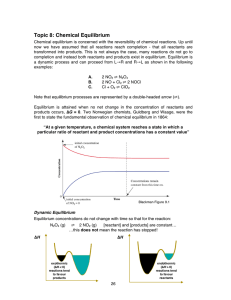
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... Q. What happens if more Cl2 (g) is injected? A. Q gets smaller, so the equilibrium shifts to produce more product If concentration increases, the system acts to consume some of it If concentration decreases, the system acts to produce some of it 2. Change in pressure The pressure of a system can be ...
... Q. What happens if more Cl2 (g) is injected? A. Q gets smaller, so the equilibrium shifts to produce more product If concentration increases, the system acts to consume some of it If concentration decreases, the system acts to produce some of it 2. Change in pressure The pressure of a system can be ...
chemistry (9189)
... bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding, other intermolecular interactions; metallic bonding) on the physical properties of substances ...
... bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding, other intermolecular interactions; metallic bonding) on the physical properties of substances ...
PDF File
... rate of the chemical step for the substrate with 2′-OH is ~ tenfold faster than that for the substrate with a 2′-fluoro group at U(–1), despite the weaker electron-withdrawing ability of 2′-OH than 2′-F [2]. As a 2′-fluoro group contains lone-pair electrons that can accept hydrogen bonds but cannot ...
... rate of the chemical step for the substrate with 2′-OH is ~ tenfold faster than that for the substrate with a 2′-fluoro group at U(–1), despite the weaker electron-withdrawing ability of 2′-OH than 2′-F [2]. As a 2′-fluoro group contains lone-pair electrons that can accept hydrogen bonds but cannot ...
chapter27
... Alcohols and Phenols • The functional group in alcohols and phenols is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. • Alcohols and phenols can be considered derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more H atoms have been replaced by -OH groups. • Phenols are derivatives of benzene in which one H has been replaced ...
... Alcohols and Phenols • The functional group in alcohols and phenols is the hydroxyl (-OH) group. • Alcohols and phenols can be considered derivatives of hydrocarbons in which one or more H atoms have been replaced by -OH groups. • Phenols are derivatives of benzene in which one H has been replaced ...
bonding
... 4. If more than one double bond is present, indicate their position by using the number of the first carbon of each double bond and use the suffix -diene (for 2 double bonds), -triene (for 3 double bonds), -tetraene (for 4 double bonds), etc. H2C ...
... 4. If more than one double bond is present, indicate their position by using the number of the first carbon of each double bond and use the suffix -diene (for 2 double bonds), -triene (for 3 double bonds), -tetraene (for 4 double bonds), etc. H2C ...
- Vijay Education Academy
... 117. The graphite electrodes in the extraction of „Al‟ by Hall-Heroult process need to be changed frequently. Why? 118. Write the chemical formulae of the following ores (a) Haematite (b) Magnetite (c) Limonite (d) Siderite. 119. Give equations for the industrial extraction of zinc from calamine. 12 ...
... 117. The graphite electrodes in the extraction of „Al‟ by Hall-Heroult process need to be changed frequently. Why? 118. Write the chemical formulae of the following ores (a) Haematite (b) Magnetite (c) Limonite (d) Siderite. 119. Give equations for the industrial extraction of zinc from calamine. 12 ...
ALCOHOLS AND ETHERS
... (Figure 15-2b). However, there is a relatively broad band around 3350 cm-l, which is characteristic of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups. The shift in frequency of about 300 cm-I arises because hydrogen bonding weakens the 0 - H bond; its absorption frequency then will be lower. The association band i ...
... (Figure 15-2b). However, there is a relatively broad band around 3350 cm-l, which is characteristic of hydrogen-bonded hydroxyl groups. The shift in frequency of about 300 cm-I arises because hydrogen bonding weakens the 0 - H bond; its absorption frequency then will be lower. The association band i ...
