Document
... Definition- materials capable of reversible change in length at operating temperatures, that is, once a load is removed the material returns to its original dimensions; a rubbery compound; Generally amorphous thermosets with Tg below room temperature to allow full chain mobility- the restoring force ...
... Definition- materials capable of reversible change in length at operating temperatures, that is, once a load is removed the material returns to its original dimensions; a rubbery compound; Generally amorphous thermosets with Tg below room temperature to allow full chain mobility- the restoring force ...
Phenol - Macmillan Academy
... Sodium phenol reacts with sodium to form an ionic salt - sodium phenoxide hydrogen is also produced this reaction is similar to that with aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol 2C6H5OH(s) ...
... Sodium phenol reacts with sodium to form an ionic salt - sodium phenoxide hydrogen is also produced this reaction is similar to that with aliphatic alcohols such as ethanol 2C6H5OH(s) ...
Full Text - Journal of the Indian Institute of Science
... from formamides, primary amides and nitroalkanes, respectively. The most noteworthy application has been in the cyclodehydration of hydroxy amides and thioamides to afford the corresponding heterocycles. Because of the mild conditions required as well as the selectivity observed, the reagent has rec ...
... from formamides, primary amides and nitroalkanes, respectively. The most noteworthy application has been in the cyclodehydration of hydroxy amides and thioamides to afford the corresponding heterocycles. Because of the mild conditions required as well as the selectivity observed, the reagent has rec ...
10.1 Intro to Organic Chemistry 10.1 Organic Chemistry
... 10.1.7 Deduce structural formulas for the isomers of the straightchain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.8 Apply IUPAC rules for naming the isomers of the straight-chain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.9 Deduce structural formulas for compounds containing up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional grou ...
... 10.1.7 Deduce structural formulas for the isomers of the straightchain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.8 Apply IUPAC rules for naming the isomers of the straight-chain alkenes up to C6. 10.1.9 Deduce structural formulas for compounds containing up to six carbon atoms with one of the following functional grou ...
08.Carboxylic acids. Functional derivates of carboxylic acids
... groups take precedence over double bonds, and double bonds take precedence over halogens and alkyl groups, in naming compounds. Carboxylic acids outrank all the common groups we have encountered to this point. Double bonds in the main chain are signaled by the ending -enoic acid, and their position ...
... groups take precedence over double bonds, and double bonds take precedence over halogens and alkyl groups, in naming compounds. Carboxylic acids outrank all the common groups we have encountered to this point. Double bonds in the main chain are signaled by the ending -enoic acid, and their position ...
Organic Chemistry - UCR Chemistry
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
... We can prevent this by using modified Cr(VI) reagents that we describe later in this section. We can also distill the intermediate aldehyde from the reaction mixture as it forms before it is oxidized further. This is often possible because boiling points of aldehydes are usually much lower than thos ...
CHEM 494 Lecture 5 - UIC Department of Chemistry
... 2.Follow all previous rules and conventions for naming/numbering alkane chains. 3.Name the compound according to the figure below. Conventions: •Previous conventions apply (e.g., first point of difference rule). •Halogens and alkyl groups are considered to have equal rank when deciding numbering. If ...
... 2.Follow all previous rules and conventions for naming/numbering alkane chains. 3.Name the compound according to the figure below. Conventions: •Previous conventions apply (e.g., first point of difference rule). •Halogens and alkyl groups are considered to have equal rank when deciding numbering. If ...
Microsoft Word
... under H2 atmosphere and/or at room temperature have higher activity than that stored under air and/or in refrigerator. iv) The catalyst stored in deionised distilled water has higher activity than that stored in 95% ethanol and 5% aqueous NaOH. The catalyst prepared at the optimum conditions gave th ...
... under H2 atmosphere and/or at room temperature have higher activity than that stored under air and/or in refrigerator. iv) The catalyst stored in deionised distilled water has higher activity than that stored in 95% ethanol and 5% aqueous NaOH. The catalyst prepared at the optimum conditions gave th ...
A Convenient Synthesis of Amino Acid Methyl Esters
... 15]. This method has been used in the transformation of N-Boc-α-amino acids into N-unprotected αamino methyl esters [16] and some other amino acid methyl esters have been prepared using this system [17-20]. In order to demonstrate the general applicability of the method, we have examined a series of ...
... 15]. This method has been used in the transformation of N-Boc-α-amino acids into N-unprotected αamino methyl esters [16] and some other amino acid methyl esters have been prepared using this system [17-20]. In order to demonstrate the general applicability of the method, we have examined a series of ...
cleavage of methyl ethers with iodotrimethylsilane
... 5. The product is sometimes contaminated with a small amount of hexamethyldisiloxane. The amount of this contaminant is minimized by using longer reaction times and by careful handling to avoid contact with atmospheric moisture. The product may become discolored during storage, in which case it may ...
