Chapter 22 and 23 Study Guide
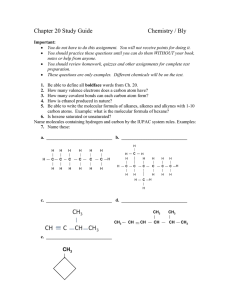
... Be able to define all boldface words from Ch. 20. How many valence electrons does a carbon atom have? How many covalent bonds can each carbon atom form? How is ethanol produced in nature? Be able to write the molecular formula of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes with 1-10 carbon atoms. Example: what is ...
... Be able to define all boldface words from Ch. 20. How many valence electrons does a carbon atom have? How many covalent bonds can each carbon atom form? How is ethanol produced in nature? Be able to write the molecular formula of alkanes, alkenes and alkynes with 1-10 carbon atoms. Example: what is ...
Selective Oxidation Reactions of Natural Compounds with
... Methyltrioxorhenium (CH3ReO3, MTO) in the presence of H2O2 has proven itself as an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst with interesting selectivity towards natural compounds, which can be oxidized under quite mild conditions [3–21]. In previous work [22] we have observed good regio- and stere ...
... Methyltrioxorhenium (CH3ReO3, MTO) in the presence of H2O2 has proven itself as an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst with interesting selectivity towards natural compounds, which can be oxidized under quite mild conditions [3–21]. In previous work [22] we have observed good regio- and stere ...
Atomic Structure
... The ratio e/m for a cathode ray (a) is the smallest when the discharge tube is filled with hydrogen (b) is fixed (c) varies with the atomic number of an element constituting the cathode in the discharge tube (d) varies with the atomic number of the gas in the discharges tube ...
... The ratio e/m for a cathode ray (a) is the smallest when the discharge tube is filled with hydrogen (b) is fixed (c) varies with the atomic number of an element constituting the cathode in the discharge tube (d) varies with the atomic number of the gas in the discharges tube ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 9 - Alkyl Halides I
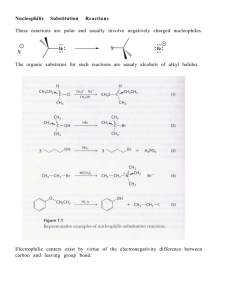
... Can a substitution reaction involve a carbon that is a stereocenter? yes Can a substitution reaction create a new stereocenter? no What happens to a stereocenter involved in an SN2 reaction? Cl ...
... Can a substitution reaction involve a carbon that is a stereocenter? yes Can a substitution reaction create a new stereocenter? no What happens to a stereocenter involved in an SN2 reaction? Cl ...
1.4 Alcohols, Ethers, and Thiols
... Primary alcohols react to form aldehydes and further to form carboxylic acids Secondary alcohols react to form ketones Tertiary alcohols do not undergo controlled oxidation We will learn more about controlled oxidation when we get to aldehydes and ...
... Primary alcohols react to form aldehydes and further to form carboxylic acids Secondary alcohols react to form ketones Tertiary alcohols do not undergo controlled oxidation We will learn more about controlled oxidation when we get to aldehydes and ...
Chapter Seven - U of L Class Index
... The Sn 1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the ratedetermining step. 3°, benzylic and allylic substrates undergo Sn 1 reaction because they form relatively stable carbocations. 1° substrates undergo Sn2 reaction because they are sterically uncluttered. 2° substrates u ...
... The Sn 1 mechanism involves the formation of a carbocation intermediate in the ratedetermining step. 3°, benzylic and allylic substrates undergo Sn 1 reaction because they form relatively stable carbocations. 1° substrates undergo Sn2 reaction because they are sterically uncluttered. 2° substrates u ...
Zinc Alkyls in Organic Synthesis
... DEZ is also useful in catalytic asymmetric addition to aldehydes or ketones forming chiral secondary or tertiary alcohols. These reactions typically involve an amine or a sulfonamide ligand in combination with tetraisopropyl titanate (TIPT). The added substituent comes from zinc alkyls such as DEZ o ...
... DEZ is also useful in catalytic asymmetric addition to aldehydes or ketones forming chiral secondary or tertiary alcohols. These reactions typically involve an amine or a sulfonamide ligand in combination with tetraisopropyl titanate (TIPT). The added substituent comes from zinc alkyls such as DEZ o ...
Final Exam Review Sheet Chemistry 110a/1998
... 5. Be able to explain the allylic bromination of organic molecules with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), using an arrow-pushing mechanism to explain how the reaction works and avoids the reaction of Br2 and the alkene. 6. Be able to rationalize the added stability of conjugated double bonds, using a resona ...
