Lecture 8a - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... • Ethers are most commonly used as single solvent because they are stable and polar enough to dissolve most Grignard reagents • Diethyl ether: low boiling point, good phase separation with most aqueous layers, the temperature in the system is moderate • Tetrahydrofuran: higher boiling point, poorer ...
... • Ethers are most commonly used as single solvent because they are stable and polar enough to dissolve most Grignard reagents • Diethyl ether: low boiling point, good phase separation with most aqueous layers, the temperature in the system is moderate • Tetrahydrofuran: higher boiling point, poorer ...
CHM230 OXIDATION OF CYCLOHEXANOL TO CYCLOHEXANONE
... graduated cylinder. The distillate should be a mixture of cyclohexanone and water that contains excess acetic acid. Transfer the distillate to a separatory funnel or beaker. 6. Add 3.5 grams of sodium carbonate to neutralize any excess acetic acid, and then add a small amount, about 3 grams of sodiu ...
... graduated cylinder. The distillate should be a mixture of cyclohexanone and water that contains excess acetic acid. Transfer the distillate to a separatory funnel or beaker. 6. Add 3.5 grams of sodium carbonate to neutralize any excess acetic acid, and then add a small amount, about 3 grams of sodiu ...
Chapter 3 Properties of organic compounds
... Ê/ iÊ>``ÌÊvÊiÝViÃÃÊ``iÊÃÊÌÊ«À`ÕViÊI3– means that there is less I2 in solution (or present as solid), and therefore the problems identified above are less likely to occur. As an equilibrium exists between the I2 and I3– ion, then, as the I2 reacts, the triiodide ion will dissociate until ...
... Ê/ iÊ>``ÌÊvÊiÝViÃÃÊ``iÊÃÊÌÊ«À`ÕViÊI3– means that there is less I2 in solution (or present as solid), and therefore the problems identified above are less likely to occur. As an equilibrium exists between the I2 and I3– ion, then, as the I2 reacts, the triiodide ion will dissociate until ...
Instructor notes
... The reaction also occurs without retention of configuration, making it unlikely that the products of such a reaction would be usefully related to the reactants. Metal complexes can participate in the reaction, but only in the context of propagating the radical chain. The oxenoid mechanism is much mo ...
... The reaction also occurs without retention of configuration, making it unlikely that the products of such a reaction would be usefully related to the reactants. Metal complexes can participate in the reaction, but only in the context of propagating the radical chain. The oxenoid mechanism is much mo ...
File - Dr KHALID SHADID
... The trigonal planar arrangement of groups around the carhonyl carbon atom means that the carbonyl carbon atom is relatively open to attack from above or below. The positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom means that it is especially susceptible to attack by a nucleophile. The negative charge on ...
... The trigonal planar arrangement of groups around the carhonyl carbon atom means that the carbonyl carbon atom is relatively open to attack from above or below. The positive charge on the carbonyl carbon atom means that it is especially susceptible to attack by a nucleophile. The negative charge on ...
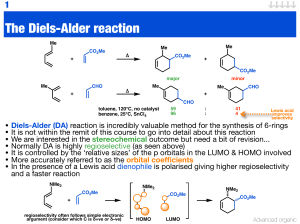
The Diels-Alder reaction
... • Normally DA is highly regioselective (as seen above) • It is controlled by the ‘relative sizes’ of the p orbitals in the LUMO & HOMO involved • More accurately referred to as the orbital coefficients • In the presence of a Lewis acid dienophile is polarised giving higher regioselectivity and a fas ...
... • Normally DA is highly regioselective (as seen above) • It is controlled by the ‘relative sizes’ of the p orbitals in the LUMO & HOMO involved • More accurately referred to as the orbital coefficients • In the presence of a Lewis acid dienophile is polarised giving higher regioselectivity and a fas ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 1
... Which one of the following statements is true? A) CH3CH2-S- is both a stronger base and more nucleophilic than CH3CH2-OB) CH3CH2-S- is a stronger base but less nucleophilic than CH3CH2-OC) CH3CH2-S- is a weaker base but is more nucleophilic than CH3CH2-OD) CH3CH2-S- is both a weaker base and less nu ...
... Which one of the following statements is true? A) CH3CH2-S- is both a stronger base and more nucleophilic than CH3CH2-OB) CH3CH2-S- is a stronger base but less nucleophilic than CH3CH2-OC) CH3CH2-S- is a weaker base but is more nucleophilic than CH3CH2-OD) CH3CH2-S- is both a weaker base and less nu ...