... 5. The product is sometimes contaminated with a small amount of hexamethyldisiloxane. The amount of this contaminant is minimized by using longer reaction times and by careful handling to avoid contact with atmospheric moisture. The product may become discolored during storage, in which case it may ...
Amines, Amides, & Amino Acids
... • General Format: RNH2 • -NH2 = amino group (Remember, N has a bonding capacity of 3.) • Since molecules can contain H bonded to N, hydrogen bonding occurs, but it is weaker than hydrogen bonding in alcohols and carboxylic ...
... • General Format: RNH2 • -NH2 = amino group (Remember, N has a bonding capacity of 3.) • Since molecules can contain H bonded to N, hydrogen bonding occurs, but it is weaker than hydrogen bonding in alcohols and carboxylic ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... The term nucleophile is more fundamental than the term base. A nucleophile is a species with an electron pair that uses that electron pair to form a new chemical bond to the atom it attacks. Based on this definition, you can see that ethoxide ion, as well as ethanol, serve as nucleophiles in both su ...
... The term nucleophile is more fundamental than the term base. A nucleophile is a species with an electron pair that uses that electron pair to form a new chemical bond to the atom it attacks. Based on this definition, you can see that ethoxide ion, as well as ethanol, serve as nucleophiles in both su ...
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones – Nucleophilic Addition
... Ketones are less susceptible than aldehydes to attack by nucleophiles, so aldol additions occur more slowly with ketones. With ketones, the reaction proceeds well only if the product is removed from the basic solution or reacts further by dehydration. ...
... Ketones are less susceptible than aldehydes to attack by nucleophiles, so aldol additions occur more slowly with ketones. With ketones, the reaction proceeds well only if the product is removed from the basic solution or reacts further by dehydration. ...
Chapter 1.4 Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols
... Alcohol, Primary Alcohol, Secondary Alcohol, Tertiary Alcohol, Phenol, Thiols, Ether ...
... Alcohol, Primary Alcohol, Secondary Alcohol, Tertiary Alcohol, Phenol, Thiols, Ether ...
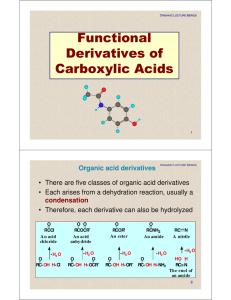
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
... Reactions with Organolithium Organolithium compounds are even more powerful nucleophiles than Grignard reagents – they react with esters to give the same types of 2°and 3°alcohols as do Grignard reagents – and often in higher yields O RCOCH3 ...
... Reactions with Organolithium Organolithium compounds are even more powerful nucleophiles than Grignard reagents – they react with esters to give the same types of 2°and 3°alcohols as do Grignard reagents – and often in higher yields O RCOCH3 ...
Esters amines and amides
... In amides, • an amino group(–NH2) replaces the –OH group of carboxylic acids. • The aromatic amine is benzamide. ...
... In amides, • an amino group(–NH2) replaces the –OH group of carboxylic acids. • The aromatic amine is benzamide. ...
Scheme A Topic Checklist Atomic Structure 1.1
... and carboxylic acids limited to chains with up to 6 carbon atoms Ethanol production know how ethanol is produced industrially by fermentation know the conditions for this reaction and understand the economic and environmental advantages and disadvantages of this process compared with the industrial ...
... and carboxylic acids limited to chains with up to 6 carbon atoms Ethanol production know how ethanol is produced industrially by fermentation know the conditions for this reaction and understand the economic and environmental advantages and disadvantages of this process compared with the industrial ...
Chapter 24. Amines
... Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
... Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
1 This is the pre-review version of the paper published in Journal of
... hydrogens relative to regular C-H hydrogens) reported. The gas-phase acidity of phenol (excluding vibrational effects) is 34.8 kcal.mol-1 higher than that of methanol. Incorporation of vinyl units between the aromatic ring and the OH group enhances the acidity of the OH group, as expected from the i ...
... hydrogens relative to regular C-H hydrogens) reported. The gas-phase acidity of phenol (excluding vibrational effects) is 34.8 kcal.mol-1 higher than that of methanol. Incorporation of vinyl units between the aromatic ring and the OH group enhances the acidity of the OH group, as expected from the i ...
Chapter 24. Amines - Houston Community College System
... Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
... Most amines that have 3 different substituents on N are not resolved because the molecules interconvert by pyramidal inversion ...
What is a protecting group?
... functional group in a poly-functional molecule. (b) It should be stable / resistant to the reagents employed in subsequent reaction steps in which the group being masked (protected) is desired to remain deactivated (protected). (c) It should be capable of being selectively removed under mild conditi ...
... functional group in a poly-functional molecule. (b) It should be stable / resistant to the reagents employed in subsequent reaction steps in which the group being masked (protected) is desired to remain deactivated (protected). (c) It should be capable of being selectively removed under mild conditi ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.