Document
... Some diamines have very derivative names indicating where they are found e.g putrescine [H2N(CH2)4NH2] and cadaverine [H2N(CH2)5NH2]! ...
... Some diamines have very derivative names indicating where they are found e.g putrescine [H2N(CH2)4NH2] and cadaverine [H2N(CH2)5NH2]! ...
Introduction to Kinetics and Equilibrium
... nonzero concentration and these concentrations are constant with i d h i ih respect to time. When an equilibrium is established, the limiting reagent has a nonzero ...
... nonzero concentration and these concentrations are constant with i d h i ih respect to time. When an equilibrium is established, the limiting reagent has a nonzero ...
Hydrolases as Catalysts for Green Chemistry and
... Interestingly, mutations of F407 to alanine or leucine led to a dramatic increase in activity but with reversed selectivity (E=3.3 and E >100 respectively towards the S isomer). On the other hand, PLE-3 isoenzyme selectively hydrolysed the correct isomer, R, with E=10. Immobilized lipase B from Cand ...
... Interestingly, mutations of F407 to alanine or leucine led to a dramatic increase in activity but with reversed selectivity (E=3.3 and E >100 respectively towards the S isomer). On the other hand, PLE-3 isoenzyme selectively hydrolysed the correct isomer, R, with E=10. Immobilized lipase B from Cand ...
1 THE BARTON-McCOMBIE REACTION STUART W. McCOMBIE 28
... (2S and 2R)-2-Deuterio-3',5'-O-(1,1,3,3-tetraisopropyldisilox-1,3-diyl)uridine [Deoxygenation of a Secondary O-(N-Phenylthiocarbamoyl) Derivative with Bu3SnD] 1,2-Diphenyl-1-methoxyethane [Deoxygenation of a Secondary O-(Phenoxythiocarbonyl) Derivative with Poly(methylhydrosiloxane) and Catalytic (B ...
... (2S and 2R)-2-Deuterio-3',5'-O-(1,1,3,3-tetraisopropyldisilox-1,3-diyl)uridine [Deoxygenation of a Secondary O-(N-Phenylthiocarbamoyl) Derivative with Bu3SnD] 1,2-Diphenyl-1-methoxyethane [Deoxygenation of a Secondary O-(Phenoxythiocarbonyl) Derivative with Poly(methylhydrosiloxane) and Catalytic (B ...
Equilibrium STUDY GUIDE by Keshara Senanayake ---
... Q is less than Keq (Q < Keq), the denominator of the reaction quotient expression is too large and the numerator is too small. This means that at the time of measurement there is too much of the reactants and too little of the products. The reaction will consume reactants and form the products to re ...
... Q is less than Keq (Q < Keq), the denominator of the reaction quotient expression is too large and the numerator is too small. This means that at the time of measurement there is too much of the reactants and too little of the products. The reaction will consume reactants and form the products to re ...
The Oxidation States of Tin
... reason that this yield was low is mainly attributed to the iodine-zinc portion of this reaction. This part of the experiment required that the zinc and iodine be combined in a flask with water and allowed to sit in an ice bath for an extended amount of time. This reaction was performed five times w ...
... reason that this yield was low is mainly attributed to the iodine-zinc portion of this reaction. This part of the experiment required that the zinc and iodine be combined in a flask with water and allowed to sit in an ice bath for an extended amount of time. This reaction was performed five times w ...
Chemical Properties of Monocyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons(5)
... • The common feature of all activating groups is that they donate electrons to the ring, thereby stabilizing the carbocation intermediate from electrophilic addition and causing it to form faster. • The common feature of all deactivating groups is that they withdraw electrons from the ring, thereby ...
... • The common feature of all activating groups is that they donate electrons to the ring, thereby stabilizing the carbocation intermediate from electrophilic addition and causing it to form faster. • The common feature of all deactivating groups is that they withdraw electrons from the ring, thereby ...
+ Br2, FeBr3 + Br2, FeBr3
... (b) What is the reactive electrophile in the above reaction? NO2+, nitronium ion. (c) If we used only pure (fuming) sulfuric acid, what would be the product(s)? mostly sulfonation of Cl benzene, both o and p, because SO3H+ becomes the superelectrophile and there is not as much protons for the dehydr ...
