File - the prayas tutorial
... Q. 6. Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Why ? Ans. Because Grignard reagents have a very strong affinity for H+ ions. In presence of water, they abstract H+ ions from water and form alkanes. To prevent this, they should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Q. 7. Hal ...
... Q. 6. Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Why ? Ans. Because Grignard reagents have a very strong affinity for H+ ions. In presence of water, they abstract H+ ions from water and form alkanes. To prevent this, they should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. Q. 7. Hal ...
Physical Organic Chemistry
... without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and nucleophilic substitution are similar in cases of affecting factors. Hence it’s a com ...
... without substituted with another atom or group. The elimination of HX molecule from alkyl derivatives. While X is a halogen or ester… etc. the hydrogen atom on adjacent carbon with X Elimination reactions and nucleophilic substitution are similar in cases of affecting factors. Hence it’s a com ...
Chapter 3. The Concept of Protecting Functional Groups
... protected substrate that is stable to the projected reactions. • The protecting group must be selectively removed in good yield by readily available reagents. • The protecting group should not have additional functionality that might provide additional sites of reaction. ...
... protected substrate that is stable to the projected reactions. • The protecting group must be selectively removed in good yield by readily available reagents. • The protecting group should not have additional functionality that might provide additional sites of reaction. ...
diazonium salt
... Whereas alkyl diazonium ions decompose under the conditions of their formation, aryl diazonium salts are stable enough to be stored in aqueous solution at 0–5°C for reasonable periods of time. Loss of nitrogen from an aryl diazonium ion generates an unstable aryl cation and is much slower than loss ...
... Whereas alkyl diazonium ions decompose under the conditions of their formation, aryl diazonium salts are stable enough to be stored in aqueous solution at 0–5°C for reasonable periods of time. Loss of nitrogen from an aryl diazonium ion generates an unstable aryl cation and is much slower than loss ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... (ROH) is weak but the leaving group (ROH) is good. Mechanism is totally as expected: •Protonation of alcohol (setting up good leaving group) •For 2o and 3o ionization to yield a carbocation with alkene formation as side product. Attack of nucleophile (second alcohol molecule) on carbocation. • For 1 ...
... (ROH) is weak but the leaving group (ROH) is good. Mechanism is totally as expected: •Protonation of alcohol (setting up good leaving group) •For 2o and 3o ionization to yield a carbocation with alkene formation as side product. Attack of nucleophile (second alcohol molecule) on carbocation. • For 1 ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... - How to calculate K from Go ( also see later under A values) Conformational analysis of cyclic compounds - cyclohexanes, chair, boat, twist conformations - proof Substituted cyclohexanes - ‘A’ values of various groups - how to determine ‘A’ values Conformational effects on reactivity - oxidation o ...
... - How to calculate K from Go ( also see later under A values) Conformational analysis of cyclic compounds - cyclohexanes, chair, boat, twist conformations - proof Substituted cyclohexanes - ‘A’ values of various groups - how to determine ‘A’ values Conformational effects on reactivity - oxidation o ...
ch07 by Dr. Dina
... An E2 Reaction Primary alcohols cannot undergo E1 dehydration because of the instability of the carbocation-like transition state in the 2nd step In the E2 dehydration the first step is again protonation of the hydroxyl to yield the good leaving group water ...
... An E2 Reaction Primary alcohols cannot undergo E1 dehydration because of the instability of the carbocation-like transition state in the 2nd step In the E2 dehydration the first step is again protonation of the hydroxyl to yield the good leaving group water ...
Lab 7
... Oxidation reactions involve the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen. First, we shall learn to identify structures that can undergo oxidation. Then, we shall learn the reagents that can oxidize the structures. Oxidation reactions require an “activated” carbon atom such as that shown in Figu ...
... Oxidation reactions involve the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen. First, we shall learn to identify structures that can undergo oxidation. Then, we shall learn the reagents that can oxidize the structures. Oxidation reactions require an “activated” carbon atom such as that shown in Figu ...
314_lect_26_tosyl_SN..
... This mechanism is not possible at tetravalent carbon (sp3) because carbon cannot bond to five groups or have more than eight electrons in its valence. However, there is a similar mechanism at carbon where trivalent carbon (sp2) of an acid chloride becomes tetravalent (sp3) in an intermediate and the ...
... This mechanism is not possible at tetravalent carbon (sp3) because carbon cannot bond to five groups or have more than eight electrons in its valence. However, there is a similar mechanism at carbon where trivalent carbon (sp2) of an acid chloride becomes tetravalent (sp3) in an intermediate and the ...
Aldehydes and Ketones Both contain the functional group C O
... Of the two reducing agents, sodium borohydride is the milder reagent and is the one of preference for aldehydes and ketones since it is specific for these two functional groups. Lithium aluminum hydride will reduce many types of compounds very quickly. Reduction to hydrocarbons (we saw this used to ...
... Of the two reducing agents, sodium borohydride is the milder reagent and is the one of preference for aldehydes and ketones since it is specific for these two functional groups. Lithium aluminum hydride will reduce many types of compounds very quickly. Reduction to hydrocarbons (we saw this used to ...
File
... The properties of alcohols are a function of the hydrogen bonding associated with the highly polar "OH" bond. Short chain alcohols like methanol, ethanol, and propanols have the unique property of being soluble in nonpolar and polar solvents. This makes them very useful for cleaning oily materials. ...