Introduction to Chemical Reactions
... 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO Magnesium atoms and oxygen gas molecules combine to form a single new product Magnesium oxide is the product of the reaction In a moment, we will also see that this reaction can also be classified as a combustion reaction ...
... 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO Magnesium atoms and oxygen gas molecules combine to form a single new product Magnesium oxide is the product of the reaction In a moment, we will also see that this reaction can also be classified as a combustion reaction ...
Organic Chemistry IB Organic Chemistry 2016
... • O and heat can be added to oxidize the OH group (in the form of Potassium dichromate VI) • Primary alcohols-oxidized to carboxylic acids • 2ndary alcohols- oxidized to ketones • Tertiary alcohols- NR ...
... • O and heat can be added to oxidize the OH group (in the form of Potassium dichromate VI) • Primary alcohols-oxidized to carboxylic acids • 2ndary alcohols- oxidized to ketones • Tertiary alcohols- NR ...
Electrochemical oxidation of cinnamic acid using stainless steel
... The IR spectrum of the product shows absorption peaks with reduced intensity and this is characteristic of the IR spectra taken using film technique. The IR spectrum of the product has absorption frequencies corresponding to aromatic stretching (2910 cm-~), aroamtic substituted alkene (1640 and 1630 ...
... The IR spectrum of the product shows absorption peaks with reduced intensity and this is characteristic of the IR spectra taken using film technique. The IR spectrum of the product has absorption frequencies corresponding to aromatic stretching (2910 cm-~), aroamtic substituted alkene (1640 and 1630 ...
Organic Reactions
... e. Reaction occurs through homolytic fission to form a free radical (HL only) i. Free radical is a element or molecule with an unpaired electron ii. Homolytic fission vs Heterolytic fission: 1. Fission means splitting apart 2. Homolytic means the bond is split in half – each side takes 1 electron an ...
... e. Reaction occurs through homolytic fission to form a free radical (HL only) i. Free radical is a element or molecule with an unpaired electron ii. Homolytic fission vs Heterolytic fission: 1. Fission means splitting apart 2. Homolytic means the bond is split in half – each side takes 1 electron an ...
Chem 263 April 11, 2006 Reductive Amination Amines can be
... Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing substances from plant sources. The study of alkaloids provided much of the growth in organic chemistry in the nineteenth century and remains today a fascinating area of research. Many alkaloids have pronounced biological properties, and many pharmaceutical agents us ...
... Alkaloids are nitrogen-containing substances from plant sources. The study of alkaloids provided much of the growth in organic chemistry in the nineteenth century and remains today a fascinating area of research. Many alkaloids have pronounced biological properties, and many pharmaceutical agents us ...
Spring 2015 CH 421 Name ________________________________________ Section ___________ Post‐lab 3: The Grignard Reaction: Preparation of an Alcohol
... 4) Aldehydes undergo reaction with a Grignard reagent to provide an alcohol product. Many aldehydes are prone to air oxidation. For instance, a bottle of benzaldehyde will turn from a clear liquid to a white solid if left open over time. What is the oxidation produ ...
... 4) Aldehydes undergo reaction with a Grignard reagent to provide an alcohol product. Many aldehydes are prone to air oxidation. For instance, a bottle of benzaldehyde will turn from a clear liquid to a white solid if left open over time. What is the oxidation produ ...
chapt13
... a the central phosphorous or carbon atoms resulting in a cleavage of the C-O or C-S bonds. Base-catalyzed hydrolysis favors attack at the phosphorous cite. Increasing the steric bulk at the at the reactive P center increases t1/2 at 20oC ...
... a the central phosphorous or carbon atoms resulting in a cleavage of the C-O or C-S bonds. Base-catalyzed hydrolysis favors attack at the phosphorous cite. Increasing the steric bulk at the at the reactive P center increases t1/2 at 20oC ...
Reductive etherification of substituted cyclohexanones with
... acid-catalysed conversion of the ketones to (hemi)acetals and consecutive Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV)-type hydride transfer to yield ethers. Until now two catalysts were always required to achieve this, i.e. a strong acid for the acetalisation and a transition metal for the reduction step.7,8 Var ...
... acid-catalysed conversion of the ketones to (hemi)acetals and consecutive Meerwein–Ponndorf–Verley (MPV)-type hydride transfer to yield ethers. Until now two catalysts were always required to achieve this, i.e. a strong acid for the acetalisation and a transition metal for the reduction step.7,8 Var ...
