Compounds with Oxygen Atoms
... Compounds of phenol are the active ingredients in the essential oils of nutmeg, thyme, cloves, and vanilla. ...
... Compounds of phenol are the active ingredients in the essential oils of nutmeg, thyme, cloves, and vanilla. ...
revised Chemical Kinetics
... time is the instantaneous speed. It's the speed that is reported by a police radar gun at the split second the officer points the device at your car. It is possible to get a speeding ticket for going 80 miles / hour even when the average speed for your journey is only 40 miles / hour. Likewise, when ...
... time is the instantaneous speed. It's the speed that is reported by a police radar gun at the split second the officer points the device at your car. It is possible to get a speeding ticket for going 80 miles / hour even when the average speed for your journey is only 40 miles / hour. Likewise, when ...
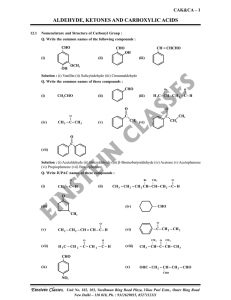
aldehyde, ketones and carboxylic acids
... approximately perpendicular to the plane of sp2 hybridised orbitals of carbonyl carbon. The hybridisation of carbon changes from sp2 to sp3 in this process, and a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate is produced. This intermediate captures a proton from the reaction medium to give the electrically neut ...
... approximately perpendicular to the plane of sp2 hybridised orbitals of carbonyl carbon. The hybridisation of carbon changes from sp2 to sp3 in this process, and a tetrahedral alkoxide intermediate is produced. This intermediate captures a proton from the reaction medium to give the electrically neut ...
Cl 2
... In a chemical reaction, an insufficient quantity of any of the reactants will limit the amount of product that forms. • An example of excess and limiting reagents is making muffins. You have more than enough flour, butter, water, and eggs. However, you only have one cup of sugar. The number of muffi ...
... In a chemical reaction, an insufficient quantity of any of the reactants will limit the amount of product that forms. • An example of excess and limiting reagents is making muffins. You have more than enough flour, butter, water, and eggs. However, you only have one cup of sugar. The number of muffi ...
Curriculum Vitae
... 106. Deluca, R. J.; Stokes, B. J.; Sigman, M. S. “The strategic generation and interception of palladiumhydrides for use in alkene functionalization reactions,” Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 395-408. 105. Xu, L.; Hilton, M. J.; Zhang, X.; Norrby, P.-O.*; Wu, Y.-D.*; Sigman, M. S.*; Wiest, O.* “Mechanis ...
... 106. Deluca, R. J.; Stokes, B. J.; Sigman, M. S. “The strategic generation and interception of palladiumhydrides for use in alkene functionalization reactions,” Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 395-408. 105. Xu, L.; Hilton, M. J.; Zhang, X.; Norrby, P.-O.*; Wu, Y.-D.*; Sigman, M. S.*; Wiest, O.* “Mechanis ...
Stereochemistry Tutorials: Assigning R/S and E/Z
... Definitions for vocabulary words can be found in the Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry, available at the course web site. Discussion: Every organic compound needs an unambiguous name that clearly delineates all structural features of the molecule. The same is true for stereocenters. Because ...
... Definitions for vocabulary words can be found in the Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry, available at the course web site. Discussion: Every organic compound needs an unambiguous name that clearly delineates all structural features of the molecule. The same is true for stereocenters. Because ...
15.1 Amines
... transition-metal catalyst. • Reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol. • Reduction a ketone gives a secondary alcohol. ...
... transition-metal catalyst. • Reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol. • Reduction a ketone gives a secondary alcohol. ...
CHAPTER-8 NCERT SOLUTIONS
... (b)Following the steps as in part (a), we have the oxidation half reaction as: And the reduction half reaction as: Multiplying the oxidation half reaction by 5 and the reduction half reaction by 2, and then by adding them, we have the net balanced redox reaction as: (c) Following the steps as in par ...
... (b)Following the steps as in part (a), we have the oxidation half reaction as: And the reduction half reaction as: Multiplying the oxidation half reaction by 5 and the reduction half reaction by 2, and then by adding them, we have the net balanced redox reaction as: (c) Following the steps as in par ...
H - CashmereChemistry
... As the non-polar alkyl chain increases in length the molecules become more non-polar and increasingly insoluble in water. Like the hydrocarbons, the melting and boiling points increase with ...
... As the non-polar alkyl chain increases in length the molecules become more non-polar and increasingly insoluble in water. Like the hydrocarbons, the melting and boiling points increase with ...
Oxygen containing organic compound
... Solubility of alcohols and ethers in water Alcohols and ethers • are more soluble in water than alkanes because the oxygen atom can hydrogen bond with water. • with 1-4 C atoms are soluble, but not with 5 or more C atoms. ...
... Solubility of alcohols and ethers in water Alcohols and ethers • are more soluble in water than alkanes because the oxygen atom can hydrogen bond with water. • with 1-4 C atoms are soluble, but not with 5 or more C atoms. ...
Chapter 16-18 - Bakersfield College
... – Reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol (-CH2OH). – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
... – Reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol (-CH2OH). – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
chemical kinetics - Berkeley City College
... Elementary Steps and Molecularity Elementary steps or elementary reactions are simple steps that together make up the reaction mechanism for a given reaction. Each elementary reaction describes individual molecular event, such as two particles combining or a particle (simple or complex) decomposing. ...
... Elementary Steps and Molecularity Elementary steps or elementary reactions are simple steps that together make up the reaction mechanism for a given reaction. Each elementary reaction describes individual molecular event, such as two particles combining or a particle (simple or complex) decomposing. ...
Free Radicals
... conditions with Oxone : Org. Lett., 2, 1173 (2000). In the presence of CuCl, aerobic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones has been accomplished in the ionic liquid 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, L19086: Org. Lett., 4, 1507 (2002). With NaOCl, α-amino or α-alkoxy alcohol ...
... conditions with Oxone : Org. Lett., 2, 1173 (2000). In the presence of CuCl, aerobic oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones has been accomplished in the ionic liquid 1-n-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate, L19086: Org. Lett., 4, 1507 (2002). With NaOCl, α-amino or α-alkoxy alcohol ...
Kinetic modelling of the Maillard reaction between proteins and sugars
... study the reactions of interest quantitatively. In this paper the main reaction products in monosaccharide-casein systems, which were heated at 120°C and neutral pH, were identified and quantified, and thereaction pathways were established. Themain reaction routes were (i) sugar isomerisation, (ii) ...
... study the reactions of interest quantitatively. In this paper the main reaction products in monosaccharide-casein systems, which were heated at 120°C and neutral pH, were identified and quantified, and thereaction pathways were established. Themain reaction routes were (i) sugar isomerisation, (ii) ...
Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules
... Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones and Chiral Molecules Oxidation and Reduction ...
... Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones and Chiral Molecules Oxidation and Reduction ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.