* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH3
Volatile organic compound wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
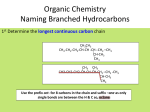
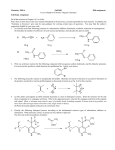
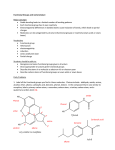
• Anaesthesia or anesthesia has traditionally meant the condition of having the perception of pain and other sensations blocked. This allows patients to undergo surgery and other procedures without the distress and pain they would otherwise experience. • It comes from the Greek roots an-, "not, without" and aesthētos, "perceptible, able to feel". The word was coined by Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr. in 1846. - blocking the conscious perception of pain - producing unconsciousness - preventing memory formation - preventing unwanted movement or muscle tone 3HC | H–C | 3HC OH CH3 | C–H | CH3 F F F F – C – O – C – C – Cl H F Cl F H F F–C–C–O–C–H H H F Cl F H Cl – C – C – O – C – H H F H Br F Cl – C – C – F H F DEFINITION OF ETHER • any of a class of organic compounds that have two hydrocarbon groups linked by an oxygen atom Nomenclature methoxymethane dimethylether methoxyethane ethylmethylether (2 – propoxycyclohexane) cyclohexylisopropylether (methoxybenzene) methylphenylether 7 6 8 5 9 2 4 1 1 Do U want to PLAY a game? All will be given a chance 2 answer I will be D’ one flashing instructions/structures on screen Then, U will be doing Ur all, to comply with the given instructions or 2 give name for every given structures. U will be doing it first on Ur notebook. Then, if you are done U just have 2 “shout out” your name 2 class and spluke D’ magic words U will be given 20 seconds 2 answer on D’ board. 3 points will be added on your quizzes or exercises for every correct answer. Good luck everyone!!! WARM - UP ETHER LINK F – C – O – C – C – Cl 1 1 2 1,1 – difluoromethoxy – 2 – chloro – 1,1,2 – trifluoroethane D’ game starts Now……… 1 2 3 4 5 6 ETHER LINK 5 – ethoxy – 2 – hexanol O ║ 4 1 2 ETHER LINK 1 4 – (2 – bromoethoxyphenol) 10 9 O ║ 8 7 6 5 3 2 1 4 ETHER LINK 4 – (propoxy – 7 – ethyl – 5 – methyl – 4,6 – dipropyldecane) O ║ 3 5 1 3 4 ETHER LINK 1 5 – (3,4 – dimethylcyclopentoxy – 1,3 – cyclohexanediol) O ║ 4 – methoxybenzoic acid p – methoxybenzoic acid Do U want some MORE? Quick Mind Twister 1. Describe and compare the different ways of naming ETHER to other organic compounds? 2.Specify the steps and factors involved in ETHER Nomenclature. 3. How does the nomenclature of ETHER differ from the rest of the family of organic compounds? 4.How can we apply the knowledge in ETHER nomenclature in real – life setting? Assignments 1. What are the ways to produce ether? 2. What are physical and chemical properties of ethers? 3. Cite some industrial uses of organic compounds ETHER. References: All organic chemistry book will do Preparations DEHYDRATION OF ALCOHOLS at 140 ᵒC 140 °C Alcohol + Alcohol ------------ ETHER + H2O Example 140°C CH3 – CH2 – OH + OH – CH3 --------- CH3 – CH2 – O – CH3 + H2O IUPAC methoxyethane COMMON ethylmethylether Williamson Synthesis ETHER FORMATION NaOH PHENOL + ALKYL HALIDES ---------------- ETHER + HYDROGEN HALIDES Δ Example + HCl + CH3Cl -------- methoxybenzene OH Anisole O – CH3 Physical Properties Table of Comparison COMPOUND MOLECULAR WEIGHT MELTING POINT BOILING POINT CH3 – OH 32 - 97 °C 64. 5 °C CH3 – CH2 – OH 46 - 115 ° C 78. 5 °C H2O 18 0° 100 °C PHENOLS 94 43.47°C 182 °C CH3 – O – CH3 46 - 140 °C - 24 °C CH3 CH2– O – CH2 CH3 74 - 116 °C 35 °C HYDROCARBON MOLECULAR WEIGHT MELTING POINT BOILING POINT CH4 16 - 117 °C - 161 °C CH3 – CH3 30 - 156 °C - 88 °C PROPERTIES OF ETHERS • • • • Much less POLAR than alcohols Slightly soluble in water More soluble than alkane Lower melting point (MP) and boiling point (BP) than water • Chemically inert • ALL are very flammable Chemical Properties ETHERS reaction • Since ethers are comparatively unreactive compounds. • The ether linkage is quite stable towards bases, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents. • In so far as D’ ether linkage itself is concerned, ethers undergo just one kind of reaction. • Trigger by an concentrated acids • And take place only under quite vigorous conditions namely acids & high temperature. ETHERS reacts w/ strong acids 130 - 140°C ETHER + ACIDS --------- ALKYL HALIDE + ALCOHOL Example methanol H – Cl CH3 – O – CH3 + HCl -------- CH3 – Cl + CH3 – OH 130 - 140°C chloromethane Example ethanol H – Br O Br + CH3CH2 – OH 2HC – CH3 + HBr ---- 130 - 140°C bromocyclopropane Example F OH H–F 130 - 140°C + H – F ------ + O fluorobenzene phenol Example CH3 H–I CH3 – CH – O – CH – CH3 + 130 - 140°C HI ---------> CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 – CH – I 2 - iodopropane + H – O – HC – CH3 isopropylalcohol