Functional Groups - Waterford Public Schools
... • The carbon of the -CN group is counted as part of the longest carbon chain • The -CN group always occupies the terminal position so no need to specify its position ...
... • The carbon of the -CN group is counted as part of the longest carbon chain • The -CN group always occupies the terminal position so no need to specify its position ...
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
... charge) away from itself into the rest of the molecule, increasing the electron density elsewhere in the molecule. This negative center facilitates a reaction with a positive reagent (electrophile). A EWG “pulls” electron density toward itself from the rest of the molecule, creating a positive cente ...
... charge) away from itself into the rest of the molecule, increasing the electron density elsewhere in the molecule. This negative center facilitates a reaction with a positive reagent (electrophile). A EWG “pulls” electron density toward itself from the rest of the molecule, creating a positive cente ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide
... cyclodecane and cyclooctane come next in ring strain. cyclopentane and heptane have very little ring strain cyclopentadecane and cyclohexane have almost no ring strain 3. angle strain makes up most of ring strain due to angles being less than the tetrahedral angles that are preferred cyclopropane is ...
... cyclodecane and cyclooctane come next in ring strain. cyclopentane and heptane have very little ring strain cyclopentadecane and cyclohexane have almost no ring strain 3. angle strain makes up most of ring strain due to angles being less than the tetrahedral angles that are preferred cyclopropane is ...
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES
... If the nucleophile that adds to the aldehyde or ketone is an O or an N, a nucleophilic addition–elimination reaction ...
... If the nucleophile that adds to the aldehyde or ketone is an O or an N, a nucleophilic addition–elimination reaction ...
reactions.html Reaction 1. Electrophilic addition of
... positively charged electrophile adds to the aromatic ring in the rate-limiting step; the resulting carbocation reverts to aromaticity by the loss of proton the relative reactivity and regiochemistry of the reaction on substituted benzene derivatives is governed by the nature of the substituent: the ...
... positively charged electrophile adds to the aromatic ring in the rate-limiting step; the resulting carbocation reverts to aromaticity by the loss of proton the relative reactivity and regiochemistry of the reaction on substituted benzene derivatives is governed by the nature of the substituent: the ...
lab 12 Multistep Synthesis of Benzilic acid
... fumes (red-‐brownish colored gas) are visible above the reaction mixture and gas bubbles are present on the stir bar. Reflux for at least 30 minutes, or until no more NO2 gas is apparent. Do not ...
... fumes (red-‐brownish colored gas) are visible above the reaction mixture and gas bubbles are present on the stir bar. Reflux for at least 30 minutes, or until no more NO2 gas is apparent. Do not ...
Phenols Like alcohols, phenols are starting materials for a wide
... Cannot readily replace the halide of aryl halides by -OH, since aryl halides are inert. The reaction can be performed in industry under high pressure and temperature: OH ...
... Cannot readily replace the halide of aryl halides by -OH, since aryl halides are inert. The reaction can be performed in industry under high pressure and temperature: OH ...
The Chemistry of Essential Oils - chemistryteaching / Chemistry
... Laboratory synthesized carvone would be a racemic mixture because there would be equal quantities of the (+) and (– )isomers or enantiomers (1). However, when an optically active compound is synthesised naturally – for example in a plant such as spearmint – only one of the enantiomers is formed. (1) ...
... Laboratory synthesized carvone would be a racemic mixture because there would be equal quantities of the (+) and (– )isomers or enantiomers (1). However, when an optically active compound is synthesised naturally – for example in a plant such as spearmint – only one of the enantiomers is formed. (1) ...
EXPERIMENT 5: Oxidation of Alcohols: Solid
... and secondary alcohols (and aldehydes) from tertiary alcohols (and ketones). The qualitative test involves the addition of a solution of CrO3 in sulfuric acid (Jones' Reagent) to a solution of the compound being tested in acetone. This reagent oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols and all aldehyde ...
... and secondary alcohols (and aldehydes) from tertiary alcohols (and ketones). The qualitative test involves the addition of a solution of CrO3 in sulfuric acid (Jones' Reagent) to a solution of the compound being tested in acetone. This reagent oxidizes primary and secondary alcohols and all aldehyde ...
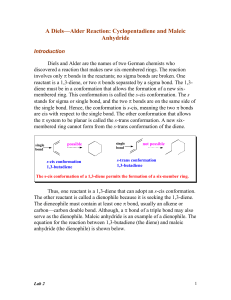
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.