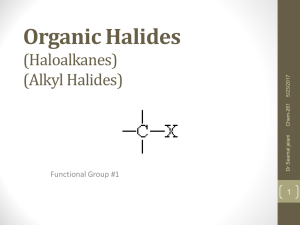alcohols03
... Alcohols and phenols have similar geometry to HOH. The R-O-H bond angle is approximately tetrahedral (109) and the ‘O’ atom is sp3 hybridized. Because of the presence of the hydroxyl group, alcohols (and phenols) have significantly higher boiling points than their constitutional (structural) is ...
... Alcohols and phenols have similar geometry to HOH. The R-O-H bond angle is approximately tetrahedral (109) and the ‘O’ atom is sp3 hybridized. Because of the presence of the hydroxyl group, alcohols (and phenols) have significantly higher boiling points than their constitutional (structural) is ...
CHAPTER V Fischer-Tropsch Syncrude
... hydrocarbons (>C20), do not have a single α-value, but two. The first α-value (α1) describes the carbon number distribution from C3 to C12, while the second α-value (α2) describes the distribution of the C20 and heavier fraction.(4) This seems to be a mathematical convenience, since the α-value seem ...
... hydrocarbons (>C20), do not have a single α-value, but two. The first α-value (α1) describes the carbon number distribution from C3 to C12, while the second α-value (α2) describes the distribution of the C20 and heavier fraction.(4) This seems to be a mathematical convenience, since the α-value seem ...
Derivatization Reagents - Sigma
... diazomethane (a yellow gas, usually used as an ethereal solution) reacts rapidly with fatty acids, forming methyl esters. Elimination of gaseous nitrogen drives the reaction. The yield is high and side reactions are minimal. However, diazomethane is carcinogenic, highly toxic, and potentially explos ...
... diazomethane (a yellow gas, usually used as an ethereal solution) reacts rapidly with fatty acids, forming methyl esters. Elimination of gaseous nitrogen drives the reaction. The yield is high and side reactions are minimal. However, diazomethane is carcinogenic, highly toxic, and potentially explos ...
C1 polymerization and related C-C bond forming - UvA-DARE
... (stereoregular) polymers which are functionalized at every carbon atom of the polymer backbone, thus providing great opportunities for the synthesis of new polymers with yet unknown properties. Some reported C1 polymerization techniques even allow a precise control over the nature of the polymer end ...
... (stereoregular) polymers which are functionalized at every carbon atom of the polymer backbone, thus providing great opportunities for the synthesis of new polymers with yet unknown properties. Some reported C1 polymerization techniques even allow a precise control over the nature of the polymer end ...
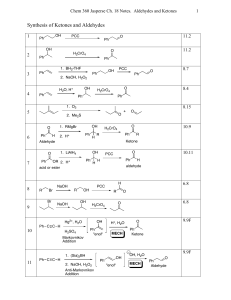
Synthesis of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
Organic Chemistry II Introduction
... Thiols do not form H-bonds (EN of S is low) Alcohols and phenols are weakly basic Alcohols and phenols are weakly acidic Phenols and Thiols are more acidic than water ...
... Thiols do not form H-bonds (EN of S is low) Alcohols and phenols are weakly basic Alcohols and phenols are weakly acidic Phenols and Thiols are more acidic than water ...
06. Alcohols. Phenols. Ethers
... In this equation, the symbol [O] represents the mild oxidizing agent. The immediate product of the oxidation of а primary alcohol is an aldehyde. Because aldehydes themselves are readily oxidized by the same oxidizing agents that oxidize alcohols, aldehydes are further converted to carboxylic acids. ...
... In this equation, the symbol [O] represents the mild oxidizing agent. The immediate product of the oxidation of а primary alcohol is an aldehyde. Because aldehydes themselves are readily oxidized by the same oxidizing agents that oxidize alcohols, aldehydes are further converted to carboxylic acids. ...
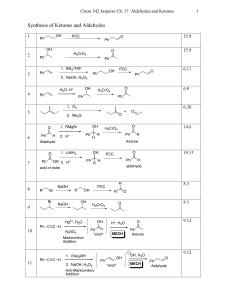
Synthesis of Ketones and Aldehydes
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
... Classification of Mechanisms Associated With Ketone/Aldehyde Reactions. • There may seem to be a dizzying number of mechanisms this chapter. But all of them simplify into some combination of acid- or base-catalyzed addition reaction, elimination reaction and/or substitution reaction. • To predict wh ...
