Carbohydrates
... Cyclic forms of monosaccharides • Aldoses form rings that have the same number of members in the ring as there are carbons in the sugar. • Ketoses form rings that have one fewer members than the number of carbons in the sugar. • Cyclic monosaccharides containing six members are called pryanoses, si ...
... Cyclic forms of monosaccharides • Aldoses form rings that have the same number of members in the ring as there are carbons in the sugar. • Ketoses form rings that have one fewer members than the number of carbons in the sugar. • Cyclic monosaccharides containing six members are called pryanoses, si ...
Chemistry XII - Kendriya Vidyalaya IIM,Lucknow
... properties of ore components. If either of ore or gangue is capable of attracted by a magnet field, then such separation is carried out. 7. Concentration by Froth Flotation Process is based on the facts that sulphide ore is wetted by oil & gangue particles are wetted by water. 8. Concentration by Le ...
... properties of ore components. If either of ore or gangue is capable of attracted by a magnet field, then such separation is carried out. 7. Concentration by Froth Flotation Process is based on the facts that sulphide ore is wetted by oil & gangue particles are wetted by water. 8. Concentration by Le ...
Organic Chemistry, 11th Edition
... Founded in 1807, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. has been a valued source of knowledge and understanding for more than 200 years, helping people around the world meet their needs and fulfill their aspirations. Our company is built on a foundation of principles that include responsibility to the communities ...
... Founded in 1807, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. has been a valued source of knowledge and understanding for more than 200 years, helping people around the world meet their needs and fulfill their aspirations. Our company is built on a foundation of principles that include responsibility to the communities ...
Chapter 16_CHEM 131
... • The N-H bond is not quite as polar as the O-H bond. • Primary and secondary amines can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. • The hydrogen bonds are not as strong as those of alcohols, so amine boiling points are somewhat lower than those of alcohols. • Simple, low molecular weight amines are ga ...
... • The N-H bond is not quite as polar as the O-H bond. • Primary and secondary amines can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. • The hydrogen bonds are not as strong as those of alcohols, so amine boiling points are somewhat lower than those of alcohols. • Simple, low molecular weight amines are ga ...
Lecture - Ch 18
... Oxidation of Thiols • Sulfides are easily oxidized by treatment with hydrogen peroxide at room temperature – Yields sulfoxide – Further oxidation of the sulfoxide with a peroxyacid yields a sulfone ...
... Oxidation of Thiols • Sulfides are easily oxidized by treatment with hydrogen peroxide at room temperature – Yields sulfoxide – Further oxidation of the sulfoxide with a peroxyacid yields a sulfone ...
Nucleophilic Additions to Carbonyl Group
... Because the oxygen is more electronegative than the carbon, it possesses the greater share of the electron density of both the σ and π bonds. Thus, the carbon has a partial positive charge, and the oxygen a partial negative charge. The difference in electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen gi ...
... Because the oxygen is more electronegative than the carbon, it possesses the greater share of the electron density of both the σ and π bonds. Thus, the carbon has a partial positive charge, and the oxygen a partial negative charge. The difference in electronegativity between the carbon and oxygen gi ...
Chapter 12 Organic Compounds with Oxygen and Sulfur
... In Tollens’ test, • Tollens’ reagent, which contains Ag+, oxidizes aldehydes but not ketones. • Ag+ is reduced to metallic Ag, which appears as a “mirror” in the test tube. ...
... In Tollens’ test, • Tollens’ reagent, which contains Ag+, oxidizes aldehydes but not ketones. • Ag+ is reduced to metallic Ag, which appears as a “mirror” in the test tube. ...
INTRODUCING PHENOL
... However, for compounds containing benzene rings, combustion is hardly ever complete, especially if they are burnt in air. The high proportion of carbon in phenol means that you need a very high proportion of oxygen to phenol to get complete combustion. Look at the equation. As a general rule, the hy ...
... However, for compounds containing benzene rings, combustion is hardly ever complete, especially if they are burnt in air. The high proportion of carbon in phenol means that you need a very high proportion of oxygen to phenol to get complete combustion. Look at the equation. As a general rule, the hy ...
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
... (i) First identifying the parent chain that contains most, if not all, the carboxyl groups. (ii) Number the parent chain from the carbon of the carboxyl group i.e the carboxyl carbon is C-1. (iii) Identify the substituents and assign each substituent a locator/address number (2,3,4…etc.) consistent ...
... (i) First identifying the parent chain that contains most, if not all, the carboxyl groups. (ii) Number the parent chain from the carbon of the carboxyl group i.e the carboxyl carbon is C-1. (iii) Identify the substituents and assign each substituent a locator/address number (2,3,4…etc.) consistent ...
