* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
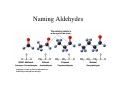
Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules 14.1 Aldehydes and Ketones Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Carbonyl Group in Aldehydes and Ketones A carbonyl group • In an aldehyde is attached to at least one H atom. • In a ketone is attached to two carbon groups. Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Naming Aldehydes An aldehyde • Has an IUPAC name in which the -e in the alkane name is changed to -al. • Has a common name for the first four aldehydes that use the prefixes form- (1C), acet- (2C), propion- (3C), and butyr(4C), followed by aldehyde. O O O ║ ║ ║ H−C−H CH3−C−H CH3−CH2−C−H methanal ethanal propanal (formaldehyde) (acetaldehyde) (propionaldehyde) Naming Aldehydes Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Aldehydes in Flavorings • Several naturally occurring aldehydes are used as flavorings for foods and fragrances. O H C Benzaldehyde (almonds) O CH=CH C H Cinnamaldehyde (cinnamon) Naming Ketones Ketones are named • In the IUPAC system by replacing the -e in the alkane name with -one. The carbonyl carbon is indicated by a number. • With a common name by indicating the alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl group in alphabetical order followed by ketone. O O ║ ║ CH3−C−CH3 CH3−C−CH2−CH3 propanone 2-butanone (dimethyl ketone) (ethyl methyl ketone) Ketones in Common Use Butter flavoring Nail polish remover, Solvent Propanone, Dimethylketone, Acetone Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Learning Check Classify each as 1) aldehyde or 2) ketone. O O || || A. CH3—CH2—C—CH3 B. CH3—C—H CH3 O | || C. CH3—C—CH2—C—H | CH3 O D. Solution A. 2) ketone B. 1) aldehyde C. 1) aldehyde D. 2) ketone Learning Check Classify each as an aldehyde (1), ketone (2), alcohol (3), or ether (4). O ║ A. CH3─CH2─C─CH3 B. CH3─O─CH3 CH3 O │ ║ C. CH3─C─CH2─C─H │ CH3 OH │ D. CH3─CH─CH3 Solution Classify each as an aldehyde (1), ketone (2), alcohol (3), or ether (4). O ║ A. CH3─CH2─C─CH3 B. CH3─O─CH3 (2) ketone (4) ether CH3 O OH │ ║ │ C. CH3─C─CH2─C─H D. CH3─CH─CH3 │ CH3 (1) aldehyde (3) alcohol Learning Check Name each of the following: O ║ 1. CH3─CH2─CH2─CH2─C─H O ║ 2. Cl─CH2─CH2─C─H O ║ 3. CH3─CH2─C─CH3 Solution O ║ 1. CH3─CH2─CH2─CH2─C─H pentanal O ║ 2. Cl─CH2─CH2─C─H 3-chloropropanal O ║ 3. CH3─CH2─C─CH3 2-butanone; ethyl methyl ketone Learning Check Name the following compounds. O || A. CH3—CH2—CH2—C—CH3 B. O CH3 O | || C. CH3—C—CH2—C—H | CH3 Solution A. 2-pentanone; methyl propyl ketone B. cyclohexanone C, 3,3-dimethylbutanal Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones, and Chiral Molecules 14.2 Physical Properties Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Polar Carbonyl Group The polar carbonyl group • Provides dipole-dipole interactions. δ+ δδ+ δC=O C=O • Does not have H on the oxygen atom. • Cannot form hydrogen bonds. Boiling Points Aldehydes and ketones have • Polar carbonyl groups (C=O). δ+ δC=O • Attractions between polar groups. δ+ δδ+ δC=O C=O • Higher boiling points than alkanes and ethers of similar mass. • Lower boiling points than alcohols of similar mass. Comparison of Boiling Points 58 Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Learning Check Select the compound in each pair that would have the Higher boiling point. A. CH3—CH2—CH3 or CH3—CH2—OH O B. or C. CH3—CH2—OH or CH3—O—CH3 Solution A. CH3—CH2—OH O B. C. CH3—CH2—OH Solubility in Water The electronegative O atom of the carbonyl group in aldehydes and ketones forms hydrogen bonds with water. Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Learning Check Indicate if each is soluble or insoluble in water. A. CH3—CH2—CH3 B. CH3—CH2—OH O || C. CH3—CH2—CH2—C—H O || D. CH3—C—CH3 Solution A. CH3—CH2—CH3 insoluble B. CH3—CH2—OH soluble O || C. CH3—CH2—CH2—C—H soluble O || D. CH3—C—CH3 soluble Chapter 14 Aldehydes, Ketones and Chiral Molecules Oxidation and Reduction Copyright © 2007 by Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings Oxidation • Aldehydes are easily oxidized to carboxylic acids. O O || [O] || CH3—C—H CH3—C—OH Acetaldehyde Acetic acid Tollens’ Test • Tollens’ reagent, which contains Ag+, oxidizes aldehydes, but not ketones. • Ag+ is reduced to metallic Ag, which appears as a “mirror” in the test tube. ERROR: stackunderflow OFFENDING COMMAND: ~ STACK: