Activity C14: Rate of a Chemical Reaction 1
... In this activity you will determine the effect of changes in concentration of the reactants on the rate of the chemical reaction. The reaction for this activity is the acidic reduction of the thiosulfate ion to sulfur and sulfur dioxide. The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) ====== ...
... In this activity you will determine the effect of changes in concentration of the reactants on the rate of the chemical reaction. The reaction for this activity is the acidic reduction of the thiosulfate ion to sulfur and sulfur dioxide. The equation for the reaction is: S2O32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) ====== ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... Specific to allyl aryl ethers, ArOCH2CH=CH2 Heating to 200–250°C leads to an o-allylphenol Result is alkylation of the phenol in an ortho position ...
... Specific to allyl aryl ethers, ArOCH2CH=CH2 Heating to 200–250°C leads to an o-allylphenol Result is alkylation of the phenol in an ortho position ...
Analyze
... This is a very exothermic reaction that occurs very fast and is therefore explosive. 5.74. Collect and Organize We are given the balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of TNT. The enthalpy change from Problem 5.73 for the explosion of ammonium nitrate with fuel oil is –7198 kJ for 3 moles ...
... This is a very exothermic reaction that occurs very fast and is therefore explosive. 5.74. Collect and Organize We are given the balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of TNT. The enthalpy change from Problem 5.73 for the explosion of ammonium nitrate with fuel oil is –7198 kJ for 3 moles ...
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles
... Amines and Heterocycles Why this Chapter? Amines and carbonyl compounds are the most abundant and have rich chemistry In addition to proteins and nucleic acids, a majority of pharmaceutical agents contain amine functional ...
... Amines and Heterocycles Why this Chapter? Amines and carbonyl compounds are the most abundant and have rich chemistry In addition to proteins and nucleic acids, a majority of pharmaceutical agents contain amine functional ...
DISTINGUISH TESTS
... because the other two products are escapable gases. Preparation of Halo alkanes from alcohols using hydrogen halides, the order of reactivity of alcohols with a given halo acid is 3°>2°>1°. The above method is not applicable for the preparation of aryl halides because the carbon-oxygen bond in p ...
... because the other two products are escapable gases. Preparation of Halo alkanes from alcohols using hydrogen halides, the order of reactivity of alcohols with a given halo acid is 3°>2°>1°. The above method is not applicable for the preparation of aryl halides because the carbon-oxygen bond in p ...
... synthesis of simple metal thiolate complexes [LM-SR]+ with three different metal ions ((Zn2+, Cu2+, and Co2+) and benzenethiol as a coloigand. These model complexes were characterized using FT-IR, UV-visible, and 1H NMR spectroscopes as well as conductometric titrations and thermal analyses. To dete ...
Microsoft Word
... alkali, alkali concentration, temperature and duration of leaching and the nature of the washing agent (tap water, distilled water, deionised distilled water, 50% ethanol, 95% ethanol) on the surface properties (such as surface area and crystal size) and catalytic activity (in the hydrogenation of o ...
... alkali, alkali concentration, temperature and duration of leaching and the nature of the washing agent (tap water, distilled water, deionised distilled water, 50% ethanol, 95% ethanol) on the surface properties (such as surface area and crystal size) and catalytic activity (in the hydrogenation of o ...
Chapter 17 lecture notes on Chemical Equilibria
... we do in life when things change? We do what we can to relieve the stress by moving away from it. We apply the same notion to chemical equilibria. In a system at equilibrium, when a change occurs a stress is imposed on the system. The system then responds by adopting new equilibrium conditions that ...
... we do in life when things change? We do what we can to relieve the stress by moving away from it. We apply the same notion to chemical equilibria. In a system at equilibrium, when a change occurs a stress is imposed on the system. The system then responds by adopting new equilibrium conditions that ...
Reductive Elimination
... Octahedral d6 complexes of Pt(IV), Pd(IV), Ir(III), and Rh(III) tend to undergo reductive elimination readily but often with initial loss of a ligand to generate a 5-coordinate intermediate, a much more reactive species than the starting 6-coordinate complex. ...
... Octahedral d6 complexes of Pt(IV), Pd(IV), Ir(III), and Rh(III) tend to undergo reductive elimination readily but often with initial loss of a ligand to generate a 5-coordinate intermediate, a much more reactive species than the starting 6-coordinate complex. ...
RES15_c2_wp
... Suggest an equation for the reaction between phenol and ethanoic acid. Name the product – is the reaction more or less likely to happen than with an alcohol? Suggest or research the conditions. Suggest five reactions that would be expected of the hypothetical molecule cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene. Give eq ...
... Suggest an equation for the reaction between phenol and ethanoic acid. Name the product – is the reaction more or less likely to happen than with an alcohol? Suggest or research the conditions. Suggest five reactions that would be expected of the hypothetical molecule cyclohexa-1,3,5-triene. Give eq ...
Full Text - Journal of the Indian Institute of Science
... The use of Burgess reagent (1) in many occasions leads to unexpected products. Cited below are a few such examples. Cyclopropanone dithioacetals with an additional electron by withdrawing ring substituent are particularly useful, especially if available in optically active form. Apart from substitut ...
