Chapter 10 for 301
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
ETHERS
... Except for the epoxides, ethers do not undergo nucleophilic substitution without prior protonation: alkoxide ion is a very poor leaving group. ...
... Except for the epoxides, ethers do not undergo nucleophilic substitution without prior protonation: alkoxide ion is a very poor leaving group. ...
Organic Chemistry I Mario Lintz 1st Year MD/PhD Candidate Mario
... 3) Number the substituents and write the name 4) Start at point of attachment and number so that subsequent substituents have the lowest # assignment 5) If two or more different alkyl groups are present, number them by alphabetic priority 6) If halogens are present, treat them like alkyl groups 7) C ...
... 3) Number the substituents and write the name 4) Start at point of attachment and number so that subsequent substituents have the lowest # assignment 5) If two or more different alkyl groups are present, number them by alphabetic priority 6) If halogens are present, treat them like alkyl groups 7) C ...
Naming Ethers Naming Ethers
... • Skunks use thiols as a defense mechanism: (E)-2butene-1-thiol, 3-methyl-1-butanethiol, and 2quinolinemethanethiol, and acetate thioesters of these. • Methanethiol is added to natural gas (methane) so that gas leaks can be detected. • The hydrosulfide ion (HS–) is a strong nucleophile and a weak ...
... • Skunks use thiols as a defense mechanism: (E)-2butene-1-thiol, 3-methyl-1-butanethiol, and 2quinolinemethanethiol, and acetate thioesters of these. • Methanethiol is added to natural gas (methane) so that gas leaks can be detected. • The hydrosulfide ion (HS–) is a strong nucleophile and a weak ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 - Snow College | It's SNOWing
... same carbon, use the number twice. When two or more substituents are identical, use prefixes When two chains are the same length, use the one with the most substituents on it. If substituents are at equall distances from the ends of the chain, go to the next substituent. Iso and cyclo are included a ...
... same carbon, use the number twice. When two or more substituents are identical, use prefixes When two chains are the same length, use the one with the most substituents on it. If substituents are at equall distances from the ends of the chain, go to the next substituent. Iso and cyclo are included a ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon ...
... Arene (Ar-H) is the generic term for an aromatic hydrocarbon ...
OCR_Organic_Chemistry_AS_summary
... • Small chain alcohols dissolve easily into water • Longer chain alcohols are less soluble, there is a decrease in solubility as the chain length increases. • Whilst smaller alcohols form hydrogen bonds with the water molecules, compensating for the hydrogen bonds broken, larger alcohols break more ...
... • Small chain alcohols dissolve easily into water • Longer chain alcohols are less soluble, there is a decrease in solubility as the chain length increases. • Whilst smaller alcohols form hydrogen bonds with the water molecules, compensating for the hydrogen bonds broken, larger alcohols break more ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from benzene and a bromine cation The intermediate is not aromatic and therefore high in energy ...
... FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from benzene and a bromine cation The intermediate is not aromatic and therefore high in energy ...
Electophilic Aromatic Substituion
... FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from benzene and a bromine cation The intermediate is not aromatic and therefore high in energy ...
... FeBr3 is added as a catalyst to polarize the bromine reagent In the first step the electrons act as a nucleophile toward Br2 (in a complex with FeBr3) This forms a cationic addition intermediate from benzene and a bromine cation The intermediate is not aromatic and therefore high in energy ...
Stereoselective Reduction of Ketones with Sodium Borohydride
... – The carbon atoms is nuclophilic – Widely used to make new carbon-carbon bonds – Used to attach carbonyl groups of aldehydes, ketones, and ...
... – The carbon atoms is nuclophilic – Widely used to make new carbon-carbon bonds – Used to attach carbonyl groups of aldehydes, ketones, and ...
Lecture 18
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 8
... can't shift e- pair and empty orbital at the same time anyway V. Stereochemistry of Reactions ...
... can't shift e- pair and empty orbital at the same time anyway V. Stereochemistry of Reactions ...
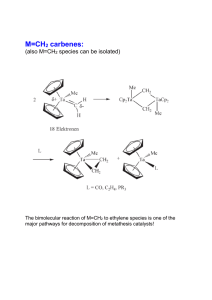
Steric protection of alkylidene is not needed:
... - X should NOT be O (dimer formation) but NR with large R group - other substituents should be electron-withdrawing (important for alkene coordination) ...
... - X should NOT be O (dimer formation) but NR with large R group - other substituents should be electron-withdrawing (important for alkene coordination) ...
無投影片標題
... m.p. and b.p. increase in the order: RCH2F < RCH2Cl < RCH2Br < RCH2I ∵ larger, more polarizable halogen atoms increase the dipole-dipole interactions between the molecules No. of carbon m.p. and b.p. ...
