RNA and Protein synthesis
... • tRNA synthetase grabs the tRNA and appropriate amino acid and links them together by using the energy of an ATP molecule. • Once the ATP’s energy is used to create a high energy bond the tRNA and amino acid are released and then travels to the ribosome. • Video ...
... • tRNA synthetase grabs the tRNA and appropriate amino acid and links them together by using the energy of an ATP molecule. • Once the ATP’s energy is used to create a high energy bond the tRNA and amino acid are released and then travels to the ribosome. • Video ...
99( I )生技所分生考題,林富邦老師部分
... A. signal sequence removed. B. glycosylation in the ER lumen. C. signal sequence synthesis on ribosomes. D. SRP binds signal sequence and subsequently binds SRP-receptor. E. ribosome dissociates. A. A, C, E, B, D B. A, C, B, D, E C. C, A, D, B, E D. C, D, A, B, E E. C, B, D, E, A 5. Translation of a ...
... A. signal sequence removed. B. glycosylation in the ER lumen. C. signal sequence synthesis on ribosomes. D. SRP binds signal sequence and subsequently binds SRP-receptor. E. ribosome dissociates. A. A, C, E, B, D B. A, C, B, D, E C. C, A, D, B, E D. C, D, A, B, E E. C, B, D, E, A 5. Translation of a ...
mRNA
... template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create an RNA copy. Although RNA polymerase traverses the template strand from 3' → 5', the coding (non-template) strand and newly-formed RNA can also be used as reference points, so transcription can be described as occu ...
... template strand and uses base pairing complementarity with the DNA template to create an RNA copy. Although RNA polymerase traverses the template strand from 3' → 5', the coding (non-template) strand and newly-formed RNA can also be used as reference points, so transcription can be described as occu ...
Chapter 17 Presentation
... the information content in DNA-- -the specific sequence of nucleotides along the DNA--strands needs to be turned into protein. ...
... the information content in DNA-- -the specific sequence of nucleotides along the DNA--strands needs to be turned into protein. ...
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2006 I
... has been inserted in the right place, the DNA-strand is prompted forward by a small helical structure (in green) in the polymerase. This spring-like structure flips back and forth thanks to constant spontaneous changes in shape of the polymerase (this is precisely the mechanism which is destroyed by ...
... has been inserted in the right place, the DNA-strand is prompted forward by a small helical structure (in green) in the polymerase. This spring-like structure flips back and forth thanks to constant spontaneous changes in shape of the polymerase (this is precisely the mechanism which is destroyed by ...
Document
... 11. What RNA polymerase(s) transcribe eukaryotic genes? Name the polymerase(s) and the type of gene(s) it transcribes. 12. In prokaryotes, regulatory elements are fixed positions with respect to the gene(s) regulated. How does the situation differ in eukaryotes ? 13. List several mechanisms a cell u ...
... 11. What RNA polymerase(s) transcribe eukaryotic genes? Name the polymerase(s) and the type of gene(s) it transcribes. 12. In prokaryotes, regulatory elements are fixed positions with respect to the gene(s) regulated. How does the situation differ in eukaryotes ? 13. List several mechanisms a cell u ...
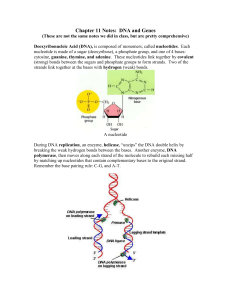
Chapter 11 Notes: DNA and Genes
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
... In transcription, a single strand of mRNA is copied from DNA, by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. In this case, however, thymine is replaced with uracil, so the “new” base pairing rule is C-G & A-U. The mRNA is then able to move through the nuclear membrane into the cytosol. Remember that all RNA i ...
Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the
... The amino acid sequence NADFDGD(E/Q)M(N/A) is conserved in all /3',A (respectively A') subunits of bacterial, eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fr ...
... The amino acid sequence NADFDGD(E/Q)M(N/A) is conserved in all /3',A (respectively A') subunits of bacterial, eucaryal and archaeal RNA polymerases known so far (3, 4, 5). Frequently, an oligonucleotide primer derived from this sequence, specifically hybridized to three G. lamblia chromosomal DNA fr ...
Chapter 13.1 and 13.2 RNA, Ribosomes, and Protein Synthesis
... amino acids to a polypeptide chain or protein. • Process of decoding mRNA to protein is “Translation”. – mRNA transcribed (transcription) in nucleus goes to cytoplasm. – On ribosome, translation begins at START codon. – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino ...
... amino acids to a polypeptide chain or protein. • Process of decoding mRNA to protein is “Translation”. – mRNA transcribed (transcription) in nucleus goes to cytoplasm. – On ribosome, translation begins at START codon. – Each codon attracts an anticodon aka tRNA – tRNA carries an amino acid. – Amino ...
DNA and Central Dogma Study Guide
... 18. What does transcription make? 19. Where does transcription take place? Why? 20. Explain transcription in three steps. You should use the terms DNA, RNA polymerase, gene, mRNA, complementary base pairing. a) b) c) 21. What does translation make? 22. Where does translation take place? 23. Explain ...
... 18. What does transcription make? 19. Where does transcription take place? Why? 20. Explain transcription in three steps. You should use the terms DNA, RNA polymerase, gene, mRNA, complementary base pairing. a) b) c) 21. What does translation make? 22. Where does translation take place? 23. Explain ...
