radicals
... The use of TRIBUTYLtin derivatives has become relatively common. The three butyl groups add molecular weight to the tin and thus lower its vapor pressure. (Tin compounds can be toxic by inhalation.) ...
... The use of TRIBUTYLtin derivatives has become relatively common. The three butyl groups add molecular weight to the tin and thus lower its vapor pressure. (Tin compounds can be toxic by inhalation.) ...
A convenient method for the preparation of oxazaborolidine catalyst
... reduction of prochiral ketones is an extremely important methodology for the synthesis of chiral secondary alcohols. The oxazaborolidine (CBS reagent)-catalyzed asymmetric reduction methodology has been extensively used for this purpose.2–4 Even though the parent catalyst H-CBS 4, prepared in situ u ...
... reduction of prochiral ketones is an extremely important methodology for the synthesis of chiral secondary alcohols. The oxazaborolidine (CBS reagent)-catalyzed asymmetric reduction methodology has been extensively used for this purpose.2–4 Even though the parent catalyst H-CBS 4, prepared in situ u ...
Powerpoint: Reaction pathways
... C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br ...
... C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br ...
PPT: Intro to Organic Chemistry
... Naming Alkenes and Alkynes 1. The C-chain MUST include the multiple bond. Use –ene or –yne, as appropriate. 2. Number so that you get to the multiple bond ASAP. -- The multiple bond takes precedence over branching or substituents. ...
... Naming Alkenes and Alkynes 1. The C-chain MUST include the multiple bond. Use –ene or –yne, as appropriate. 2. Number so that you get to the multiple bond ASAP. -- The multiple bond takes precedence over branching or substituents. ...
m4 organic reaction pathways
... C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br ...
... C2H5Br + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> C2H5NH2 + HBr HBr + NH3 (aq / alc) ——> NH4Br ...
Carbonyl Compounds Prior Knowledge
... be able to apply IUPAC rules for nomenclature to alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids limited to chains with up to 6 carbon atoms understand that alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary understand that tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidised understand that primar ...
... be able to apply IUPAC rules for nomenclature to alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids limited to chains with up to 6 carbon atoms understand that alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary understand that tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidised understand that primar ...
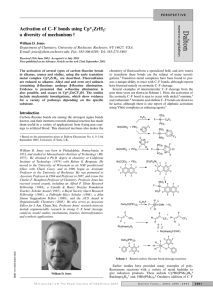
Activation of C–F bonds using Cp*2ZrH2: a
... result in smaller conversions to the same products. This reaction can be explained by two reasonable mechanisms: (1) olefin insertion/β-fluoride elimination, or (2) hydride attack/fluoride metathesis as shown in Scheme 6. Olefin insertion is well known for this zirconium hydride, and regioselective inse ...
... result in smaller conversions to the same products. This reaction can be explained by two reasonable mechanisms: (1) olefin insertion/β-fluoride elimination, or (2) hydride attack/fluoride metathesis as shown in Scheme 6. Olefin insertion is well known for this zirconium hydride, and regioselective inse ...
phenol - Knockhardy
... • the OH group is electron releasing • it increases the electron density of the delocalised system • it makes substitution much easier compared to benzene • the electron density is greatest at the 2,4 and 6 positions • substitution takes place at the 2,4 and 6 positions • phenol reacts readily with ...
... • the OH group is electron releasing • it increases the electron density of the delocalised system • it makes substitution much easier compared to benzene • the electron density is greatest at the 2,4 and 6 positions • substitution takes place at the 2,4 and 6 positions • phenol reacts readily with ...
11.Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
... (iii)PCl3 (iv) SOCl2/Pyridine.The reaction with SOCl2/Pyridine is preferred because in this case side products are gaseous and can be expelled during distillation. Halogenation of alkenes in the presence of peroxides takes place through free radicals as intermediates and results in anti-Markownikoff ...
... (iii)PCl3 (iv) SOCl2/Pyridine.The reaction with SOCl2/Pyridine is preferred because in this case side products are gaseous and can be expelled during distillation. Halogenation of alkenes in the presence of peroxides takes place through free radicals as intermediates and results in anti-Markownikoff ...
Imine formation
... Imine Formation Major concepts The imine is a functional group in which Carbon and Nitrogen are double bonded Aldehydes and ketones react with primary amines under acid catalyzed conditions to form imines The Aldol condensation and imine formation are mechanistically similar, so they can be re ...