... m.p. and b.p. increase in the order: RCH2F < RCH2Cl < RCH2Br < RCH2I ∵ larger, more polarizable halogen atoms increase the dipole-dipole interactions between the molecules No. of carbon m.p. and b.p. ...
Practice Problem
... • Reaction distinction is more selective with bromine than chlorine • Reaction with Br. is much less exergonic • T.Sbromination resembles the alkyl radical more closely than does T.Schlorination ...
... • Reaction distinction is more selective with bromine than chlorine • Reaction with Br. is much less exergonic • T.Sbromination resembles the alkyl radical more closely than does T.Schlorination ...
Ch. 09 Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides
... Reaction of Ethers with Strong Acid • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. • HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleo ...
... Reaction of Ethers with Strong Acid • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. • HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleo ...
ALDOL CONDENSATION
... independently published on this topic in 1880 and 1881. An example is the synthesis of dibenzylideneacetone. MECHANISM: The first part of this reaction is an aldol reaction, the second part a dehydration—an elimination reaction. Dehydration may be accompanied by decarboxylation when an activat ...
... independently published on this topic in 1880 and 1881. An example is the synthesis of dibenzylideneacetone. MECHANISM: The first part of this reaction is an aldol reaction, the second part a dehydration—an elimination reaction. Dehydration may be accompanied by decarboxylation when an activat ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... 1. (a) Lower value of bond dissociation energy of F 2 is due to strong repulsion between the non bonding elements of F atom in F2 molecule.( 1) (b)Due to the absence of the d- orbitals, multiple bonding cannot occour(1). 2. Shape selective catalysis is a chemical reaction in which the rate depends ...
... 1. (a) Lower value of bond dissociation energy of F 2 is due to strong repulsion between the non bonding elements of F atom in F2 molecule.( 1) (b)Due to the absence of the d- orbitals, multiple bonding cannot occour(1). 2. Shape selective catalysis is a chemical reaction in which the rate depends ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Notes Sheet
... • These destabilizing effects, angle strain and torsional strain are known together as ring strain. • The smaller cycloalkanes, cyclopropane and cyclobutane, have particularly high ring strains because their bond angles deviate substantially from 109.5° and their hydrogens eclipse each other. • Cycl ...
... • These destabilizing effects, angle strain and torsional strain are known together as ring strain. • The smaller cycloalkanes, cyclopropane and cyclobutane, have particularly high ring strains because their bond angles deviate substantially from 109.5° and their hydrogens eclipse each other. • Cycl ...
KINETIC AND MECHANISTIC STUDY OF OXIDATION OF ESTER
... negligible effect on the rate. For reactions in solution the nature of solvent plays an important role which has been discussed in detail by Aims . In present investigation, effect of solvent could not be studies because of reactivity of solvent such as alcohol ...
... negligible effect on the rate. For reactions in solution the nature of solvent plays an important role which has been discussed in detail by Aims . In present investigation, effect of solvent could not be studies because of reactivity of solvent such as alcohol ...
Lecture 18
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
... to be reasonable soluble in water so that it can be transported through the blood. Since amines are weak bases, they are often converted to salts with some acid and therefore may oral drugs have amine salts as part of their structure. One reason for their presence is that they confer some water solu ...
chapter 8 lecture
... formed. The slow step is unimolecular, involving only the alkyl halide. • The E1 and E2 mechanisms both involve the same number of bonds broken and formed. The only difference is timing. In an E1, the leaving group comes off before the proton is removed, and the reaction occurs in two steps. In an ...
... formed. The slow step is unimolecular, involving only the alkyl halide. • The E1 and E2 mechanisms both involve the same number of bonds broken and formed. The only difference is timing. In an E1, the leaving group comes off before the proton is removed, and the reaction occurs in two steps. In an ...
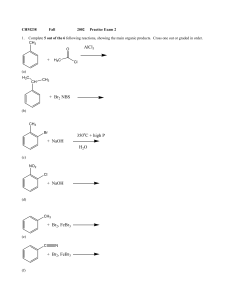
+ NaOH 350 C + high P H2O + H3C AlCl3 + NaOH + Br2, FeBr3
... (b) What is the reactive electrophile in the above reaction? ...
... (b) What is the reactive electrophile in the above reaction? ...
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement

The Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement (TDR) is the chemical reaction of a 1-aminomethyl-cycloalkanol with nitrous acid to form an enlarged cycloketone.The Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion, Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement, or TDR, provides an easy way to increase amino-substituted cycloalkanes and cycloalkanols in size by one carbon. Ring sizes from cyclopropane through cyclooctane are able to undergo Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion with some degree of success. Yields decrease as initial ring size increases, and the ideal use of TDR is for synthesis of five, six, and seven membered rings. A principal synthetic application of Tiffeneau–Demjanov ring expansion is to bicyclic or polycyclic systems. Several reviews on this reaction have been published.