File
... Proteins may bind to regions of the mRNA strand preventing the ribosomes from translating it. Post-translational Prevent the protein from becoming functional Ex: Proteins are often not fully functional after translation. Proinsulin is a precursor to insulin. It needs to be cut into 2 polypep ...
... Proteins may bind to regions of the mRNA strand preventing the ribosomes from translating it. Post-translational Prevent the protein from becoming functional Ex: Proteins are often not fully functional after translation. Proinsulin is a precursor to insulin. It needs to be cut into 2 polypep ...
Protein Synthesis Simulation
... 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green window over it and click. 7. Build the protein by dragging the correct amino acid sequence from the “Universal Genetic Code Chart” into the box. Record the amino ...
... 6. The “Met” amino acid is the “start” codon and allows protein synthesis to begin. Find this codon on the RNA strand. Position the green window over it and click. 7. Build the protein by dragging the correct amino acid sequence from the “Universal Genetic Code Chart” into the box. Record the amino ...
CHAPTER 4, PART 2
... 1. Allmost all have coding sequences (exons) interrupted by noncoding sequences (introns) 2. After transcription, introns are removed and exons are joined accurately by splicing at evolutionarily conserved sequences. 3. Exon polarity (5`Æ3`) is retained after splicing 4. Protein domains coded by exo ...
... 1. Allmost all have coding sequences (exons) interrupted by noncoding sequences (introns) 2. After transcription, introns are removed and exons are joined accurately by splicing at evolutionarily conserved sequences. 3. Exon polarity (5`Æ3`) is retained after splicing 4. Protein domains coded by exo ...
Protein Synthesis
... Transcription, cont. • Promoters are regions on DNA that show where RNA Polymerase must bind to begin the Transcription of RNA • Specific base sequences act as signals to stop • Called the termination signal ...
... Transcription, cont. • Promoters are regions on DNA that show where RNA Polymerase must bind to begin the Transcription of RNA • Specific base sequences act as signals to stop • Called the termination signal ...
Vocabulary Quiz Key Terms
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
protein
... 1、promoter Eukaryotic promoter is a group of transcriptioncontrolling elements around the binding site of RNA polymerase, including at least a transcription initiation site and more than one functional element. ...
... 1、promoter Eukaryotic promoter is a group of transcriptioncontrolling elements around the binding site of RNA polymerase, including at least a transcription initiation site and more than one functional element. ...
Slide 1 - Ommbid.com
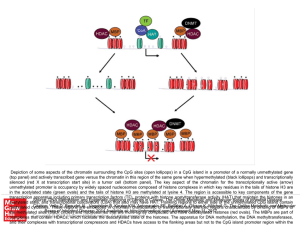
... (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (a ...
... (top panel) and actively transcribed gene versus the chromatin in this region of the same gene when hypermethylated (black lollipops) and transcriptionally silenced (red X at transcription start site) in a tumor cell (bottom panel). The key aspect of the chromatin for the transcriptionally active (a ...
Bacterial Genetics Summary
... b. Messenger RNA (mRNA) (1) carries information for sequencing one protein (2) sequence of codons (a) three nitrogen bases that specify an amino acid (b) 64 different codons (3) start signal - initiation codon (AUG) (4) stop signal - termination codon (one of three) ...
... b. Messenger RNA (mRNA) (1) carries information for sequencing one protein (2) sequence of codons (a) three nitrogen bases that specify an amino acid (b) 64 different codons (3) start signal - initiation codon (AUG) (4) stop signal - termination codon (one of three) ...
pdf
... 1. Repressor-operator: requires a protein binding to a specific site in the presence of Trp to decrease the efficiency of initiation of transcription. 2. Attenuation: the elongation (and termination) of transcription by RNA polymerase is linked to the progress of translation by a ribosome. In the pr ...
... 1. Repressor-operator: requires a protein binding to a specific site in the presence of Trp to decrease the efficiency of initiation of transcription. 2. Attenuation: the elongation (and termination) of transcription by RNA polymerase is linked to the progress of translation by a ribosome. In the pr ...
