Neuman Chapter - Department of Chemistry
... The leaving group L (Figure 9.02) is a halogen X. Because we refer to the C-X carbon as Cα, and its adjacent C-H carbon as Cβ, we say that the H on Cβ is a β-hydrogen or a β-H. The elimination reactions of haloalkanes illustrate the fundamental features and mechanisms of many elimination reactions t ...
... The leaving group L (Figure 9.02) is a halogen X. Because we refer to the C-X carbon as Cα, and its adjacent C-H carbon as Cβ, we say that the H on Cβ is a β-hydrogen or a β-H. The elimination reactions of haloalkanes illustrate the fundamental features and mechanisms of many elimination reactions t ...
Microsoft Word
... Hydroboration of alkene 7 with 9-BBN dimer in THF afforded organoborane intermediate 31 that was coupled with iodo compound 8 using Suzuki reaction in the presence of K3PO4 and Pd(PPh3)4 in 1,4-dioxane to furnish trisubstituted alkene 32 with concomitant deprotection of acetal group under reaction c ...
... Hydroboration of alkene 7 with 9-BBN dimer in THF afforded organoborane intermediate 31 that was coupled with iodo compound 8 using Suzuki reaction in the presence of K3PO4 and Pd(PPh3)4 in 1,4-dioxane to furnish trisubstituted alkene 32 with concomitant deprotection of acetal group under reaction c ...
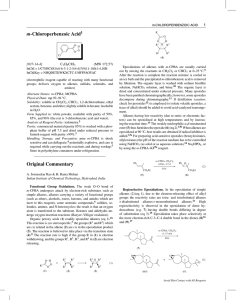
3.2 Organic Synthesis (Reaction Pathways)
... Though alkenes can be made by the cracking of alkanes (can be called dehydrogenation), this would only be used on a specific alkane (e.g. propane) to produce a specific alkene (e.g.propene) when part of a Synthesis. The other option would be to perform an Elimination reaction on either an alcohol (a ...
... Though alkenes can be made by the cracking of alkanes (can be called dehydrogenation), this would only be used on a specific alkane (e.g. propane) to produce a specific alkene (e.g.propene) when part of a Synthesis. The other option would be to perform an Elimination reaction on either an alcohol (a ...
Chapters E-18 review - Bakersfield College
... 10. How can we convert thé first compound into thé second compound? Détermine thé type of chemical reaction, catalyst (if it is necessary) and other necessary conditions: a) Benzène to Chlorobenzene ...
... 10. How can we convert thé first compound into thé second compound? Détermine thé type of chemical reaction, catalyst (if it is necessary) and other necessary conditions: a) Benzène to Chlorobenzene ...
Forward
... ketones. There we’ll discuss their hydration, a reaction in which water adds to the CœO group. After we use this reaction to develop some general principles, we’ll then survey a number of related reactions of synthetic, mechanistic, or biological interest. ...
... ketones. There we’ll discuss their hydration, a reaction in which water adds to the CœO group. After we use this reaction to develop some general principles, we’ll then survey a number of related reactions of synthetic, mechanistic, or biological interest. ...
carboxylic acids and their derivatives
... deserves some thought. In the most widely used sense, acids are proton donors but, as we have seen, their abilities to donate a proton to water vary over an whereas HI has a K, of lo9.This enormous range: CH, has a K, of < represents a difference in ionization energies of more than 70 kcal mole-l. T ...
... deserves some thought. In the most widely used sense, acids are proton donors but, as we have seen, their abilities to donate a proton to water vary over an whereas HI has a K, of lo9.This enormous range: CH, has a K, of < represents a difference in ionization energies of more than 70 kcal mole-l. T ...
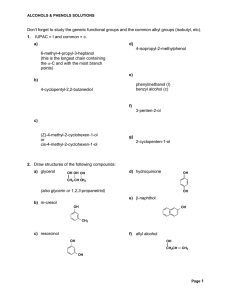
Don`t forget to study the generic functional groups and the common
... 11. This one is tougher. Note the addition of the ethyl group. The only methods we’ve learned for adding Carbon groups are 1) chain lengthening terminal alkynes, 2) FC alkylations/acylations to aromatics, 3) Grignards, organosodium and Gilman reactions. Obviously the first two don’t apply here, so l ...
... 11. This one is tougher. Note the addition of the ethyl group. The only methods we’ve learned for adding Carbon groups are 1) chain lengthening terminal alkynes, 2) FC alkylations/acylations to aromatics, 3) Grignards, organosodium and Gilman reactions. Obviously the first two don’t apply here, so l ...
CHM 235 Course Outline and Homework in McMurry (6th ed.)
... Enantiomers, chirality, specific rotation Sequence rules for R and S Diastereomers and meso compounds Racemic mixtures and their resolution (chiral drugs!) Fischer projections Stereochemistry in reactions (addition of HBr, Br2) ...
... Enantiomers, chirality, specific rotation Sequence rules for R and S Diastereomers and meso compounds Racemic mixtures and their resolution (chiral drugs!) Fischer projections Stereochemistry in reactions (addition of HBr, Br2) ...
