
This article was published in an Elsevier journal. The attached copy
... on coupling this cycle with possible energy sources, improving energy efficiency for separations and reaction processes, and modifying the cycle by involving more chemical species so as to lower the energy demand. Sadhankar [9] reported the work that the Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL) engaged ...
... on coupling this cycle with possible energy sources, improving energy efficiency for separations and reaction processes, and modifying the cycle by involving more chemical species so as to lower the energy demand. Sadhankar [9] reported the work that the Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (AECL) engaged ...
IChO 2012
... isoelectronic with C–C. Furthermore, the radius of carbon and its electronegativity are roughly the average of those properties for B and N. One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia-borane adduct. Pyrolysis of this compound leads to the generation of H2 gas and polyborazy ...
... isoelectronic with C–C. Furthermore, the radius of carbon and its electronegativity are roughly the average of those properties for B and N. One of the simplest boron-nitrogen compounds is H3N–BH3, the ammonia-borane adduct. Pyrolysis of this compound leads to the generation of H2 gas and polyborazy ...
mass-mass problems.
... Think about making pies! 5 apples + 1 crust → 1 pie What if you have 16 apples and 2 crusts. How many pies can be made? The ingredient (reactant) that runs out and stops the reaction is the limiting reagent. The reactant that is left over is said to be “in excess”. ...
... Think about making pies! 5 apples + 1 crust → 1 pie What if you have 16 apples and 2 crusts. How many pies can be made? The ingredient (reactant) that runs out and stops the reaction is the limiting reagent. The reactant that is left over is said to be “in excess”. ...
E Reprint 212 - Trade Science Inc
... ABSTRACT Barium dichromate is used as an efficient oxidizing agent for the conversion of different types of thiols to their corresponding disulfides. Overoxidation does not occur and both aromatic and aliphatic thiols undergo oxidation in the same manner. 2006 Trade Science Inc. -INDIA ...
... ABSTRACT Barium dichromate is used as an efficient oxidizing agent for the conversion of different types of thiols to their corresponding disulfides. Overoxidation does not occur and both aromatic and aliphatic thiols undergo oxidation in the same manner. 2006 Trade Science Inc. -INDIA ...
Unit 1
... The CORE STSE component of this unit incorporates a broad range of Chemistry 3202 outcomes. More specifically, it targets (in whole or in part) ACC-1, ACC-2, ACC-3, 116-4, 116-2, and 117-7. The STSE component, Smog, Catalytic Converters and You, can be found in ...
... The CORE STSE component of this unit incorporates a broad range of Chemistry 3202 outcomes. More specifically, it targets (in whole or in part) ACC-1, ACC-2, ACC-3, 116-4, 116-2, and 117-7. The STSE component, Smog, Catalytic Converters and You, can be found in ...
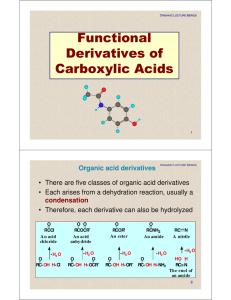
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... • Nucleophilic acyl substitution: An additionelimination sequence resulting in substitution of one nucleophile for another. O ...
... • Nucleophilic acyl substitution: An additionelimination sequence resulting in substitution of one nucleophile for another. O ...
215-216 HH W12-notes
... An atom with a formal charge: incorporate its charge # to its oxidation number. Namely, if an atom has a +1 charge, add +1 to its oxidation number. ...
... An atom with a formal charge: incorporate its charge # to its oxidation number. Namely, if an atom has a +1 charge, add +1 to its oxidation number. ...
Chapter 13. Alcohols, Diols, and Ethers
... An atom with a formal charge: incorporate its charge # to its oxidation number. Namely, if an atom has a +1 charge, add +1 to its oxidation number. ...
... An atom with a formal charge: incorporate its charge # to its oxidation number. Namely, if an atom has a +1 charge, add +1 to its oxidation number. ...
Synthesis of esterified solid fat from fractionated
... defined as dimensionless in the RSM (Myers & Montgomery, 2002). Regression coefficients were determined by employing least squares technique to predict quadratic polynomial models for SFC at different temperature (10 and 30 °C, respectively) is shown in Table 2. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of respo ...
... defined as dimensionless in the RSM (Myers & Montgomery, 2002). Regression coefficients were determined by employing least squares technique to predict quadratic polynomial models for SFC at different temperature (10 and 30 °C, respectively) is shown in Table 2. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) of respo ...
Dehydration of n-propanol and methanol to produce
... Ethers that could result from methanol-contaminated glycerol dehydration, i.e., DPE and MPE have been of interest in chemical and pharmaceutical industry. DPE, a common oxygenated hydrocarbon, is used widely in industry as a solvent [5,6]. MPE is an isomer of diethyl ether, and has found many applic ...
