Synthesis of Benzyl Acetate from Acetic Anhydride
... Another way to upset the equilibrium is to remove water. This can be done by adding to the reaction mixture molecular sieves, an artificial zeolite, which preferentially adsorb water. Most other drying agents, such as anhydrous sodium sulfate or calcium chloride, will not remove water at the tempera ...
... Another way to upset the equilibrium is to remove water. This can be done by adding to the reaction mixture molecular sieves, an artificial zeolite, which preferentially adsorb water. Most other drying agents, such as anhydrous sodium sulfate or calcium chloride, will not remove water at the tempera ...
A Model for Catalytically Active Zinc(I1) Ion in Liver
... (11). Identification of reaction products was performed by coinjection of reaction mixtures with standards onto HPLC column and/or by IH N M R measurements of isolated products. HPLC analysis was performed by a 5 pm Lichrospher Si60 column (250 X $50 mm) eluted with 1:l n-hexanelethyl acetate at 1.5 ...
... (11). Identification of reaction products was performed by coinjection of reaction mixtures with standards onto HPLC column and/or by IH N M R measurements of isolated products. HPLC analysis was performed by a 5 pm Lichrospher Si60 column (250 X $50 mm) eluted with 1:l n-hexanelethyl acetate at 1.5 ...
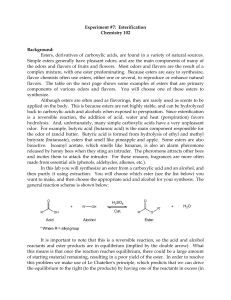
Esterification
... Homework • Describe and explain the formation of phenyl benzoate from benzyl chloride and phenol including a detailed explanation of recrystallization. ...
... Homework • Describe and explain the formation of phenyl benzoate from benzyl chloride and phenol including a detailed explanation of recrystallization. ...
Organic Chem Functional Groups
... opposite sides of the double bond. This is known as the trans isomer. (trans : from latin meaning "across" - as in transatlantic). In the other, the two chlorine atoms are locked on the same side of the double bond. This is know as the cis isomer. (cis : from latin meaning "on this side" cis & trans ...
... opposite sides of the double bond. This is known as the trans isomer. (trans : from latin meaning "across" - as in transatlantic). In the other, the two chlorine atoms are locked on the same side of the double bond. This is know as the cis isomer. (cis : from latin meaning "on this side" cis & trans ...
Group B_reaction of alkynes
... of the catalyst- both H are delivered to the same side of the double bond. Only syn addition of H. Syn addition of H to an internal alkyne forms a cis alkene. ...
... of the catalyst- both H are delivered to the same side of the double bond. Only syn addition of H. Syn addition of H to an internal alkyne forms a cis alkene. ...
Experiment 2. Oxidation of an Alcohol (see Ege`s: pp 515-519)
... 1. The TLC spot of neither any of the alcohol we use nor the ketone product could be visible under the 254 nm UV lamp. Use the vanillin stain (this stain contains vanillin and conc. sulfuric acid in ethanol). After developing the spots, evaporate off the solvent from the plate and strongly heat the ...
... 1. The TLC spot of neither any of the alcohol we use nor the ketone product could be visible under the 254 nm UV lamp. Use the vanillin stain (this stain contains vanillin and conc. sulfuric acid in ethanol). After developing the spots, evaporate off the solvent from the plate and strongly heat the ...
Experiment 7 — Nucleophilic Substitution
... SN1 reactions. Test the same series of organo-halides with the AgNO3/EtOH solution. Bromides first, then the allylic and benzylic compounds. Warm or cool if necessary. Write a brief discussion that addresses the same points that were raised in the context of the SN2. Of course the key to SN1 reactiv ...
... SN1 reactions. Test the same series of organo-halides with the AgNO3/EtOH solution. Bromides first, then the allylic and benzylic compounds. Warm or cool if necessary. Write a brief discussion that addresses the same points that were raised in the context of the SN2. Of course the key to SN1 reactiv ...
EXPERIMENT 5: Oxidation of Alcohols: Solid
... General Concepts Efficient preparation of aldehydes and ketones is essential considering their importance in organic synthesis. ...