Initiation
... 1. Initiation – attachment of mRNA to the ribosome (This was already covered in Step # 3) 2. Elongation – the addition of amino acids to the growing protein chain A Site ...
... 1. Initiation – attachment of mRNA to the ribosome (This was already covered in Step # 3) 2. Elongation – the addition of amino acids to the growing protein chain A Site ...
Chp 11 Notes
... c. The RNA polymerase can now make the enzymes needed for lactose metabolism d. Lactose is the inducer in this example 9. The ability to turn genes on and off makes cells much more efficient C. Gene Expression in Eukaryotes 1. Very different than prokaryotes. Much more complex. Explain: More Chromos ...
... c. The RNA polymerase can now make the enzymes needed for lactose metabolism d. Lactose is the inducer in this example 9. The ability to turn genes on and off makes cells much more efficient C. Gene Expression in Eukaryotes 1. Very different than prokaryotes. Much more complex. Explain: More Chromos ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... bonds are broken between the two strands by __Helicase___. 2) ______RNA____ __primers______ are added to both strands 3) DNA polymerase makes a new strand in the ____5’-->3’________ direction. For the ____leading_____ _____strand____, synthesis occurs toward the replication fork. For the ____lagging ...
... bonds are broken between the two strands by __Helicase___. 2) ______RNA____ __primers______ are added to both strands 3) DNA polymerase makes a new strand in the ____5’-->3’________ direction. For the ____leading_____ _____strand____, synthesis occurs toward the replication fork. For the ____lagging ...
Prokaryotic Gene Expression Mechanisms RNA Types of RNA Other
... repressor for lacO to 2 x 1010, but the affinity for random DNA sequences remains the same. So the specificity of repressor for lacO drops 3 orders of magnitude (or 1000-fold). Under these conditions, you can calculate that less than 3% of the lacO sites should have repressor bound to them (when IPT ...
... repressor for lacO to 2 x 1010, but the affinity for random DNA sequences remains the same. So the specificity of repressor for lacO drops 3 orders of magnitude (or 1000-fold). Under these conditions, you can calculate that less than 3% of the lacO sites should have repressor bound to them (when IPT ...
Slide 1
... D) Once the pre-mRNA has been converted to mRNA. E) As soon as the DNA introns are removed from the template. B ...
... D) Once the pre-mRNA has been converted to mRNA. E) As soon as the DNA introns are removed from the template. B ...
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Composed of nucleotides, but differs from DNA in three ways. 1. Single strand of nucleotides instead of double stranded 2. Has uracil instead of thymine 3. Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose ...
... Composed of nucleotides, but differs from DNA in three ways. 1. Single strand of nucleotides instead of double stranded 2. Has uracil instead of thymine 3. Contains ribose instead of deoxyribose ...
Chapter 14 Review
... • Each person from your team may go up to the board to assist someone one time. After that they may not be a helper for the remainder of the game. No direct communication between the group and the board. • You must show your work with appropriate units for math ...
... • Each person from your team may go up to the board to assist someone one time. After that they may not be a helper for the remainder of the game. No direct communication between the group and the board. • You must show your work with appropriate units for math ...
1. The term peptidyltransferase relates to A. base additions during
... 6. Please describe the Base excision repair in E. coli. (5%) 7. Please describe the role played by RecABCD proteins in E. coli. (5%) 8. How does a retrovirus complete its life cycle? (5%) 9. Explain why E. coli lacZ is often used as a reporter gene in yeast cells but not in E. coli cells. (5 %) 10. ...
... 6. Please describe the Base excision repair in E. coli. (5%) 7. Please describe the role played by RecABCD proteins in E. coli. (5%) 8. How does a retrovirus complete its life cycle? (5%) 9. Explain why E. coli lacZ is often used as a reporter gene in yeast cells but not in E. coli cells. (5 %) 10. ...
Chapter 17 Molecular Genetics
... – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. – Ribosomes are required to produce proteins on the mRNA template. ...
... – Messenger RNA molecules carry this information to the cytoplasm, where proteins are synthesized. – Messenger RNA serves as a template for protein synthesis. – Ribosomes are required to produce proteins on the mRNA template. ...
In the nucleus
... will transcibe mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. rRNA and ribosomal proteins are synthesis in the nucleolus. A complimentary strand of RNA is made from one strand of DNA. RNA are modified in the nucleus then exit through pores in the nuclear membrane. ...
... will transcibe mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA. rRNA and ribosomal proteins are synthesis in the nucleolus. A complimentary strand of RNA is made from one strand of DNA. RNA are modified in the nucleus then exit through pores in the nuclear membrane. ...
No Slide Title
... -dissociable into small (30S) and large (50S) subunits -30S contains 16S RNA, 21 polypeptides -50S contains 5S, 23S RNA + 31 polypeptides “Although the ribosome has been crystallized…it is such a complex entity that it will be many years before its structure is known in molecular detail” - Voet and ...
... -dissociable into small (30S) and large (50S) subunits -30S contains 16S RNA, 21 polypeptides -50S contains 5S, 23S RNA + 31 polypeptides “Although the ribosome has been crystallized…it is such a complex entity that it will be many years before its structure is known in molecular detail” - Voet and ...