Unit 2
... that is _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ by an industrial process called _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. To start with, liquid crude oil is fed into a _ _ _ _ _ _ where it is vaporized. The _ _ _ mixture of gases then passes into a fractionating _ _ _ _ _ _ and begins its journey upwards from the hott ...
... that is _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ by an industrial process called _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. To start with, liquid crude oil is fed into a _ _ _ _ _ _ where it is vaporized. The _ _ _ mixture of gases then passes into a fractionating _ _ _ _ _ _ and begins its journey upwards from the hott ...
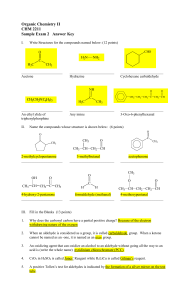
Organic Chemistry II CHM 2211 Sample Exam 2 Answer Key
... When an aldehyde is considered as a group, it is called carbaldehyde group. When a ketone cannot be named as an -one, it is named as an oxo- group. ...
... When an aldehyde is considered as a group, it is called carbaldehyde group. When a ketone cannot be named as an -one, it is named as an oxo- group. ...
Scope and Limitations - Organic Reactions Wiki
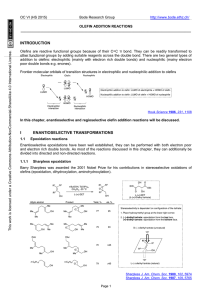
... Osmium tetroxide has since established itself as the reagent of choice for the syndihydroxylation of olefins, primarily because of its inertness toward other functional groups and lack of over-oxidation products.4 Researchers from the UpJohn company reported a convenient and reliable procedure for ...
... Osmium tetroxide has since established itself as the reagent of choice for the syndihydroxylation of olefins, primarily because of its inertness toward other functional groups and lack of over-oxidation products.4 Researchers from the UpJohn company reported a convenient and reliable procedure for ...
Unit 13: Organic Chemistry
... International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Naming System The steps in the IUPAC naming system are as follow: 1. The number of carbons in the longest continuous unbroken chain is used to determine the prefix of the parent molecule name. The longest continuous chain may look like it b ...
... International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Naming System The steps in the IUPAC naming system are as follow: 1. The number of carbons in the longest continuous unbroken chain is used to determine the prefix of the parent molecule name. The longest continuous chain may look like it b ...
Chapter-16B
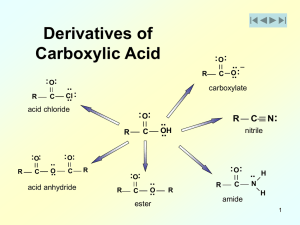
... Esters are hydrolyzed only slowly, even in boiling water Hydrolysis becomes more rapid if they are heated with either aqueous acid or aqueous base Hydrolysis in aqueous acid is the reverse of Fischer esterification O R ...
... Esters are hydrolyzed only slowly, even in boiling water Hydrolysis becomes more rapid if they are heated with either aqueous acid or aqueous base Hydrolysis in aqueous acid is the reverse of Fischer esterification O R ...
研 究 業 績 リ ス ト
... (92) Ruthenium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization of 3-Butyne-1,2-diols into Furans Y. Yada, Y. Miyake, and Y. Nishibayashi Org. Lett., to be submitted. (93) Novel Monophosphido-Bridged Diruthenium Complexes: Efficient Preparative Method and Their Catalytic Activity toward Condensation of Aldehyde ...
... (92) Ruthenium-Catalyzed Intramolecular Cyclization of 3-Butyne-1,2-diols into Furans Y. Yada, Y. Miyake, and Y. Nishibayashi Org. Lett., to be submitted. (93) Novel Monophosphido-Bridged Diruthenium Complexes: Efficient Preparative Method and Their Catalytic Activity toward Condensation of Aldehyde ...
CH3
... Much less POLAR than alcohols Slightly soluble in water More soluble than alkane Lower melting point (MP) and boiling point (BP) than water • Chemically inert • ALL are very flammable ...
... Much less POLAR than alcohols Slightly soluble in water More soluble than alkane Lower melting point (MP) and boiling point (BP) than water • Chemically inert • ALL are very flammable ...
Bio 2 alkanes+isomerism
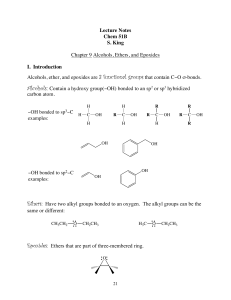
... groups are not called alcohols, but are instead called carboxylic acids.) Alcohols are one of the most widely found functional groups in nature. We name alcohols by adding the suffix -ol to the end of the name of the parent alkane, using a numerical prefix if the position of the OH group on the chai ...