Lecture - Ch 19
... • A few simple and well-known aldehydes have common names recognized by IUPAC ...
... • A few simple and well-known aldehydes have common names recognized by IUPAC ...
幻灯片 1
... • Regiochemistry of Elimination of Alkyl Halides- Zaitsev’s Rule • What products result from loss of HX from an unsymmetrical halide? According to a rule of formulated in 1875 by the Russian chemist Alexander Zaitsev, base-induced elimination reactions generally give the ...
... • Regiochemistry of Elimination of Alkyl Halides- Zaitsev’s Rule • What products result from loss of HX from an unsymmetrical halide? According to a rule of formulated in 1875 by the Russian chemist Alexander Zaitsev, base-induced elimination reactions generally give the ...
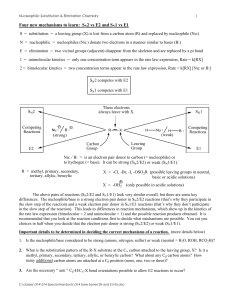
Four new mechanisms to learn: SN2 vs E2 and SN1 vs E1
... SN1 and E1 Competition – Multistep Reactions SN1 and E1 reactions are multistep reactions and also compete with one another. Both of these reactions begin with the same rate-limiting step of carbocation formation from an R-X compound. Carbocations (R+) are very reactive electron deficient carbon int ...
... SN1 and E1 Competition – Multistep Reactions SN1 and E1 reactions are multistep reactions and also compete with one another. Both of these reactions begin with the same rate-limiting step of carbocation formation from an R-X compound. Carbocations (R+) are very reactive electron deficient carbon int ...
OC 2/e Ch 15
... like alcohols, add to the C=O of aldehydes and ketones to give tetrahedral carbonyl addition products The sulfur atom of a thiol is a better nucleophile than the oxygen atom of an alcohol A common sulfur nucleophile used for this purpose is 1,3-propanedithiol • the product is a 1,3-dithiane O ...
... like alcohols, add to the C=O of aldehydes and ketones to give tetrahedral carbonyl addition products The sulfur atom of a thiol is a better nucleophile than the oxygen atom of an alcohol A common sulfur nucleophile used for this purpose is 1,3-propanedithiol • the product is a 1,3-dithiane O ...
4.7 Preparation of Alkyl Halides from Alcohols and Hydrogen
... Reaction of Primary Alcohols with Hydrogen Halides. ...
... Reaction of Primary Alcohols with Hydrogen Halides. ...
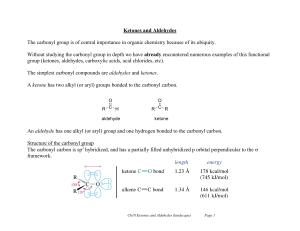
Ketones and Aldehydes
... In ketones the two alkyl substituents create more steric hindrance than the single substituent that aldehydes have. Therefore ketones offer more steric resistance to nucleophilic attack. (Aldehydes more reactive than ketones). Therefore both factors make aldehydes more reactive than ketones. ...
... In ketones the two alkyl substituents create more steric hindrance than the single substituent that aldehydes have. Therefore ketones offer more steric resistance to nucleophilic attack. (Aldehydes more reactive than ketones). Therefore both factors make aldehydes more reactive than ketones. ...
chm121 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... The following are common drying agent for organic solutions but which of them has high capacity, fast speed, and good efficiency as its chemical property. (a) CaSO4 (b) CaCl 2 (c) K2CO3 (d) MgSO4 All except ------------- is not employed as an adsorbents in column chromatography (a) Starch (b) Silica ...
... The following are common drying agent for organic solutions but which of them has high capacity, fast speed, and good efficiency as its chemical property. (a) CaSO4 (b) CaCl 2 (c) K2CO3 (d) MgSO4 All except ------------- is not employed as an adsorbents in column chromatography (a) Starch (b) Silica ...
Chapter 19. Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition Reactions
... produced artificially, and also occurring naturally in beet-root molasses and its residues. The listed pronunciation indicates it has the exact same emphasis as “cocaine”. Cocaine \Co"ca*ine\, n. (Chem.) A powerful alkaloid, {C17H21NO4}, obtained from the leaves of coca So – if you say “co-ca-ee ...
... produced artificially, and also occurring naturally in beet-root molasses and its residues. The listed pronunciation indicates it has the exact same emphasis as “cocaine”. Cocaine \Co"ca*ine\, n. (Chem.) A powerful alkaloid, {C17H21NO4}, obtained from the leaves of coca So – if you say “co-ca-ee ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.