... General Concepts Efficient preparation of aldehydes and ketones is essential considering their importance in organic synthesis. ...
aldehydes and ketones
... magnitude of the positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom. Hence, any substituent that increases the positive charge on the carbonyl carbon must increase its reactivity towards addition reactions. The introduction of negative group ( -I effect) increases the reactivity, while introduction of alky ...
... magnitude of the positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom. Hence, any substituent that increases the positive charge on the carbonyl carbon must increase its reactivity towards addition reactions. The introduction of negative group ( -I effect) increases the reactivity, while introduction of alky ...
15 - MSU Chemistry
... The starting material for the second reaction is also achiral as it too has a plane of symmetry. The stereochemistry merely shows that the two OTs groups are on the same side of th ...
... The starting material for the second reaction is also achiral as it too has a plane of symmetry. The stereochemistry merely shows that the two OTs groups are on the same side of th ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive Coupling with
... employed the complex of TiCl2(AlCl3)2 with hexamethylbenzene to form pinacols from ketones [8], The partly defined complex H T iC 10.5T H F has been implicated as an active reagent in the McMurry reaction [9] and the complex, Ti(MgCl)2 xTHF has also been shown to serve as a reagent for such ketone c ...
... employed the complex of TiCl2(AlCl3)2 with hexamethylbenzene to form pinacols from ketones [8], The partly defined complex H T iC 10.5T H F has been implicated as an active reagent in the McMurry reaction [9] and the complex, Ti(MgCl)2 xTHF has also been shown to serve as a reagent for such ketone c ...
Alcohols, Aldehydes and Ketones
... This shows that Propan 1-ol, Propan 2-ol and Propanal are oxidized only, being a primary, secondary alcohol and aldehdye. 2 Methyl propan2-ol is a tertiary alcohol and Propanone a ketone which can not be oxidized. The Fehlings solution has changed colour which is a result of the formation of Cu 2+ b ...
... This shows that Propan 1-ol, Propan 2-ol and Propanal are oxidized only, being a primary, secondary alcohol and aldehdye. 2 Methyl propan2-ol is a tertiary alcohol and Propanone a ketone which can not be oxidized. The Fehlings solution has changed colour which is a result of the formation of Cu 2+ b ...
organic synthesis
... • one optical isomer usually works better than the other • in some cases the other optical isomer may cause dangerous side effects • laboratory reactions usually produce both optical isomers • naturally occurring reactions usually produce just one optical isomer ...
... • one optical isomer usually works better than the other • in some cases the other optical isomer may cause dangerous side effects • laboratory reactions usually produce both optical isomers • naturally occurring reactions usually produce just one optical isomer ...
Expanding cements with controlled hardening time
... expansion concomitant with this reaction leads to destructive changes in the cement stone structure. In particular, this accounts for a lower amount of gypsum stone in general cements in comparison with the estimated amount. By thermodynamic calculations and complex physical and chemical analisis me ...
... expansion concomitant with this reaction leads to destructive changes in the cement stone structure. In particular, this accounts for a lower amount of gypsum stone in general cements in comparison with the estimated amount. By thermodynamic calculations and complex physical and chemical analisis me ...
16A
... A hemiacetal can react further with an alcohol to form an acetal plus water this reaction is acid catalyzed the functional group of an acetal is a carbon bonded to two -OR groups ...
... A hemiacetal can react further with an alcohol to form an acetal plus water this reaction is acid catalyzed the functional group of an acetal is a carbon bonded to two -OR groups ...
Chem 174-Lecture 15a..
... ansa-metallocenes because the bridge locks the Cp-rings and also changes the reactivity of the metal center based on X Variations of the cyclopentadiene moiety leads to the formation of catalyst that yield different forms of polypropylene (atatic, isotactic, syndiotactic) ...
... ansa-metallocenes because the bridge locks the Cp-rings and also changes the reactivity of the metal center based on X Variations of the cyclopentadiene moiety leads to the formation of catalyst that yield different forms of polypropylene (atatic, isotactic, syndiotactic) ...