... groups are not called alcohols, but are instead called carboxylic acids.) Alcohols are one of the most widely found functional groups in nature. We name alcohols by adding the suffix -ol to the end of the name of the parent alkane, using a numerical prefix if the position of the OH group on the chai ...
Organic Chemistry II with Dr Roche
... Ethers are stable to bases, but acidic conditions leads to the protonation of the ether oxygen, which then can undergo substitution reactions. ...
... Ethers are stable to bases, but acidic conditions leads to the protonation of the ether oxygen, which then can undergo substitution reactions. ...
Alkyl halide
... 12.3 Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alcohols Many common methods have been developed to transform alcohols into alkyl halides • Treat the alcohol with HCl, HBr, or HI • Simplest method • The reaction works best with tertiary alcohols, R3COH • Primary and secondary alcohols react slowly and at higher ...
... 12.3 Preparing Alkyl Halides from Alcohols Many common methods have been developed to transform alcohols into alkyl halides • Treat the alcohol with HCl, HBr, or HI • Simplest method • The reaction works best with tertiary alcohols, R3COH • Primary and secondary alcohols react slowly and at higher ...
organic practice problems
... ____ 60. Which of the following molecules is ethanol? a. C2H6 b. CH3CO2H c. CH3CHO d. CH3CH2OH e. CH3OCH3 ____ 61. Which functional group does not contain an oxygen atom? a. alcohol b. amine c. amide d. ester e. ether ____ 62. The functional group RCO2R' is characteristic of an ________. a. ether b. ...
... ____ 60. Which of the following molecules is ethanol? a. C2H6 b. CH3CO2H c. CH3CHO d. CH3CH2OH e. CH3OCH3 ____ 61. Which functional group does not contain an oxygen atom? a. alcohol b. amine c. amide d. ester e. ether ____ 62. The functional group RCO2R' is characteristic of an ________. a. ether b. ...
Air-Stable Trialkylphosphonium Salts
... that is currently in Phase 3 clinical trials: Scott, John W. Presented at Chiral USA 2000, Boston, MA, 2000. Org. Lett., Vol. 3, No. 26, 2001 ...
... that is currently in Phase 3 clinical trials: Scott, John W. Presented at Chiral USA 2000, Boston, MA, 2000. Org. Lett., Vol. 3, No. 26, 2001 ...
CHM 103 Lecture 28 S07
... Quaternary (4°) amines also possible (4 C groups attached to nitrogen atom) ...
... Quaternary (4°) amines also possible (4 C groups attached to nitrogen atom) ...
Aldehydes And Ketones
... • They are also oxidized by Ag(I) – in one method, a solution of the aldehyde in aqueous ethanol or THF is shaken with a slurry of silver oxide O CH ...
... • They are also oxidized by Ag(I) – in one method, a solution of the aldehyde in aqueous ethanol or THF is shaken with a slurry of silver oxide O CH ...
10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
... Monohalogen derivatives of alkanes (haloalkanes) can be prepared by the following methods: i. From halogenation of alkanes: a. Direct halogenation of alkanes in the presence of UV light, heat or suitable catalyst gives the corresponding alkyl halides. b. The displacement of H-atom from hydrocarbon d ...
... Monohalogen derivatives of alkanes (haloalkanes) can be prepared by the following methods: i. From halogenation of alkanes: a. Direct halogenation of alkanes in the presence of UV light, heat or suitable catalyst gives the corresponding alkyl halides. b. The displacement of H-atom from hydrocarbon d ...
Slide 1
... Recall that electron donors (Nu: -’s) add to the electrophilic carbonyl C in aldehydes and ketones. The C=O p bond breaks and the pair of electrons are stabilized on the electronegative O atom. R (alkyl groups) and hydrogens (H) bonded to the C=O carbon remain in place. R- and H- are too reactive (p ...
... Recall that electron donors (Nu: -’s) add to the electrophilic carbonyl C in aldehydes and ketones. The C=O p bond breaks and the pair of electrons are stabilized on the electronegative O atom. R (alkyl groups) and hydrogens (H) bonded to the C=O carbon remain in place. R- and H- are too reactive (p ...
Chapter 21: Organic Chemistry
... open chain) hydrocarbons which contain less hydrogen per carbon atom than alkanes. Hence, alkenes and alkynes are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes have a general formula CnH2n ...
... open chain) hydrocarbons which contain less hydrogen per carbon atom than alkanes. Hence, alkenes and alkynes are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes have a general formula CnH2n ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.