... (b) What is the reactive electrophile in the above reaction? NO2+, nitronium ion. (c) If we used only pure (fuming) sulfuric acid, what would be the product(s)? mostly sulfonation of Cl benzene, both o and p, because SO3H+ becomes the superelectrophile and there is not as much protons for the dehydr ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
... • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
... • many things can happen during the course of an experiment that cause the loss of product • the amount of product that is made in a reaction is called the actual yield generally less than the theoretical yield, never more! ...
Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... Formaldehyde was chosen since it is the simplest hydrocarbon containing oxygen, and an understanding of its ligand effects on Fe+ may provide information on the mechanism of hydroformylation and many other catalytic processes, such as those involved in the synthesis of aldehydes and other oxygenated ...
... Formaldehyde was chosen since it is the simplest hydrocarbon containing oxygen, and an understanding of its ligand effects on Fe+ may provide information on the mechanism of hydroformylation and many other catalytic processes, such as those involved in the synthesis of aldehydes and other oxygenated ...
Chemistry 8.2
... The heat and smoke of burning charcoal are the products of a combustion reaction. Combustion is one of the five general types of chemical reactions. If you can recognize a reaction as being a particular type, you may be able to predict the products of the reaction. ...
... The heat and smoke of burning charcoal are the products of a combustion reaction. Combustion is one of the five general types of chemical reactions. If you can recognize a reaction as being a particular type, you may be able to predict the products of the reaction. ...
Carboxylic Acids
... Carboxylic acid derivatives differ in the nature of the group bound to the acyl group. -OH is an acid -Cl is the acid chloride -OCOR' is the anhydride -OR' is the ester -NR2 is the amide Nucleophilic acyl substitution can interconvert all of these different acid derivatives. Ch20 Carboxylic Acids (l ...
... Carboxylic acid derivatives differ in the nature of the group bound to the acyl group. -OH is an acid -Cl is the acid chloride -OCOR' is the anhydride -OR' is the ester -NR2 is the amide Nucleophilic acyl substitution can interconvert all of these different acid derivatives. Ch20 Carboxylic Acids (l ...
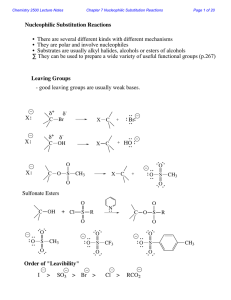
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... Two mechanisms apply to most substitution reactions: SN1 and SN2 SN1: Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular SN2: Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular Which mechanism applies depends on the structure of your substrate. ...
... Two mechanisms apply to most substitution reactions: SN1 and SN2 SN1: Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular SN2: Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular Which mechanism applies depends on the structure of your substrate. ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Stoichiometry of Chemical Reactions
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
... common patterns of behavior. When two humans exchange information, we say they are communicating. When they exchange blows with their fists or feet, we say they are fighting. Faced with a wide range of varied interactions between chemical substances, scientists have likewise found it convenient (or ...
Amines and amides
... This reaction involves breaking the C-N bond at the carbonyl carbon. a. acid hydrolysis: forms “ammonium” ion and carboxylic acid b. alkaline hydrolysis: forms carboxylate ion and amine Condensation Polymers As we have seen –COOH (and COCl) react with amines to form 2ry amides A Condensation reactio ...
... This reaction involves breaking the C-N bond at the carbonyl carbon. a. acid hydrolysis: forms “ammonium” ion and carboxylic acid b. alkaline hydrolysis: forms carboxylate ion and amine Condensation Polymers As we have seen –COOH (and COCl) react with amines to form 2ry amides A Condensation reactio ...
Activation of Alcohols Toward Nucleophilic Substitution: Conversion
... used in the Lucas reagent is required. This reaction was improved by adding zinc chloride and had the advantage of milder conditions and commercial availability, making it an efficient reagent system in industry. One way to prepare this reagent is by bubbling hydrogen chloride gas into a solution of ...
... used in the Lucas reagent is required. This reaction was improved by adding zinc chloride and had the advantage of milder conditions and commercial availability, making it an efficient reagent system in industry. One way to prepare this reagent is by bubbling hydrogen chloride gas into a solution of ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.