... Ethers that could result from methanol-contaminated glycerol dehydration, i.e., DPE and MPE have been of interest in chemical and pharmaceutical industry. DPE, a common oxygenated hydrocarbon, is used widely in industry as a solvent [5,6]. MPE is an isomer of diethyl ether, and has found many applic ...
Catalytic Nucleophilic Fluorination of Secondary and Tertiary
... to the pharmaceutical[1] and agrochemical industries,[2] positron-emission tomography,[3] and materials science.[4] Catalytic fluorination has been the focus of many investigations,[5] in which either electrophilic or nucleophilic fluorine sources have been used.[6] Despite these significant advance ...
... to the pharmaceutical[1] and agrochemical industries,[2] positron-emission tomography,[3] and materials science.[4] Catalytic fluorination has been the focus of many investigations,[5] in which either electrophilic or nucleophilic fluorine sources have been used.[6] Despite these significant advance ...
Retrosynthetic Analysis of Nabumetone
... Grignard reactions that produce secondary alcohols, will require oxidation to the corresponding ketone to arrive at the desired product. Starting with the bond between the ring and the side chain, we are given two pairs of synthons as shown in Scheme 2. The synthetic equivalent to the aromatic anion ...
... Grignard reactions that produce secondary alcohols, will require oxidation to the corresponding ketone to arrive at the desired product. Starting with the bond between the ring and the side chain, we are given two pairs of synthons as shown in Scheme 2. The synthetic equivalent to the aromatic anion ...
PDF File
... the observed K1/2 values equal the dissociation constants Kd (see also ref 37): The same K1/2 values were observed in concentration dependences in which the maximal rate constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the ...
... the observed K1/2 values equal the dissociation constants Kd (see also ref 37): The same K1/2 values were observed in concentration dependences in which the maximal rate constant for reaction varied by more than 10-fold, which was accomplished by a 2′-H substitution at position -1 and by varying the ...
JOURNAL OF FLOW CHEMISTRY (ISSN: 2062
... enantiomerically pure compounds, the armoury of novel stereoselective synthetic methods is continuously expanding. The use of biocatalysts for these purposes grows with this expansion16-19 since biocatalysis often requires milder conditions in stereoselective reaction than chemocatalysis. Hydrolases ...
... enantiomerically pure compounds, the armoury of novel stereoselective synthetic methods is continuously expanding. The use of biocatalysts for these purposes grows with this expansion16-19 since biocatalysis often requires milder conditions in stereoselective reaction than chemocatalysis. Hydrolases ...
Introduction to Nanochemistry
... of mechanism, water exchange rates, formation of complexes from aqueous ions, equation and base hydrolysis, attack on ligands. Reaction of Square complexes: mechanism of ligand displacement reactions, the trans effect, cis-effect. Metal Cabonyl reactions: Reactions of octahedral, reactions of binucl ...
... of mechanism, water exchange rates, formation of complexes from aqueous ions, equation and base hydrolysis, attack on ligands. Reaction of Square complexes: mechanism of ligand displacement reactions, the trans effect, cis-effect. Metal Cabonyl reactions: Reactions of octahedral, reactions of binucl ...
Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective
... in organic synthesis [3]. However, the preparation of carboxylic acid esters of tertiary alcohols by an acid catalyzed process is very difficult because of the very high reactivity of tert-alcohols. Take synthesis of tert-butanol esters, for example, under acidic condition, tert-butanol undergoes de ...
... in organic synthesis [3]. However, the preparation of carboxylic acid esters of tertiary alcohols by an acid catalyzed process is very difficult because of the very high reactivity of tert-alcohols. Take synthesis of tert-butanol esters, for example, under acidic condition, tert-butanol undergoes de ...
CHAPTER 11 BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE:
... Alkyl group names are used for simple alkyl group substituents. When there are two or more substituents, the positions around the ring are numbered beginning with the substituent first in the alphabet. ...
... Alkyl group names are used for simple alkyl group substituents. When there are two or more substituents, the positions around the ring are numbered beginning with the substituent first in the alphabet. ...
T_AllylCF3paperBM[5]
... for the CF3-cations A1-A5 are significantly higher than ω value (13.4 eV) for the cation C1, therefore cations A1-A5 are much more electrophilic. Due to electron withdrawing effect of CF3-group cation A1 has a greater charge on carbon C4 and lower charge on C2, in comparison with C1 having similar c ...
... for the CF3-cations A1-A5 are significantly higher than ω value (13.4 eV) for the cation C1, therefore cations A1-A5 are much more electrophilic. Due to electron withdrawing effect of CF3-group cation A1 has a greater charge on carbon C4 and lower charge on C2, in comparison with C1 having similar c ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.

















![Neutral ionic liquid [BMIm]BF4 promoted highly selective](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017897985_1-047f9869d5604c115b21339541ccfffe-300x300.png)

![T_AllylCF3paperBM[5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003584459_1-3decab572f7fca68901a941affab18ea-300x300.png)