Document
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
Functional Group Isomerism
... molecules of the cis isomers than between trans isomers. • The difference between the two is that the cis isomer is a polar molecule whereas the trans isomer is non-polar. Both molecules contain polar chlorine-carbon bonds, but in the cis isomer they are both on the same side of the molecule. That m ...
... molecules of the cis isomers than between trans isomers. • The difference between the two is that the cis isomer is a polar molecule whereas the trans isomer is non-polar. Both molecules contain polar chlorine-carbon bonds, but in the cis isomer they are both on the same side of the molecule. That m ...
Esterification and Esters
... For the properties of these compounds, see ESTERS, ORGANIC. For esters of inorganic acids, see the articles on nitric acid, phosphoric acids, sulfuric acid, etc. Esters are most commonly prepared by the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol with the elimination of water. Esters are also forme ...
... For the properties of these compounds, see ESTERS, ORGANIC. For esters of inorganic acids, see the articles on nitric acid, phosphoric acids, sulfuric acid, etc. Esters are most commonly prepared by the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol with the elimination of water. Esters are also forme ...
Chapter 12
... The common name for an aldehyde is derived from the common name of the corresponding carboxylic acid by changing the suffix –ic to –aldehyde. O ...
... The common name for an aldehyde is derived from the common name of the corresponding carboxylic acid by changing the suffix –ic to –aldehyde. O ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 23: Amines
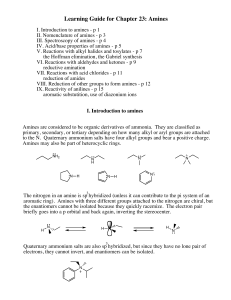
... VII. Reactions with acid chlorides - p 11 reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are considered to be organic derivatives of ammonia. They are classified ...
... VII. Reactions with acid chlorides - p 11 reduction of amides VIII. Reduction of other groups to form amines - p 12 IX. Reactivity of anilines - p 15 aromatic substutition, use of diazonium ions I. Introduction to amines Amines are considered to be organic derivatives of ammonia. They are classified ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
... • Alcohols contain one or more hydroxyl groups, —OH. • They are named from the parent hydrocarbon; the suffix is changed to -ol and a number designates the carbon to which the hydroxyl is attached. Organic and Biological Chemistry ...
FUNCTIONAL GROUP IDENTIFICATION WORKSHEET
... 1) Draw the structures for the following alcohols: a) 1-propanol b) 2-propanol c) 2-methyl-2-butanol ...
... 1) Draw the structures for the following alcohols: a) 1-propanol b) 2-propanol c) 2-methyl-2-butanol ...
Chapter 16-18 - Bakersfield College
... – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
... – Reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol (-CHOH-). ...
Amines
... Amides, RCONR'2, can be reduced to the amine, RCH2NR'2 by conversion of the C=O to -CH2Amides can be reduced by LiAlH4 but NOT the less reactive NaBH4 Typical reagents : LiAlH4 / ether solvent, followed by aqueous work-up. Note that this reaction is different to that of other C=O compounds which red ...
... Amides, RCONR'2, can be reduced to the amine, RCH2NR'2 by conversion of the C=O to -CH2Amides can be reduced by LiAlH4 but NOT the less reactive NaBH4 Typical reagents : LiAlH4 / ether solvent, followed by aqueous work-up. Note that this reaction is different to that of other C=O compounds which red ...
Class Notes
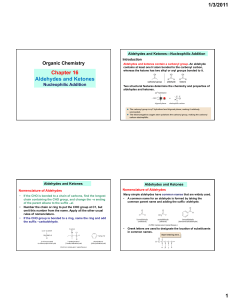
... • The carbanion R’ adds to the carbonyl carbon • The carbonyl =O gets replaced by –OH • For formaldehyde, aldehydes, and ketones: the two attachments on the original carbonyl carbon remain attached as spectators • For esters or acid chlorides: the one non-heteroatom attachment on the original carbon ...
... • The carbanion R’ adds to the carbonyl carbon • The carbonyl =O gets replaced by –OH • For formaldehyde, aldehydes, and ketones: the two attachments on the original carbonyl carbon remain attached as spectators • For esters or acid chlorides: the one non-heteroatom attachment on the original carbon ...
Anhydrides, Esters and Amides
... • The carboxylic acid formed in the hydrolysis reacts with hydroxide ion to form a carboxylic acid anion. • Each mole of ester hydrolyzed requires one mole of ...
... • The carboxylic acid formed in the hydrolysis reacts with hydroxide ion to form a carboxylic acid anion. • Each mole of ester hydrolyzed requires one mole of ...
File
... The chemical properties (and toxicity) of organic compounds are determined by the compound as a whole. As a substitute in a molecule, a phenyl group ring does not have the same properties as benzene. ...
... The chemical properties (and toxicity) of organic compounds are determined by the compound as a whole. As a substitute in a molecule, a phenyl group ring does not have the same properties as benzene. ...
Chem 314 Preorganic Evaluation
... SN2, the two examples we will emphasize at 2o RX centers are carboxylates (SN2 > E2) vs hydroxide and alkoxides (E2 > SN2) and cyanide (SN2 > E2) vs terminal acetylides (E2 > SN2) we will consider neutral solvent molecules such as water, alcohols and acids to be weak nucleophiles (favors SN1 and E1) ...
... SN2, the two examples we will emphasize at 2o RX centers are carboxylates (SN2 > E2) vs hydroxide and alkoxides (E2 > SN2) and cyanide (SN2 > E2) vs terminal acetylides (E2 > SN2) we will consider neutral solvent molecules such as water, alcohols and acids to be weak nucleophiles (favors SN1 and E1) ...
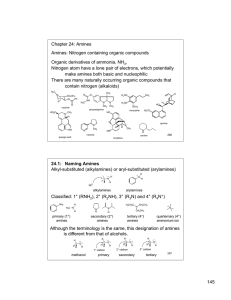
145 Chapter 24: Amines Amines: Nitrogen containing organic
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hy ...
... Alkyl ammonium ions, R3NH+ X-, have pKa values in the range of 10-11 (ammonium ion, H4N+ X-, has a pKa ~ 9.25) The ammonium ions of aryl amines and heterocyclic aromatic amines are considerably less basic than alkyl amines (pKa ~ 5 or less). The nitrogen lone pair is less basic if it is in an sp2 hy ...
Oxidation
... Carbon is often more electronegative (2.5) than some of the other atom which it bonds such as hydrogen has electronegativity 2.2. So in this case what we have to do? Unlike metal-metal bond, carbon bonds are found all over the organic chemistry then how can we calculate the oxidation state. ...
... Carbon is often more electronegative (2.5) than some of the other atom which it bonds such as hydrogen has electronegativity 2.2. So in this case what we have to do? Unlike metal-metal bond, carbon bonds are found all over the organic chemistry then how can we calculate the oxidation state. ...
Disproportionation of Monolithium Acetylide into
... This Note establishes for the first time that disproportionation of lithium acetylide into dilithium carbide and acetylene is a reversible process in THF at 0 °C and that such an equilibrium may be readily displaced by addition of an electrophile (Scheme 2). Addition of a 1.6 M solution of n-butylli ...
... This Note establishes for the first time that disproportionation of lithium acetylide into dilithium carbide and acetylene is a reversible process in THF at 0 °C and that such an equilibrium may be readily displaced by addition of an electrophile (Scheme 2). Addition of a 1.6 M solution of n-butylli ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.