Gene to protein
... 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; ...
... 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; ...
Ch 1617 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
... 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; ...
... 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
... DNA Secondary Structure Double Helix ...
... DNA Secondary Structure Double Helix ...
RNA
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
myoD
... the acidic activation domain can activate transcription from a downstream enhancer site while the proline domain only activates weakly and the glutamine domain not at all. Proposed targets of different transcriptional activators include: • Chromatin structure; • Interaction with TFIID through specif ...
... the acidic activation domain can activate transcription from a downstream enhancer site while the proline domain only activates weakly and the glutamine domain not at all. Proposed targets of different transcriptional activators include: • Chromatin structure; • Interaction with TFIID through specif ...
divergent transcription
... In the more complicated posttranscriptional processing of eukaryotic mRNAs, sequences called introns (intravening sequences) are removed from the primary transcript and the remaining segments, termed exons (expressed sequences), are ligated to form a functional RNA. This process involves a large com ...
... In the more complicated posttranscriptional processing of eukaryotic mRNAs, sequences called introns (intravening sequences) are removed from the primary transcript and the remaining segments, termed exons (expressed sequences), are ligated to form a functional RNA. This process involves a large com ...
DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation assessment
... 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence of DNA 2.7.3 State that DNA replication is semi-conservative 2.7.4 Compare the structure of DNA and RNA 2.7.5 Outline DNA transcription in terms of the formation of an RNA strand complementary to th ...
... 2.7.2 Explain the significance of complementary base pairing in the conservation of the base sequence of DNA 2.7.3 State that DNA replication is semi-conservative 2.7.4 Compare the structure of DNA and RNA 2.7.5 Outline DNA transcription in terms of the formation of an RNA strand complementary to th ...
Protein synthesis and mut ppt
... a single mRNA strand is used to make many copies of the polypeptides it codes for simultaneously Many ribosome's can be bonded to the same mRNA strip all at once Polypeptides with specific destinations Some polypeptides need to leave the cell Therefore they are made in bound ribosome's on th ...
... a single mRNA strand is used to make many copies of the polypeptides it codes for simultaneously Many ribosome's can be bonded to the same mRNA strip all at once Polypeptides with specific destinations Some polypeptides need to leave the cell Therefore they are made in bound ribosome's on th ...
國立嘉義大學九十二學年度
... (4) The AT/GC ratio does not matter. (5) They should anneal rapidly, before the larger DNA strands reanneal. 3. Forensic uses of DNA to identify victims or criminals exploit the following trait in DNA: (1) Differences in sizes of DNA fragments (RFLPs). (2) Footprinting. (3) Site directed mutations. ...
... (4) The AT/GC ratio does not matter. (5) They should anneal rapidly, before the larger DNA strands reanneal. 3. Forensic uses of DNA to identify victims or criminals exploit the following trait in DNA: (1) Differences in sizes of DNA fragments (RFLPs). (2) Footprinting. (3) Site directed mutations. ...
File - Down the Rabbit Hole
... instructions for making a protein molecule • Started and controlled by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. – RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a special point (start signal) – RNA polymerase unwinds and separates the two DNA strands – RNA polymerase adds and links complementary RNA nucleotides as it “ ...
... instructions for making a protein molecule • Started and controlled by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. – RNA polymerase binds to the DNA at a special point (start signal) – RNA polymerase unwinds and separates the two DNA strands – RNA polymerase adds and links complementary RNA nucleotides as it “ ...
RNA - Humble ISD
... separates strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble an RNA copy. ...
... separates strands, then uses one strand as a template to assemble an RNA copy. ...
Protein synthesis
... Hydrogen bonds between DNA bases so that transcription can begin • RNA (or DNA) Polymerase – transcription enzyme that adds RNA nucleotides to the DNA template by helping to form Hydrogen bonds between the bases of DNA and mRNA ...
... Hydrogen bonds between DNA bases so that transcription can begin • RNA (or DNA) Polymerase – transcription enzyme that adds RNA nucleotides to the DNA template by helping to form Hydrogen bonds between the bases of DNA and mRNA ...
