* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Groups and nomenclature Major concepts Stable
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
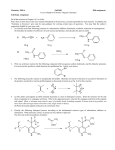
Functional Groups and nomenclature Major concepts Stable bonding leads to a limited number of bonding patterns Each functional group has its own reactivity Electronegativity differences in bonded atoms cause induction of bonds, which leads to partial charges Molecules can be categorized by structure (functional groups) or reactivity (Lewis acids or Lewis bases) Vocabulary Functional group Heteroatom electronegativity induction Lewis acid/Lewis base Partial charge Students should be able to: Recognize and name functional groups given a structure Draw appropriate structures given functional groups Describe the atoms in a molecule as electron rich or electron poor Describe carbon atoms of functional groups as Lewis acids or Lewis bases Daily Problems 1. Label all the functional groups you find in these molecules. Choices include: aldehyde, amide, amine, alcohol, ether, alkene, carboxylic acid, benzene, phenol, ketone. In the compound that is very similar to morphine, label a primary carbon atom, a secondary carbon atom, a tertiary carbon atom, and a quaternary carbon atom (Q). amide HO H N Phenol Phenol 20 ether O Q 30 Q O alcohol 30 alkene Tylenol 20 N HO HO 30 Carboxylic acid amine 1 benzene OH 0 very similar to morphine O Advil alkane 2. Draw a bond-line representation that fit the following parameters: 1. A five carbon ester O O O O 2. A cyclic ether that contains 4 carbon atoms O O 3. An alkene with eight carbons that also contains a hydroxyl group OH OH 4. An unsaturated aldehyde O H 5. A seven carbon alkane that contains one tertiary carbon 3. Draw bond-line formulas for these condensed formulas. Notice the conventions used in these functional groups. a. CH3CH2CH2CHO (“CHO” is the aldehyde functional group.) O H b. CH3CH2CH2COOH (“COOH” is the carboxylic acid functional group.) O OH c. CH3CH2CH2CO2H (“CO2H” is also the carboxylic acid functional group.) O OH d. CH3CH2CH2OH (an alcohol) OH e. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3 (an alcohol) OH f. CH3CH2CH2OCH3 (an ether—how is this different than part e?) O 4. Many functional groups contain a structure called a “carbonyl”, which is the carbon/oxygen double bond, C=O. Draw examples of 4 carbon molecules containing the following functional groups, then clearly state what is distinct about each functional group. a. aldehyde O The C=O (carbonyl) must contain an H (hydrogen) H b. carboxylic acid O The C=O must contain an OH (hydroxyl) OH c. ketone O Both sides of the C=O must be carbons! d. ester O The C=O must contain an OR group (in this example –OCH3) O e. amide O The C=O must connect to an –NHR group (in this example –NHCH3) N H 5. Indicate whether you would consider each of these atoms to be Lewis acidic (LA) or Lewis basic (LB). Explain your thinking. a. The oxygen atom of an alcohol LB; the dipole (by induction) points toward the more electronegative atom b. The carbon atoms of an alkene LB c. The carbon atom of a ketone. LA; the dipole arrow points to oxygen because it’s more electronegative d. The nitrogen atom of an amine LB; nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon e. The carbon attached to chlorine of an alkyl halide LA; chlorine is more electronegative, so the dipole points away from carbon 6. Application to Biology: Here are the structures of some biological molecules. Use the names of the molecules or the hints given to match the name with the structure. A. Histamine B. Alanine (an amino acid) C. Acetylcholine (the only structure with atypical bonding) D. Cholesterol H N O NH 2 N NH 2 HO B A O C N O D HO 7. Draw dipole arrows designating any polar bonds in these molecules. Indicate any carbon atoms that are Lewis acidic (LA). Indicate any hydrogen atoms that are partially positive (δ+). LA O O O + δ LA OH Cl NH 2 Cumulative problems 8. Redraw these compounds in bond-line formula and indicate any partial charges on carbon atoms due to induction. O H 3C C H C H C CH3 CH3 CH3 H 3C H OH C C H CH3 CH 3 O δ+ OH δ+ O H 3C H C C CH3 H 3C CH3 H Cl H C C C H H H CH3 O δ+ δ+ Cl 9. Application to Medicine: Antihistamines are drugs commonly used to treat allergy symptoms. Newer antihistamines are blockbuster drugs because they do not cause drowsiness (due to the fact that they don’t cross the blood-brain barrier.) The structure of fexofenadine (Allegra) is shown below. How many carbons are in this molecule? How many lone pairs does it have? Name all of its functional groups. OH 32 carbons Amine O N OH Alcohol OH Phenyl group or benzene ring Alcohol Carboxylic acid 10. In this class, we will discuss functional group transformations. We will eventually learn about how these reactions happen, and what reagents are required. For now, just name the functional groups in the starting materials and the products. OH O Br + Alkyl bromide (halide) phenol ether O O + OCH3 CH3OH OH ester Alcohol Carboxylic acid Cl Alkyl chloride (halide) alkene 11. Application to Environmental Chemistry: Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a biodegradable plastic made from chemically connecting many individual molecules (monomers) of hydroxybuteric acid into a long chain. What functional group(s) are in the monomer? In the polymer? Based on this information, what general class of polymers does PHB belong to? (Hint: popular clothing material of the 1970’s.) What environmentally friendly small molecule is the side-product of this reaction? (Look at the atoms lost during the reaction.) O HO alcohol Carboxylic acid OH monomer ester O O O O unit 1 Side product: H2O (water) O unit 2 The polymer is known as polyester O O unit 3 Extension problems 11. Nomenclature is the systematic way we name compounds. The end of the name indicates the major functional group in the molecule. Using this information, match the structure to the most likely name. A. pentanamide B. 4-chloropent-1-yne C. 4-methoxypentanal D.4,4-dimethylpentan-2-ol E. cyclohexanone E C B A D