chapter-15
... Ketones are not normally oxidized by H2CrO4; in fact this reagent is used to oxidize 2° alcohols to ketones • they are oxidized by HNO3 at higher temperatures • oxidation is via the enol O ...
... Ketones are not normally oxidized by H2CrO4; in fact this reagent is used to oxidize 2° alcohols to ketones • they are oxidized by HNO3 at higher temperatures • oxidation is via the enol O ...
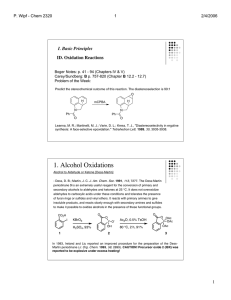
1. Alcohol Oxidations
... insoluble products, and reacts slowly enough with secondary amines and sulfides to make it possible to oxidize alcohols in the presence of these functional groups. ...
... insoluble products, and reacts slowly enough with secondary amines and sulfides to make it possible to oxidize alcohols in the presence of these functional groups. ...
Chapter Thirteen - Wright State University
... • The boiling points of compounds depend on how strongly they stick together: The more strongly they stick together, the higher the boiling point (the more heat it takes to rip them apart). • There are two main forces that hold molecules together: -Hydrogen bonds These require both positive hydrogen ...
... • The boiling points of compounds depend on how strongly they stick together: The more strongly they stick together, the higher the boiling point (the more heat it takes to rip them apart). • There are two main forces that hold molecules together: -Hydrogen bonds These require both positive hydrogen ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Schiff bases have a large number of synthetic uses in organic chemistry. Acylation of Schiff bases by acid anhydrides, acid chlorides and acyl cyanides is initiated by attack at the nitrogen atom and leads to net addition of the acylation agent to the carbon-nitrogen double bond. Reactions of this t ...
... Schiff bases have a large number of synthetic uses in organic chemistry. Acylation of Schiff bases by acid anhydrides, acid chlorides and acyl cyanides is initiated by attack at the nitrogen atom and leads to net addition of the acylation agent to the carbon-nitrogen double bond. Reactions of this t ...
- Opus: Online Publications Store
... Additional problems associated with the activation of C–H bonds are their low dipole moments, low HOMO and high LUMO energy levels [9]. Furthermore, the activation methods developed should be able to introduce different functionalities under the same reaction conditions [1c,10]. Because of the previ ...
... Additional problems associated with the activation of C–H bonds are their low dipole moments, low HOMO and high LUMO energy levels [9]. Furthermore, the activation methods developed should be able to introduce different functionalities under the same reaction conditions [1c,10]. Because of the previ ...
Equilibrium - Clayton State University
... - Many reactions do not go to completion - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
... - Many reactions do not go to completion - Amount of products formed or reactants consumed cannot be predicted from stoichiometry alone - These reactions achieve a condition of equilibrium ...
Unit 5 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolved in water is designated (aq). A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate ...
... formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolved in water is designated (aq). A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate ...
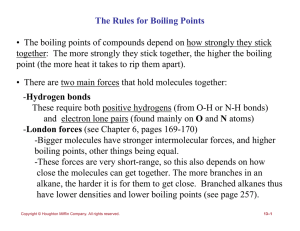
The Rules for Boiling Points • The boiling points of compounds
... • The boiling points of compounds depend on how strongly they stick together: The more strongly they stick together, the higher the boiling point (the more heat it takes to rip them apart). • There are two main forces that hold molecules together: -Hydrogen bonds These require both positive hydrogen ...
... • The boiling points of compounds depend on how strongly they stick together: The more strongly they stick together, the higher the boiling point (the more heat it takes to rip them apart). • There are two main forces that hold molecules together: -Hydrogen bonds These require both positive hydrogen ...
aq - Haverford Alchemy
... becomes more positive) • A reduction occurs when an atom or ion gains electrons. (It becomes more negative) Aqueous Reactions ...
... becomes more positive) • A reduction occurs when an atom or ion gains electrons. (It becomes more negative) Aqueous Reactions ...
Unit 4 Chemistry of Carbon
... compound, it will also help you to determine the main chain. (ie. ane, ene, one, anol etc) 2. Find the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain which includes any functional groups. That main chain will identify the length of the main chain name used near the end of the name. (ie. 6 C’s in uses hex.) 3a ...
... compound, it will also help you to determine the main chain. (ie. ane, ene, one, anol etc) 2. Find the longest continuous hydrocarbon chain which includes any functional groups. That main chain will identify the length of the main chain name used near the end of the name. (ie. 6 C’s in uses hex.) 3a ...
ANSWERS Problem Set 5a – Chemical Reactions
... 16) List the diatomic elements – give their names and molecular formulas. H2 (g) – hydrogen, O2 (g) oxygen, N2 (g) nitrogen, F2( g) fluorine, Cl2 (g) chlorine, Br2 (l) bromine, I2 (s) iodine (H O N Cl Br I F) Multiple Choice Section (again, record your answers on this sheet) 17) _B_ This law states ...
... 16) List the diatomic elements – give their names and molecular formulas. H2 (g) – hydrogen, O2 (g) oxygen, N2 (g) nitrogen, F2( g) fluorine, Cl2 (g) chlorine, Br2 (l) bromine, I2 (s) iodine (H O N Cl Br I F) Multiple Choice Section (again, record your answers on this sheet) 17) _B_ This law states ...
17: Oxidation and Reduction
... We can imagine that chromate ion (CrO4-2) forms from dichromate (Cr2O7-2) by loss of chromium trioxide (CrO3), or that it forms from addition of H2O to CrO3 followed by deprotonation. The three "chromate" species, or the three "dichromate" species, are simply differently protonated froms of CrO4-2 o ...
... We can imagine that chromate ion (CrO4-2) forms from dichromate (Cr2O7-2) by loss of chromium trioxide (CrO3), or that it forms from addition of H2O to CrO3 followed by deprotonation. The three "chromate" species, or the three "dichromate" species, are simply differently protonated froms of CrO4-2 o ...
13-4 Ligands in Organometallic Chemistry
... Bridging ligand - μ Subscript indicating the number of metal atoms bridged. ...
... Bridging ligand - μ Subscript indicating the number of metal atoms bridged. ...
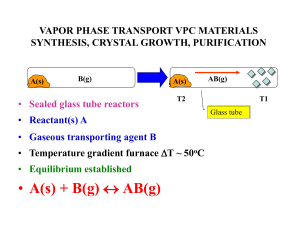
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... + 4HI(g) • The antithetical nature of these two reactions allows W/WO2 mixtures which often form together to be separated at different ends of the gradient reactor using H2O/I2 as the VPT reagents ...
... + 4HI(g) • The antithetical nature of these two reactions allows W/WO2 mixtures which often form together to be separated at different ends of the gradient reactor using H2O/I2 as the VPT reagents ...
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution and Substituted Benzenes
... [1] Vinyl halides and aryl halides do not react in FriedelCrafts alkylation. ...
... [1] Vinyl halides and aryl halides do not react in FriedelCrafts alkylation. ...
PIB - Unit 6 - Chemical Reactions - Student
... formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolved in water is designated (aq). A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate ...
... formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolved in water is designated (aq). A catalyst is a substance that increases reaction rate ...
Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally inv ...
... years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally inv ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.