PHYSICAL SCIENCE PAPER 2 QUESTIONS SECTION A
... QUESTION 2: FALSE ITEMS Each of the five statements below is FALSE. Correct each statement so that it is TRUE. Write only the correct statement next to the question number (2.1 – 2.5). NOTE: Correction by using the negative of the statement, for example "… IS NOT …", will ...
... QUESTION 2: FALSE ITEMS Each of the five statements below is FALSE. Correct each statement so that it is TRUE. Write only the correct statement next to the question number (2.1 – 2.5). NOTE: Correction by using the negative of the statement, for example "… IS NOT …", will ...
Chem 341 Review for Finals Key Reactions Mechanisms
... – Exchange of ketone a-hydrogens with D2O – Aldol condensation: addition of enolate anion to an aldehyde carbonyl carbon • Carboxylic acid derivatives – Relative reactivity: Acid halides > Anhydrides > Esters > Amides > ...
... – Exchange of ketone a-hydrogens with D2O – Aldol condensation: addition of enolate anion to an aldehyde carbonyl carbon • Carboxylic acid derivatives – Relative reactivity: Acid halides > Anhydrides > Esters > Amides > ...
ch07 by Dr. Dina
... medium (for example platinum, palladium or nickel catalysts) Homogeneous catalysts: catalyst is soluble in the reaction medium (for examples rhodium or ruthenium based) Wilkinson’s catalyst is Rh[(C6H5)3P]3Cl This process is called a reduction or hydrogenation An unsaturated compound becomes ...
... medium (for example platinum, palladium or nickel catalysts) Homogeneous catalysts: catalyst is soluble in the reaction medium (for examples rhodium or ruthenium based) Wilkinson’s catalyst is Rh[(C6H5)3P]3Cl This process is called a reduction or hydrogenation An unsaturated compound becomes ...
Discussion Worksheet #10 Formation of Alcohols Skill 1: Functional
... There are ways to control regiochemistry and stereochemistry with alcohol formation ...
... There are ways to control regiochemistry and stereochemistry with alcohol formation ...
Oxidation of Cyclohexanol to Cyclohexanone Notes
... Standard bleach is an approximately 0.74 M solution of Sodium hypochlorite in water. A new commercial concentrated bleach is 1.11 M. Make note of the type (regular or concentrated) of bleach used during the experiment. 5. The acetic acid is a catalyst which transforms the sodium hypochlorite into hy ...
... Standard bleach is an approximately 0.74 M solution of Sodium hypochlorite in water. A new commercial concentrated bleach is 1.11 M. Make note of the type (regular or concentrated) of bleach used during the experiment. 5. The acetic acid is a catalyst which transforms the sodium hypochlorite into hy ...
Dissertation:
... Poly(lactide) (PLA) is a aliphatic polyester obtained from renewable sources, and is intensively used in the pharmaceutical and medical industries and in the production of packages devoted to food products. The performed alcoholysis reactions of PLLA and L-LA showed significant catalytic activity of ...
... Poly(lactide) (PLA) is a aliphatic polyester obtained from renewable sources, and is intensively used in the pharmaceutical and medical industries and in the production of packages devoted to food products. The performed alcoholysis reactions of PLLA and L-LA showed significant catalytic activity of ...
20130409085519
... An amine is an organic base derived from ammonia in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. ...
... An amine is an organic base derived from ammonia in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. ...
SMJK PEREMPUAN CHINA PULAU PINANG CHEMISTRY FORM 5
... (i) Define oxidation and reduction in terms of the change in the oxidation number. (ii) Name the compounds that undergo oxidation and reduction. (iii) State the change in the oxidation number of each element that you have named in (b)(ii). (iv) Name the oxidizing agent and reducing agent. (v) Write ...
... (i) Define oxidation and reduction in terms of the change in the oxidation number. (ii) Name the compounds that undergo oxidation and reduction. (iii) State the change in the oxidation number of each element that you have named in (b)(ii). (iv) Name the oxidizing agent and reducing agent. (v) Write ...
ESTERIFICATION
... and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, ...
... and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.