Nucleic acid recognition from prokaryotes to eukaryotes: Case
... small angle X-ray scattering data, we propose a model of adjustable binding registers as a means for universal recognition of diverse 3' splice sites by U2AF65. Altogether, these two examples demonstrate the diversity of conformational changes used by proteins to accomplish gene regulation, from the ...
... small angle X-ray scattering data, we propose a model of adjustable binding registers as a means for universal recognition of diverse 3' splice sites by U2AF65. Altogether, these two examples demonstrate the diversity of conformational changes used by proteins to accomplish gene regulation, from the ...
Jacob and Monod were the first scientists to elucidate a
... A bacterium's prime source of food is glucose, since it does not have to be modified to enter the repiratory pathway. So if both glucose and lactose are around, the bacterium wants to turn off lactose metabolism in favour of glucose metabolism. There are sites upstream of the Lac genes that respond ...
... A bacterium's prime source of food is glucose, since it does not have to be modified to enter the repiratory pathway. So if both glucose and lactose are around, the bacterium wants to turn off lactose metabolism in favour of glucose metabolism. There are sites upstream of the Lac genes that respond ...
Document
... ▫ Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA ...
... ▫ Long strands of RNA nucleotides that are formed complementary to one strand of DNA ...
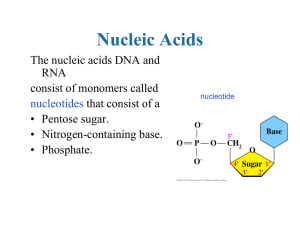
Nucleic acids
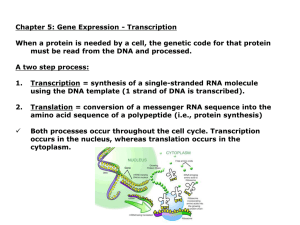
... Gene Expression The process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product: Proteins • Transcription • RNA processing • RNA export • Translation • Folding • Protein transport ...
... Gene Expression The process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product: Proteins • Transcription • RNA processing • RNA export • Translation • Folding • Protein transport ...
What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
Unit 4: Genetics Name: Date: Aim #23 Translation: How does DNA
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. What is Translation? Where does translation occur? What are the steps of translation? ...
... nucleus, allowing the mRNA strand to leave the nucleus with the genetic message and head for the ribosome to make proteins through another process called translation. What is Translation? Where does translation occur? What are the steps of translation? ...
Promoters
... • The role of β in phosphodiester bond formation : The core subunitβ binds nucleotides at the active site of the RNA polymerase where phosphodiester bonds are formed. Rifampicin can block initiation by preventing the formation of that first bond. • The core subunit β’can bind weakly to DNA by itself ...
... • The role of β in phosphodiester bond formation : The core subunitβ binds nucleotides at the active site of the RNA polymerase where phosphodiester bonds are formed. Rifampicin can block initiation by preventing the formation of that first bond. • The core subunit β’can bind weakly to DNA by itself ...
PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... (the details) Protein Synthesis involves two main steps: Transcription Translation ...
... (the details) Protein Synthesis involves two main steps: Transcription Translation ...
Identification of novel drug targets using model organisms
... contacts across a large interface, which might not traditionally be considered a good target. Nevertheless, Andre et al. 10 identified a series of small molecules that inhibit the RNA polymerase-s interaction, indicating that even an extensive interaction surface can be effectively targeted. Ribosom ...
... contacts across a large interface, which might not traditionally be considered a good target. Nevertheless, Andre et al. 10 identified a series of small molecules that inhibit the RNA polymerase-s interaction, indicating that even an extensive interaction surface can be effectively targeted. Ribosom ...
Chapter Outline - Ltcconline.net
... 5. The function of a gene is to: 6. A protein may consist of two or more different polypeptides G. From Nucleotides to Amino Acids: An Overview 1. Genetic information in DNA is: 2. A codon is: H. The Genetic Code 1. The genetic code is: 2. Of the 64 triplets, a. 61 code for amino acids and b. 3 are ...
... 5. The function of a gene is to: 6. A protein may consist of two or more different polypeptides G. From Nucleotides to Amino Acids: An Overview 1. Genetic information in DNA is: 2. A codon is: H. The Genetic Code 1. The genetic code is: 2. Of the 64 triplets, a. 61 code for amino acids and b. 3 are ...
DNA
... – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
... – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...