* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 20130409085519
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
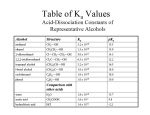
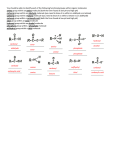
Other Organic Compounds Hydrocarbon derivatives are organic molecules that contain one or more elements in addition to carbon and hydrogen. A functional group is an atom or group of atoms in hydrocarbon derivatives that contain elements in addition to carbon and hydrogen. In developing a general formula for types of organic compounds, the symbol R is used. R represents a hydrocarbon fragment. Example: methyl group The symbol R is from the German radikal. A second R group is called R and a third R group is called R. Alcohols Alcohols have the general formula ROH. In the case of alcohols, the 1 hydroxyl group, OH is a substituent on a hydrocarbon. Alcohols are named by replacing the e on the end of the parent hydrocarbon with ol. Numbering may be necessary. The hydroxyl group is to be on the lowest number carbon. Example: CH3OH is methanol because the R group comes from methane. ethanol CH3CH2OH 1-propanol CH3CH2CH2OH 2-propanol CH3CHCH3 OH 6-bromo-2-methyl-2-hexanol CH3 CH3CCH2CH2CH2CH2Br OH Ethers An ether is an organic compound in which two hydrocarbon groups are joined to an oxygen. The general formula for an ether is ROR It is named with oxy in between the R group names. CH3OCH2CH3 is named methoxyethane methoxymethane CH3OCH3 ethoxyethane CH3CH2OCH2CH3 Ethoxyethane (commonly called diethyl ether) was once the ether most widely used as an anesthetic in surgery. Aldehydes The carbonyl group is C=O. An aldehyde is an organic compound containing the carbonyl group bonded to at least one hydrogen. The general formula of an aldehyde is O ║ R C H Aldehydes are named with the suffix al instead of the usual hydrocarbon ending. The aldehyde carbon is always assigned as number one for referencing substituent positions in the name. Therefore, numbering is not necessary. The name of the parent chain includes the carbon in the aldehyde. CH3CH2CHO is propanal. ethanal CH3CHO butanal CH3CH2CH2CHO Ketones A ketone is an organic compound containing the carbonyl group. The general formula of a ketone is O ║ R C R Ketones are named with the final e being replaced by one and a number indicates the position of the carbonyl group where necessary. The name of the parent chain includes the carbon in the ketone. CH3COCH2CH3 is called 2-butanone. propanone CH3COCH3 2-pentanone CH3COCH2CH2CH3 Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound containing the carboxyl group. A carboxylic acid has the general formula RCOOH. O ║ R C OH Carboxylic acids are named by changing the suffix of the parent hydrocarbon to oic acid. The carbons are numbered so the carbon in the carboxyl group is the number one carbon. CH3COOH is ethanoic acid. pentanoic acid CH3CH2CH2CH2COOH butanoic acid CH3CH2CH2COOH 3-bromo-2-methylbutanoic acid Br CH3 CH3CHCHCOOH Esters An ester is an organic compound produced by the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Esters often have a sweet, fruity odor that is in contrast to the often pungent odors of the parent carboxylic acids. An ester has the general formula RCOOR. O ║ R C O R Esters are named by naming the R groups on either side of the COO group. The R group bonded to the oxygen will have a yl ending and the R group bonded to the C=O will have an oate ending. The carbon in the carbonyl group is counted with the carbon to which it is attached. CH3CH2CH2OOCCH3 is propyl ethanoate octyl ethanoate O ║ CH3CO(CH2)7CH3 methyl methanoate HCOOCH3 isopropyl 3-methylbutanoate CH3 CH3 CH3CHCH2COOCHCH3 Amines An amine is an organic base derived from ammonia in which one or more of the hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An amine has the general structure RNH2. Amines are named with by changing the parent hydrocarbon’s suffix to amine. ethanamine CH3CH2NH2 Amines can be classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary depending on the number of NH bonds that have been replaced by NC bonds. CH3NH2 is a primary amine. (CH3)2NH is a secondary amine. (CH3)3N is a tertiary amine. Amides An amide is an organic compound whose molecules have any one of the following groups: CONH2 CONHR CONR2 Amides are named by changing the parent hydrocarbon’s suffix to amide. ethanamide CH3CONH2 pentanamide CH3CH2CH2CH2CONH2 Nitriles Nitriles have the general formula RCN. Nitriles are named by adding the word “nitrile” to the parent hydrocarbon. butanenitrile CH3CH2CH2CN pentanenitrile CH3CH2CH2CH2CN