Discussion Guide Chapter 15
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
... 6. Differentiate between the three main replication enzymes. (see Science Focus p. 218) Helicase DNA Polymerase DNA Ligase ...
Gene expression - El Camino College
... Gene regulation during transcription Transcription factors turn genes on by attaching to DNA regions called enhancers Making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to DNA and begin transcription ...
... Gene regulation during transcription Transcription factors turn genes on by attaching to DNA regions called enhancers Making it easier for RNA polymerase to bind to DNA and begin transcription ...
DNA - wwphs
... AUG encodes methionine. Methionine can be used within a protein sequence and is often the first amino acid cueing the beginning of translation. UAA, UAG, and UGA do not encode an amino acid These codons signal termination of the protein. ...
... AUG encodes methionine. Methionine can be used within a protein sequence and is often the first amino acid cueing the beginning of translation. UAA, UAG, and UGA do not encode an amino acid These codons signal termination of the protein. ...
From Gene to Protein
... Any downstream bases will be affected Almost always causes protein to be nonfunctional ...
... Any downstream bases will be affected Almost always causes protein to be nonfunctional ...
Ch 10
... • Bacteria replicate DNA and use binary fission to reproduce – How to they produce new gene combinations? ...
... • Bacteria replicate DNA and use binary fission to reproduce – How to they produce new gene combinations? ...
THREE POSSIBILE MODELS FOR REPLICATION
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) MESSENGER RNA carries DNA message from nucleus to cytoplasm; mMessage is read in “triplets” called CODONS 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; REDUNDANCY OR ”WOBBLE” - codons for sa ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) MESSENGER RNA carries DNA message from nucleus to cytoplasm; mMessage is read in “triplets” called CODONS 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; REDUNDANCY OR ”WOBBLE” - codons for sa ...
THREE POSSIBILE MODELS FOR REPLICATION
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) MESSENGER RNA carries DNA message from nucleus to cytoplasm; mMessage is read in “triplets” called CODONS 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; REDUNDANCY OR ”WOBBLE” - codons for sa ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) MESSENGER RNA carries DNA message from nucleus to cytoplasm; mMessage is read in “triplets” called CODONS 64 different codons code for 20 different amino acids; AUG = START codon; UAA, UAG, UGA are STOP codons; REDUNDANCY OR ”WOBBLE” - codons for sa ...
Chapter 12
... most coding for internal methionines or representing out of phase codons. Binding of mRNA to rRNA via the Shine Dalgarno sequence may stimulate initiation by increasing the local concentration of AUG near the correct site on the ribosome. Other sequences, in addition to the AUG and Shine-Dalgarn ...
... most coding for internal methionines or representing out of phase codons. Binding of mRNA to rRNA via the Shine Dalgarno sequence may stimulate initiation by increasing the local concentration of AUG near the correct site on the ribosome. Other sequences, in addition to the AUG and Shine-Dalgarn ...
Slides
... cells – We call this EXPRESSION. • Muscle cells make the proteins that make them muscle cells (eg, the contractile filaments) • Kidney cells make the proteins that make them kidney cells (their shape and function is completely different) • Yet every cell has the DNA (the ‘genes’) required for these ...
... cells – We call this EXPRESSION. • Muscle cells make the proteins that make them muscle cells (eg, the contractile filaments) • Kidney cells make the proteins that make them kidney cells (their shape and function is completely different) • Yet every cell has the DNA (the ‘genes’) required for these ...
Gene Expression
... • A region of ~25 bases “upstream” from the gene • Contains the transcription start point • Often includes a “TATA box” ...
... • A region of ~25 bases “upstream” from the gene • Contains the transcription start point • Often includes a “TATA box” ...
2009 Dental Biochemistry (Questions)
... A) virtually absent in the blood of the uncontrolled diabetic. B) readily oxidized in the brain in response to excessive intake of carbohydrates. C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the other two ketone bodies. D) present only in the liver mitochondrion where it is used for energy produc ...
... A) virtually absent in the blood of the uncontrolled diabetic. B) readily oxidized in the brain in response to excessive intake of carbohydrates. C) the “ketone body” that can be converted into the other two ketone bodies. D) present only in the liver mitochondrion where it is used for energy produc ...