... 5. Be able to explain the allylic bromination of organic molecules with N-bromosuccinimide (NBS), using an arrow-pushing mechanism to explain how the reaction works and avoids the reaction of Br2 and the alkene. 6. Be able to rationalize the added stability of conjugated double bonds, using a resona ...
View/Open
... by any means—graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping, Web distribution, information storage and retrieval systems, or in any other manner—without the written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America ...
... by any means—graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, taping, Web distribution, information storage and retrieval systems, or in any other manner—without the written permission of the publisher. Printed in the United States of America ...
PDF - TU Darmstadt Chemie
... aldehyde group and either the C-4-OH or C-5OH. Cyclization involving O-4 results in a fivemembered ring structurally related to furan and therefore designated as a furanose, whilst hemiacetal formation with O-5 gives rise to an essentially strain-free, hence sterically more favored, six-membered rin ...
... aldehyde group and either the C-4-OH or C-5OH. Cyclization involving O-4 results in a fivemembered ring structurally related to furan and therefore designated as a furanose, whilst hemiacetal formation with O-5 gives rise to an essentially strain-free, hence sterically more favored, six-membered rin ...
Mock Exam One
... b.) In general, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones. c.) Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl groups can be catalyzed by acid or base. d.) Addition of a nucleophile to a carbonyl group changes the hybridization of the carbonyl carbon from sp3 to sp2. ...
... b.) In general, aldehydes are more reactive than ketones. c.) Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl groups can be catalyzed by acid or base. d.) Addition of a nucleophile to a carbonyl group changes the hybridization of the carbonyl carbon from sp3 to sp2. ...
Modified polyacrylamide-supported chlorochromate as a
... During the past years, there have been several important advances in the field of organic synthesis; the use of polymer-supported reagents is one of them.1 Polymeric reagents can be defined as functionalized polymers used in stoichiometric amounts in one-step processes to transform low-molecular-wei ...
... During the past years, there have been several important advances in the field of organic synthesis; the use of polymer-supported reagents is one of them.1 Polymeric reagents can be defined as functionalized polymers used in stoichiometric amounts in one-step processes to transform low-molecular-wei ...
20 More About Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... In this reaction, Cu+ loses an electron, so Cu+ is oxidized. Fe 3+ gains an electron, so Fe 3+ is reduced. The reaction demonstrates two important points about oxidation– reduction reactions. First, oxidation is always coupled with reduction. In other words, a compound cannot gain electrons (be redu ...
... In this reaction, Cu+ loses an electron, so Cu+ is oxidized. Fe 3+ gains an electron, so Fe 3+ is reduced. The reaction demonstrates two important points about oxidation– reduction reactions. First, oxidation is always coupled with reduction. In other words, a compound cannot gain electrons (be redu ...
Unit 16: Chemistry for Biology Technicians
... Functional groups: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature; classes of compounds; alkanes; alkenes; alcohols; haloalkanes; carboxylic acids; aldehydes; ketones; esters; amines; amides; recognition of functional groups in complex molecules, eg carbohydrates, fats, amino ...
... Functional groups: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) nomenclature; classes of compounds; alkanes; alkenes; alcohols; haloalkanes; carboxylic acids; aldehydes; ketones; esters; amines; amides; recognition of functional groups in complex molecules, eg carbohydrates, fats, amino ...
alcohols - A-Level Chemistry
... Suggest how methanol could be made in two steps from methane. i) ...
... Suggest how methanol could be made in two steps from methane. i) ...
PREPARATION OF ALDEHYDES
... EXAMPLES OF NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO ALDEHYDES & KETONES Addition of HCN (neutral-basic conditions). CN Ө is a very good nucleophile (ionic nucleophile). The use of the actual compound HCN is not experimentally feasible, as it is a lethal gas, bp 26 oC. Addition of the elements of HCN to a C=O grou ...
... EXAMPLES OF NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION TO ALDEHYDES & KETONES Addition of HCN (neutral-basic conditions). CN Ө is a very good nucleophile (ionic nucleophile). The use of the actual compound HCN is not experimentally feasible, as it is a lethal gas, bp 26 oC. Addition of the elements of HCN to a C=O grou ...
3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways)
... Most organic molecules have a mainly hydrocarbon portion to their structures, and as the hydrocarbon chain increases in length the number of London Dispersion forces will increase. As a result, more energy is needed to move the molecules further apart. Branched molecules tend to be more compact and ...
... Most organic molecules have a mainly hydrocarbon portion to their structures, and as the hydrocarbon chain increases in length the number of London Dispersion forces will increase. As a result, more energy is needed to move the molecules further apart. Branched molecules tend to be more compact and ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.