... Imine Formation Major concepts The imine is a functional group in which Carbon and Nitrogen are double bonded Aldehydes and ketones react with primary amines under acid catalyzed conditions to form imines The Aldol condensation and imine formation are mechanistically similar, so they can be re ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 PART-A
... The diazotization of aniline in moderately concentrated acid has been found to be second order in HNO2. Explain. How will you determine the configuration of a) () mandelic acid with respect to (+) lactic acid? b) () lactic acid with respect to (+) tartaric acid? How will you correlate the configur ...
... The diazotization of aniline in moderately concentrated acid has been found to be second order in HNO2. Explain. How will you determine the configuration of a) () mandelic acid with respect to (+) lactic acid? b) () lactic acid with respect to (+) tartaric acid? How will you correlate the configur ...
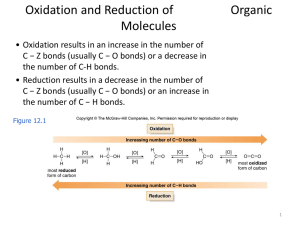
Oxidation and Reduction of Organic Molecules
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
... number of rings in the original compound. • For example, if a molecule with a formula C8H12 was converted to C8H14 upon hydrogenation, the original molecule contains one bond and two rings. • Carbonyl groups (C=O) in a molecule can also undergo hydrogenation to form alcohols since they contain a ...
Additional file 1
... stirred solution of alcohol 2 (1.8 g, 9.0 mmol) and powdered 4Å molecular sieve (0.75 g) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (50 mL) at 0°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, then diluted with anhydrous ether and filtered through celite. The filtrate was concentra ...
... stirred solution of alcohol 2 (1.8 g, 9.0 mmol) and powdered 4Å molecular sieve (0.75 g) in anhydrous CH2Cl2 (50 mL) at 0°C. After the addition was complete, the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h, then diluted with anhydrous ether and filtered through celite. The filtrate was concentra ...
CHEMISTRY 3.5 Paper 1 Describe the structure and reactions of
... litmus as testing reagents. A M E _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________ ...
... litmus as testing reagents. A M E _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________ ...
Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation by Reductive
... employed the complex of TiCl2(AlCl3)2 with hexamethylbenzene to form pinacols from ketones [8], The partly defined complex H T iC 10.5T H F has been implicated as an active reagent in the McMurry reaction [9] and the complex, Ti(MgCl)2 xTHF has also been shown to serve as a reagent for such ketone c ...
... employed the complex of TiCl2(AlCl3)2 with hexamethylbenzene to form pinacols from ketones [8], The partly defined complex H T iC 10.5T H F has been implicated as an active reagent in the McMurry reaction [9] and the complex, Ti(MgCl)2 xTHF has also been shown to serve as a reagent for such ketone c ...
Carboxylic Acids
... 4. Draw and name the isomers of C5H8 ( some may not be alkynes) 5. Construct a model of an acetylene lamp that could have been used as a lantern for early automobiles. Explain how your model works to make the light and direct the light down the road. 6. Write the formula equations for each of the fo ...
... 4. Draw and name the isomers of C5H8 ( some may not be alkynes) 5. Construct a model of an acetylene lamp that could have been used as a lantern for early automobiles. Explain how your model works to make the light and direct the light down the road. 6. Write the formula equations for each of the fo ...
Name Page 1 F.05.215e3p1 I.
... related oxidizing agents, a 1,2-diol is formed. When phenylacetylene (Compound E) is treated with oxidizing agents such as OsO4, the corresponding addition reaction product is not observed; instead it is proposed that the initial addition reaction product, which is an ene-diol, undergoes an isomeriz ...
... related oxidizing agents, a 1,2-diol is formed. When phenylacetylene (Compound E) is treated with oxidizing agents such as OsO4, the corresponding addition reaction product is not observed; instead it is proposed that the initial addition reaction product, which is an ene-diol, undergoes an isomeriz ...
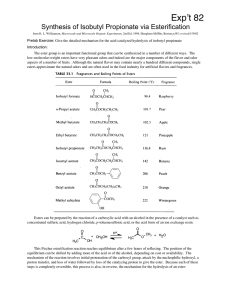
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... Another way to upset the equilibrium is to remove water. This can be done by adding to the reaction mixture molecular sieves, an artificial zeolite, which preferentially adsorb water. Most other drying agents, such as anhydrous sodium sulfate or calcium chloride, will not remove water at the tempera ...