... The properties of alcohols are a function of the hydrogen bonding associated with the highly polar "OH" bond. Short chain alcohols like methanol, ethanol, and propanols have the unique property of being soluble in nonpolar and polar solvents. This makes them very useful for cleaning oily materials. ...
constitutional isomers
... that no two are the same is to name them all. If the names are different, the isomers are different. If the names are the same, you drew the same thing twice. Nomenclature also makes it easier for us to talk about organic chemistry in situations where we can’t just draw the molecules. Nomenclature i ...
... that no two are the same is to name them all. If the names are different, the isomers are different. If the names are the same, you drew the same thing twice. Nomenclature also makes it easier for us to talk about organic chemistry in situations where we can’t just draw the molecules. Nomenclature i ...
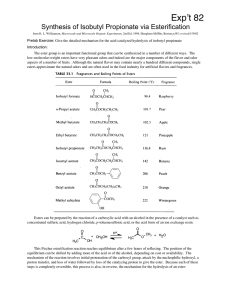
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
... we can, by Le Chatelier's principle, increase the concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester ...
Organic Chemistry
... 1. Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. 2. Hydrocarbons are compounds of C and H. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, CH4, which is used for heating and in gas stoves for cooking. 3. Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds. (Saturated means “full.” Saturated hydrocar ...
... 1. Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. 2. Hydrocarbons are compounds of C and H. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, CH4, which is used for heating and in gas stoves for cooking. 3. Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds. (Saturated means “full.” Saturated hydrocar ...
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS 1 ORGANIC
... only), acid-catalyzed hydration (both), hydroboration (both), acetylide anion formation/ alkylation (alkynes only) While there are no multiple choice or fill-in-the-blank questions on the exam, answering the following review questions will help assess your understanding of the concepts above and you ...
... only), acid-catalyzed hydration (both), hydroboration (both), acetylide anion formation/ alkylation (alkynes only) While there are no multiple choice or fill-in-the-blank questions on the exam, answering the following review questions will help assess your understanding of the concepts above and you ...
N-METAL COMPOUNDS
... n the 85 years following Kekulk's brilliant proposal for the structure of benzene, organic chemistry underwent a tremendous expansion, and in the process a wide variety of paradigms or working hypotheses were developed about what kinds of compounds could "exist" and what kinds of reactions could occ ...
... n the 85 years following Kekulk's brilliant proposal for the structure of benzene, organic chemistry underwent a tremendous expansion, and in the process a wide variety of paradigms or working hypotheses were developed about what kinds of compounds could "exist" and what kinds of reactions could occ ...
- University at Albany
... Also, alkyl halide reactivity decreases from methyl to 10 to 20 to 30. In fact, 30 alkyl halides do not react by SN2. Leaving group: The substrate should have a good leaving group. A good leaving group should be electron withdrawing, relatively stable, and polarizable. They are weak bases. Examples ...
... Also, alkyl halide reactivity decreases from methyl to 10 to 20 to 30. In fact, 30 alkyl halides do not react by SN2. Leaving group: The substrate should have a good leaving group. A good leaving group should be electron withdrawing, relatively stable, and polarizable. They are weak bases. Examples ...
Alcohols from Alkenes: Oxymercuration–Demercuration
... Mechanism of Oxymercuration–Demercuration ...
... Mechanism of Oxymercuration–Demercuration ...
Functional Groups
... Properties of Alcohols Compared to alkenes alcohols have higher boiling points. This is explained by the OH group which allows hydrogen bonding. This functional group also makes alcohols polar which allows simple (small) alcohols to dissolve in water. Long chain alcohols act as nonpolar molecules ma ...
... Properties of Alcohols Compared to alkenes alcohols have higher boiling points. This is explained by the OH group which allows hydrogen bonding. This functional group also makes alcohols polar which allows simple (small) alcohols to dissolve in water. Long chain alcohols act as nonpolar molecules ma ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
PTT102 Aldehydes and Ketones
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
... 1. Claisen Condensation Condensation of Two Ester Molecules. The product of a Claisen condensation is a βketo ester. In a Claisen condensation, one molecule of carbonyl compound is the nucleophile and second molecule is electrophile. The new C-C bond connect the α-carbon of one molecule and t ...
5-3 - U of L Class Index
... They are classified based on the carbon the halogen is attached to If the carbon is attached to one other carbon that carbon is primary (1o) and the alkyl halide is also 1o If the carbon is attached to two other carbons, that carbon is secondary (2o) and the alkyl halide is 2o If the carbon is ...
... They are classified based on the carbon the halogen is attached to If the carbon is attached to one other carbon that carbon is primary (1o) and the alkyl halide is also 1o If the carbon is attached to two other carbons, that carbon is secondary (2o) and the alkyl halide is 2o If the carbon is ...
File
... • There are only single covalent bonds between the carbon atoms. • Each successive member of the alkane series differs from the next by a CH2 group. • Successive members are similar in structure but differ in formula. The general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2 If n = 7 formula = C7H16 ...
... • There are only single covalent bonds between the carbon atoms. • Each successive member of the alkane series differs from the next by a CH2 group. • Successive members are similar in structure but differ in formula. The general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2 If n = 7 formula = C7H16 ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.