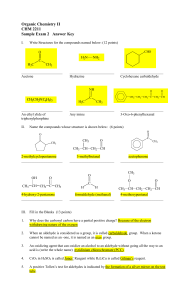
Organic Chemistry II CHM 2211 Sample Exam 2 Answer Key
... When an aldehyde is considered as a group, it is called carbaldehyde group. When a ketone cannot be named as an -one, it is named as an oxo- group. ...
... When an aldehyde is considered as a group, it is called carbaldehyde group. When a ketone cannot be named as an -one, it is named as an oxo- group. ...
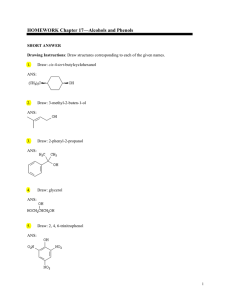
HOMEWORK Chapter 17—Alcohols and Phenols
... In m-nitrophenol, the inductive effect of the electron-withdrawing nitro group helps to stabilize the negative charge on oxygen. However, when the nitro group is para to the oxygen, direct conjugation of the negative charge on oxygen with the nitro group can occur. p-Nitrophenolate ion is, thus, mor ...
... In m-nitrophenol, the inductive effect of the electron-withdrawing nitro group helps to stabilize the negative charge on oxygen. However, when the nitro group is para to the oxygen, direct conjugation of the negative charge on oxygen with the nitro group can occur. p-Nitrophenolate ion is, thus, mor ...
$doc.title
... • Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield an amino alcohol (carbinolamine) • Protona3on of OH converts it into water as the leaving group • Result is iminium ion, which loses proton • ...
... • Proton is lost from N and adds to O to yield an amino alcohol (carbinolamine) • Protona3on of OH converts it into water as the leaving group • Result is iminium ion, which loses proton • ...
For Peer Review Only
... Vegetable oils can be epoxidized (reaction A, Table 1), leading to interesting building blocks for biobased chemistry 21. The most currently used method to epoxidize vegetable oil is based on peracetic acid formed in situ from reaction between acetic acid ...
... Vegetable oils can be epoxidized (reaction A, Table 1), leading to interesting building blocks for biobased chemistry 21. The most currently used method to epoxidize vegetable oil is based on peracetic acid formed in situ from reaction between acetic acid ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
Chapter 15
... OH’s attached to the same carbon) that is nucleophilic and can attack another molecule of chromic acid to form a second chromate ester. Removal of the second proton forms the carboxylic acid. H ...
... OH’s attached to the same carbon) that is nucleophilic and can attack another molecule of chromic acid to form a second chromate ester. Removal of the second proton forms the carboxylic acid. H ...
研 究 業 績 リ ス ト
... (92) Ruthenium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization of 3-Butyne-1,2-diols into Furans Y. Yada, Y. Miyake, and Y. Nishibayashi Org. Lett., to be submitted. (93) Novel Monophosphido-Bridged Diruthenium Complexes: Efficient Preparative Method and Their Catalytic Activity toward Condensation of Aldehyde ...
... (92) Ruthenium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization of 3-Butyne-1,2-diols into Furans Y. Yada, Y. Miyake, and Y. Nishibayashi Org. Lett., to be submitted. (93) Novel Monophosphido-Bridged Diruthenium Complexes: Efficient Preparative Method and Their Catalytic Activity toward Condensation of Aldehyde ...
A Simple and Advantageous Protocol for the Oxidation of Alcohols
... between solvents are their stability to IBX and the slight solubility (or lack thereof) of the IBX-derived byproducts. We regard EtOAc and DCE as the solvents of choice because they are inert and all byproducts are insoluble at room temperature, such that no purification is required beyond simple fi ...
... between solvents are their stability to IBX and the slight solubility (or lack thereof) of the IBX-derived byproducts. We regard EtOAc and DCE as the solvents of choice because they are inert and all byproducts are insoluble at room temperature, such that no purification is required beyond simple fi ...
the suzuki-miyaura reaction and boron reagents – mechanism
... Properties of boronic acids. ¤ Are highly reactive towards transmetalation and are atom efficient. ¤ Can be difficult to handle as well as purify, many decompose in air. ¤ Are susceptible to side reactions in the SM coupling. n Under SM conditions base-catalysed protodeboronation is common31 ...