Reactions of alcohols File
... -CH2OH -C-CH(OH)-Calcohols! NB Oxidant = hot acidified Cr2O72- [dichromate(VI)] ion] Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
... -CH2OH -C-CH(OH)-Calcohols! NB Oxidant = hot acidified Cr2O72- [dichromate(VI)] ion] Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
Handout 3
... attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens. Negatively charged ion is considered a nucleophile. However, neutral H2O molecule (or ROH) may react as a nucleophile also using lone pair’s electrons of oxygen atom. Addition of X2 or X & OH: anti-addition (trans product). ...
... attached to the carbon with the most hydrogens. Negatively charged ion is considered a nucleophile. However, neutral H2O molecule (or ROH) may react as a nucleophile also using lone pair’s electrons of oxygen atom. Addition of X2 or X & OH: anti-addition (trans product). ...
Lecture - Ch 16
... • On a general basis, there are no reactions between nucleophiles and halobenzenes that do not have electron withdrawing substituents – High temperatures can be used to make chlorobenzene react ...
... • On a general basis, there are no reactions between nucleophiles and halobenzenes that do not have electron withdrawing substituents – High temperatures can be used to make chlorobenzene react ...
4.7 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... The product of this step is a carbocation. It is an intermediate in the overall process. ...
... The product of this step is a carbocation. It is an intermediate in the overall process. ...
Research in our group encompasses the following 4 areas in
... 3] Development of Novel Protecting-Group-Free Synthesis An ideal synthesis demands no use of protecting groups, enabling shorter synthesis and overall economy. Keeping this in mind, many of the earlier synthesis involving lengthy sequences have been shortened based on efficient protecting-group-free ...
... 3] Development of Novel Protecting-Group-Free Synthesis An ideal synthesis demands no use of protecting groups, enabling shorter synthesis and overall economy. Keeping this in mind, many of the earlier synthesis involving lengthy sequences have been shortened based on efficient protecting-group-free ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Modified LiAlH4 reagent LiAl[OC(CH3)3]3H required to prevent over-reduction to alcohols ...
... Modified LiAlH4 reagent LiAl[OC(CH3)3]3H required to prevent over-reduction to alcohols ...
Fluorination Chemistry - Sigma
... of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC. Celatom is a registered trademark of EP Minerals, LLC. IKA is a registered trademark of IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG Trifluoromethylator is a registered trademark of Catylix, Inc. Halar is a registered trademark of Solvay Group. Ace-Thred is a trademark of Ace Glass, Inc. PhenoF ...
... of Sigma-Aldrich Co. LLC. Celatom is a registered trademark of EP Minerals, LLC. IKA is a registered trademark of IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG Trifluoromethylator is a registered trademark of Catylix, Inc. Halar is a registered trademark of Solvay Group. Ace-Thred is a trademark of Ace Glass, Inc. PhenoF ...
Tin-Catalyzed Esterification and Transesterification Reactions: A
... conversion of 87% was achieved at the same reaction time. Probably the catalyst Sn (II) activates the carbonyl group of the fatty acid, favoring his attack by the hydroxyl group of ethanol, thereby generating an increased formation of ethyl oleate. The carbon chain length of alcohol can affect both t ...
... conversion of 87% was achieved at the same reaction time. Probably the catalyst Sn (II) activates the carbonyl group of the fatty acid, favoring his attack by the hydroxyl group of ethanol, thereby generating an increased formation of ethyl oleate. The carbon chain length of alcohol can affect both t ...
NOTES ON THE INTERPRETATION OF NMR SPECTRA The nuclei
... A correlation chart at the end of this appendix shows some typical H values for common functional groups. Note that most protons in organic compounds absorb in the range H 0-10 but very acidic protons have values >10 H. Correlation charts must be used with some caution since in a complex molecule ...
... A correlation chart at the end of this appendix shows some typical H values for common functional groups. Note that most protons in organic compounds absorb in the range H 0-10 but very acidic protons have values >10 H. Correlation charts must be used with some caution since in a complex molecule ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.