... Another way to upset the equilibrium is to remove water. This can be done by adding to the reaction mixture molecular sieves, an artificial zeolite, which preferentially adsorb water. Most other drying agents, such as anhydrous sodium sulfate or calcium chloride, will not remove water at the tempera ...
sn2 reactions of alkyl halides
... 1-chlorobutane? Explain how the nature of the leaving group affects the rate of an SN 2 reaction. Would 1-iodobutane react faster or slower than the other halides? How would we know that the ...
... 1-chlorobutane? Explain how the nature of the leaving group affects the rate of an SN 2 reaction. Would 1-iodobutane react faster or slower than the other halides? How would we know that the ...
DODH by Molybdenum Innovation Introduction DODH by Rhenium
... reductant and catalyst were carried out. To the right are shown the kinetic profiles for the standard experiment (green), less reductant (blue) and less catalyst (red), figure 5. This kinetic behaviour can be explained by a catalytic cycle driven by the reduction of Re(VII) to Re(V) by oxidation of ...
... reductant and catalyst were carried out. To the right are shown the kinetic profiles for the standard experiment (green), less reductant (blue) and less catalyst (red), figure 5. This kinetic behaviour can be explained by a catalytic cycle driven by the reduction of Re(VII) to Re(V) by oxidation of ...
Hydrothermal Reactions from Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate to Phenol
... On the basis of the observation of the final product phenol and intermittent formic acid and formaldehyde in the hydrothermal reactions, we propose a possible reaction mechanism for phenol formation. Scheme 1 illustrates the main process of the hydrothermal reactions (see details in Supporting Infor ...
... On the basis of the observation of the final product phenol and intermittent formic acid and formaldehyde in the hydrothermal reactions, we propose a possible reaction mechanism for phenol formation. Scheme 1 illustrates the main process of the hydrothermal reactions (see details in Supporting Infor ...
Reactions to know from Chapters 17, 18, 19
... and an OR- group. Here, the oxygen of the alcohol attacks and bonds with the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone If the alcohol group and the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or ketone are on the same molecule, a cyclic hemi-acetal can be formed. (shown below) O ...
... and an OR- group. Here, the oxygen of the alcohol attacks and bonds with the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone If the alcohol group and the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or ketone are on the same molecule, a cyclic hemi-acetal can be formed. (shown below) O ...
Addition reactions
... Electrophilic addition Electrophilic addition: an alkene or alkyne serves as the Nu: and donates : to the electropositive atom of a molecule, typically an acid • Substrate is unsaturated • Reactant is often an acid • The two halves (electropositive & electronegative) are both added “across” the dou ...
... Electrophilic addition Electrophilic addition: an alkene or alkyne serves as the Nu: and donates : to the electropositive atom of a molecule, typically an acid • Substrate is unsaturated • Reactant is often an acid • The two halves (electropositive & electronegative) are both added “across” the dou ...
Wolff–Kishner reduction

The Wolff–Kishner reduction is a reaction used in organic chemistry to convert carbonyl functionalities into methylene groups. In the context of complex molecule synthesis, it is most frequently employed to remove a carbonyl group after it has served its synthetic purpose of activating an intermediate in a preceding step. As such, there is no obvious retron for this reaction. Originally reported by Nikolai Kischner in 1911 and Ludwig Wolff in 1912, it has been applied to the total synthesis of scopadulcic acid B, aspidospermidine and dysidiolide.In general, the reaction mechanism first involves the in situ generation of a hydrazone by condensation of hydrazine with the ketone or aldehyde substrate. Sometimes it is however advantageous to use a pre-formed hydrazone as substrate (see modifications). The hydrazone is deprotonated by alkoxide base followed by a concerted, rate-determining step in which a diimide anion is formed. Collapse of this alkyldiimde with loss of N2 leads to formation of an alkylanion which can be protonated by solvent to give the desired product.Because the Wolff–Kishner reduction requires highly basic conditions, it is unsuitable for base-sensitive substrates. However, this method can be superior over the related Clemmensen reduction for acid-sensitive compounds such as pyrroles and for high-molecular weight compounds.