... Properties of boronic acids. ¤ Are highly reactive towards transmetalation and are atom efficient. ¤ Can be difficult to handle as well as purify, many decompose in air. ¤ Are susceptible to side reactions in the SM coupling. n Under SM conditions base-catalysed protodeboronation is common31 ...
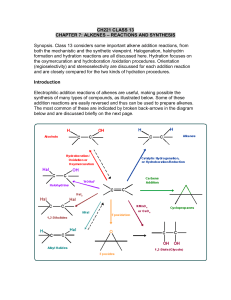
CH221 CLASS 13
... Addition of water to alkenes to give alcohols is one of the most important reactions of alkenes. In industry, this is accomplished by the use of strong acid catalysts and high temperatures, but this is not really of much value in the laboratory. However, tertiary alcohols can be produced from highly ...
... Addition of water to alkenes to give alcohols is one of the most important reactions of alkenes. In industry, this is accomplished by the use of strong acid catalysts and high temperatures, but this is not really of much value in the laboratory. However, tertiary alcohols can be produced from highly ...
Forward
... Many are made in the laboratory from alkenes, alkynes, arenes, and alcohols by reactions that you already know about and are summarized in Table 17.1. To the synthetic chemist, the most important of the reactions in Table 17.1 are the last two: the oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes and seco ...
... Many are made in the laboratory from alkenes, alkynes, arenes, and alcohols by reactions that you already know about and are summarized in Table 17.1. To the synthetic chemist, the most important of the reactions in Table 17.1 are the last two: the oxidation of primary alcohols to aldehydes and seco ...
Organic synthesis and methodology related to the malaria drug artemisinin
... Malaria is a global epidemic, resulting in the deaths of nearly one million people every year. Part 1 of this dissertation will focus on the history of Malaria and ways to combat this devastating disease. Artemisinin has emerged as the drug of choice for treatment of malaria due to its effectiveness ...
... Malaria is a global epidemic, resulting in the deaths of nearly one million people every year. Part 1 of this dissertation will focus on the history of Malaria and ways to combat this devastating disease. Artemisinin has emerged as the drug of choice for treatment of malaria due to its effectiveness ...
C−C, C−O, C−N Bond Formation on sp2 Carbon by Pd(II)
... with π-nucleophiles such as olefins, alkynes, and arenes. The mechanisms of these processes have been extensively studied. A typical reaction with alkenes starts with the complexation of the olefin by the Pd(II) salt, as shown in Scheme 1, left-hand side. The resulting π-olefin complex A can undergo ...
... with π-nucleophiles such as olefins, alkynes, and arenes. The mechanisms of these processes have been extensively studied. A typical reaction with alkenes starts with the complexation of the olefin by the Pd(II) salt, as shown in Scheme 1, left-hand side. The resulting π-olefin complex A can undergo ...
Synthesis of a TREN in Which the Aryl Substituents are... Atom Macrocycle ̈ller *
... reduction at all.3 Ligands that were not based on TREN frameworks were also unsuccessful.4 It was clear that much free ligand, (HIPTNHCH2CH2)3N, was present at the end of a catalytic reaction. Protonation of an amido ligand, or strong Hbonding of [LutH]+ to it, was proposed to be the beginning of a ...
... reduction at all.3 Ligands that were not based on TREN frameworks were also unsuccessful.4 It was clear that much free ligand, (HIPTNHCH2CH2)3N, was present at the end of a catalytic reaction. Protonation of an amido ligand, or strong Hbonding of [LutH]+ to it, was proposed to be the beginning of a ...
Chapter 12 Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, Aldehydes, and Ketones
... When a secondary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • a ketone is produced. [O] secondary alcohol ...
... When a secondary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • a ketone is produced. [O] secondary alcohol ...
Reactions of Alcohols and Thiols
... When a secondary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • a ketone is produced. [O] secondary alcohol ...
... When a secondary alcohol is oxidized, [O], • one H is removed from the –OH. • another H is removed from the carbon bonded to the OH. • a ketone is produced. [O] secondary alcohol ...
Elias James Corey

Elias James ""E.J."" Corey (born July 12, 1928) is an American organic chemist. In 1990, he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry ""for his development of the theory and methodology of organic synthesis"", specifically retrosynthetic analysis. Regarded by many as one of the greatest living chemists, he has developed numerous synthetic reagents, methodologies and total syntheses and has advanced the science of organic synthesis considerably.