the process of gene expression if the gene for RNA polymerase was mutated. 6. Each amino acid has a tRNA synthetase enzyme that is responsible for attaching it to a tRNA molecule. Explain what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene encoding one of these enzy ...
... 5. Explain what would happen to the process of gene expression if the gene for RNA polymerase was mutated. 6. Each amino acid has a tRNA synthetase enzyme that is responsible for attaching it to a tRNA molecule. Explain what would happen if there was a mutation in the gene encoding one of these enzy ...
Introduction to Biology
... enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
... enzymatic ingredients necessary for RNA transcription and translation. The synthetic virus was able to successfully replicate itself from this mixture.” ...
differential gene expression
... upstream (thousands of nucleotides away) called a enhancers. – DNA enhancers can work by a protein (activator) attaching to the enhancer. – The DNA then loops the DNA back on itself to attach to the promoter region. ...
... upstream (thousands of nucleotides away) called a enhancers. – DNA enhancers can work by a protein (activator) attaching to the enhancer. – The DNA then loops the DNA back on itself to attach to the promoter region. ...
Review-Qs-for-modern-genetics
... 1. The main enzyme involved in DNA replication is RNA polymerase. FALSE – DNA polymerase. 2. To determine the amino acid, look up the three base anticodon on the genetic dictionary FALSE – codon. 3. Ligase joins DNA fragments of the lagging strand. TRUE 4. DNA polymerase lengthens the new strands fr ...
... 1. The main enzyme involved in DNA replication is RNA polymerase. FALSE – DNA polymerase. 2. To determine the amino acid, look up the three base anticodon on the genetic dictionary FALSE – codon. 3. Ligase joins DNA fragments of the lagging strand. TRUE 4. DNA polymerase lengthens the new strands fr ...
9/16
... •Each cell contains ~6 billion base pairs of DNA. •This DNA is ~2 meters long and 2 nm wide. •~3% directly codes for amino acids •~10% is genes •In a single human cell only about 5-10% of genes are expressed at a time. ...
... •Each cell contains ~6 billion base pairs of DNA. •This DNA is ~2 meters long and 2 nm wide. •~3% directly codes for amino acids •~10% is genes •In a single human cell only about 5-10% of genes are expressed at a time. ...
Powerpoint file - revised
... •The glnA gene encodes glutamine synthetase, which synthesizes glutamine from glutamic acid and ammonia. • The 54-containing RNA polymerase binds to the glnA promoter, forming a closed complex, before being activated. • In response to low levels of glutamine, a protein kinase called NtrB phosphoryl ...
... •The glnA gene encodes glutamine synthetase, which synthesizes glutamine from glutamic acid and ammonia. • The 54-containing RNA polymerase binds to the glnA promoter, forming a closed complex, before being activated. • In response to low levels of glutamine, a protein kinase called NtrB phosphoryl ...
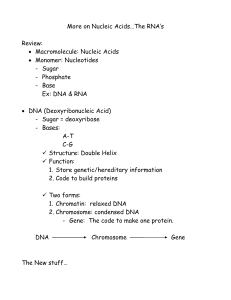
Notes: More on Nucleic Acids
... 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
... 2. Code to build proteins Two forms: 1. Chromatin: relaxed DNA 2. Chromosome: condensed DNA - Gene: The code to make one protein. DNA ...
Ch 10
... • Bacteria replicate DNA and use binary fission to reproduce – How to they produce new gene combinations? ...
... • Bacteria replicate DNA and use binary fission to reproduce – How to they produce new gene combinations? ...