... The use of Burgess reagent (1) in many occasions leads to unexpected products. Cited below are a few such examples. Cyclopropanone dithioacetals with an additional electron by withdrawing ring substituent are particularly useful, especially if available in optically active form. Apart from substitut ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... How many shoes do you own? Because shoes come in twos, you would most likely count them by the pair rather than individually. The counting units you use depend on what you are counting. For example, you might count eggs by the dozen or paper by the ream. Chemists also need practical units for counti ...
... How many shoes do you own? Because shoes come in twos, you would most likely count them by the pair rather than individually. The counting units you use depend on what you are counting. For example, you might count eggs by the dozen or paper by the ream. Chemists also need practical units for counti ...
Chemistry
... Hybridizations of orbitals, implications of hybridization on the concept of bond length, bond energy, bond angles, shape of the molecules with the examples of molecules given below: (i) CH4, H3O+, –CH3, RNH2 (ii) C2H4, +CH3, carbonyl compounds and (iii) C2H2, R-CN, allene, ketene. Nature of covalent ...
... Hybridizations of orbitals, implications of hybridization on the concept of bond length, bond energy, bond angles, shape of the molecules with the examples of molecules given below: (i) CH4, H3O+, –CH3, RNH2 (ii) C2H4, +CH3, carbonyl compounds and (iii) C2H2, R-CN, allene, ketene. Nature of covalent ...
Topic 10
... The compound, 2-bromobutane, CH3CHBrCH2CH3, can react with sodium hydroxide to form compounds F, G and H. Compound F, C4H10O, exists as a pair of optical isomers. Compounds G and H, C4H8, are structural isomers, and compound H exists as a pair of geometrical isomers. ...
... The compound, 2-bromobutane, CH3CHBrCH2CH3, can react with sodium hydroxide to form compounds F, G and H. Compound F, C4H10O, exists as a pair of optical isomers. Compounds G and H, C4H8, are structural isomers, and compound H exists as a pair of geometrical isomers. ...
Hydrocarbons
... because of restricted rotation about a carboncarbon double bond, an alkene with two different groups on each carbon of the double bond shows cis-trans isomerism How many isomers are possible for a compound with the formula C4H8? ...
... because of restricted rotation about a carboncarbon double bond, an alkene with two different groups on each carbon of the double bond shows cis-trans isomerism How many isomers are possible for a compound with the formula C4H8? ...
Final Study Guide (Semester 2) Answer Key
... b. The hottest part of the tower is at the ( top / bottom ). The coolest part is at the ( top / bottom ). c. Which chemical would condense first, heptane (7 carbons) or decane (10 carbons)? 24. Name one commercial item made from petroleum. What petroleum product is used to make it? Basketballs are m ...
... b. The hottest part of the tower is at the ( top / bottom ). The coolest part is at the ( top / bottom ). c. Which chemical would condense first, heptane (7 carbons) or decane (10 carbons)? 24. Name one commercial item made from petroleum. What petroleum product is used to make it? Basketballs are m ...
13: Carbonyl Compounds: Ketones, Aldehydes, Carboxylic Acids
... Details of Oxidation Number Calculations. The rules used to calculate these numbers are similar to those used for inorganic molecules. The H atoms are assigned an oxidation number of +1 when they are bonded to C or to more electronegative atoms. In contrast, oxygen atoms, whether singly or doubly bo ...
... Details of Oxidation Number Calculations. The rules used to calculate these numbers are similar to those used for inorganic molecules. The H atoms are assigned an oxidation number of +1 when they are bonded to C or to more electronegative atoms. In contrast, oxygen atoms, whether singly or doubly bo ...
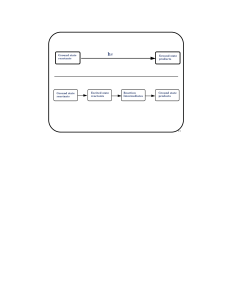
Ground state reactants Ground state products Ground state
... BR will undergo biradical-specific reactions when they interact with paramagnetic ...
... BR will undergo biradical-specific reactions when they interact with paramagnetic ...
Asymmetric induction

Asymmetric induction (also enantioinduction) in stereochemistry describes the preferential formation in a chemical reaction of one enantiomer or diastereoisomer over the other as a result of the influence of a chiral feature present in the substrate, reagent, catalyst or environment. Asymmetric induction is a key element in asymmetric synthesis.Asymmetric induction was introduced by Hermann Emil Fischer based on his work on carbohydrates. Several types of induction exist.Internal asymmetric induction makes use of a chiral center bound to the reactive center through a covalent bond and remains so during the reaction. The starting material is often derived from chiral pool synthesis. In relayed asymmetric induction the chiral information is introduced in a separate step and removed again in a separate chemical reaction. Special synthons are called chiral auxiliaries. In external asymmetric induction chiral information is introduced in the transition state through a catalyst of chiral ligand. This method of asymmetric synthesis is economically most desirable.