9: Formation of Alkenes and Alkynes. Elimination Reactions
... The leaving group L (Figure 9.02) is a halogen X. Because we refer to the C-X carbon as Cα, and its adjacent C-H carbon as Cβ, we say that the H on Cβ is a β-hydrogen or a β-H. The elimination reactions of haloalkanes illustrate the fundamental features and mechanisms of many elimination reactions t ...
... The leaving group L (Figure 9.02) is a halogen X. Because we refer to the C-X carbon as Cα, and its adjacent C-H carbon as Cβ, we say that the H on Cβ is a β-hydrogen or a β-H. The elimination reactions of haloalkanes illustrate the fundamental features and mechanisms of many elimination reactions t ...
AddCorrections(KKH) - Spiral
... AgOTf was the first group 11 metal catalyst reported to catalyse the intramolecular addition of carboxylic acids (X = O) and alcohols (X = H2, R2) to C=C bonds.[17] In refluxing DCE, a wide range of substrates underwent excellent conversions to furnish great selectivity for the Markovnikov product. ...
... AgOTf was the first group 11 metal catalyst reported to catalyse the intramolecular addition of carboxylic acids (X = O) and alcohols (X = H2, R2) to C=C bonds.[17] In refluxing DCE, a wide range of substrates underwent excellent conversions to furnish great selectivity for the Markovnikov product. ...
McMurray-Fay Chapter 22 Presentation Slides
... • any carbon with 4 different substituents is called a chiral center • a pair of non-superimposable mirror images are called a pair of enantiomers ...
... • any carbon with 4 different substituents is called a chiral center • a pair of non-superimposable mirror images are called a pair of enantiomers ...
Chapter Thirteen - Wright State University
... • Reduction is the reverse of the oxidation reaction. Reduction of a carbonyl group is the addition of hydrogens across the double bond to produce an –OH group. • Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols, and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols. • Reduction of the carbonyl group occurs by for ...
... • Reduction is the reverse of the oxidation reaction. Reduction of a carbonyl group is the addition of hydrogens across the double bond to produce an –OH group. • Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols, and ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols. • Reduction of the carbonyl group occurs by for ...
15.1 Amines
... Common- end with “amine” •EX-CH3NH2-IUPAC: methanamine; Common: Methyl amine (both are primary) •Aliphatic amines- Have alkyl groups (methyl amine) •Aromatic amines- one or more of the groups bonded to nitrogen are aryl groups Ex-aniline (aminobenzene); •Heterocyclic- N is part of the ring (ex-purin ...
... Common- end with “amine” •EX-CH3NH2-IUPAC: methanamine; Common: Methyl amine (both are primary) •Aliphatic amines- Have alkyl groups (methyl amine) •Aromatic amines- one or more of the groups bonded to nitrogen are aryl groups Ex-aniline (aminobenzene); •Heterocyclic- N is part of the ring (ex-purin ...
Chloroperbenzoic_aci..
... m-CPBA undergoes attack by electron-rich substrates such as simple alkenes, alkenes carrying a variety of functional groups (such as ethers, alcohols, esters, ketones, and amides which are inert to this reagent), some aromatic compounds,6 sulfides, selenides, amines, and N-heterocycles; the result i ...
... m-CPBA undergoes attack by electron-rich substrates such as simple alkenes, alkenes carrying a variety of functional groups (such as ethers, alcohols, esters, ketones, and amides which are inert to this reagent), some aromatic compounds,6 sulfides, selenides, amines, and N-heterocycles; the result i ...
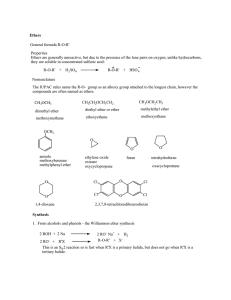
Ethers General formula R-O-R` Properties Ethers are generally
... Ethers General formula R-O-R' Properties Ethers are generally unreactive, but due to the presence of the lone pairs on oxygen, unlike hydrocarbons, they are soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid: R-O-R' + H 2 SO4 ...
... Ethers General formula R-O-R' Properties Ethers are generally unreactive, but due to the presence of the lone pairs on oxygen, unlike hydrocarbons, they are soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid: R-O-R' + H 2 SO4 ...
Reductive Coupling Reactions of Nitrones and Imines
... benzaldehyde or aromatic imines, resulted in the formation of homocoupling products. These two examples suggest the necessity for balancing the activation of the substrates and the strength of the reductant for efficient cross coupling. The steric bulk of the Į-substituents on the imine also plays a ...
... benzaldehyde or aromatic imines, resulted in the formation of homocoupling products. These two examples suggest the necessity for balancing the activation of the substrates and the strength of the reductant for efficient cross coupling. The steric bulk of the Į-substituents on the imine also plays a ...
Full Text
... a number of compounds of biological and synthetic interest, including nucleosides, carbohydrates, steroids, macrolides, polyethers, and the side chain of some amino acids or in large numbers of intermediates in total syntheses of complex natural products.2 Diverse protecting groups have been develop ...
... a number of compounds of biological and synthetic interest, including nucleosides, carbohydrates, steroids, macrolides, polyethers, and the side chain of some amino acids or in large numbers of intermediates in total syntheses of complex natural products.2 Diverse protecting groups have been develop ...
Unit-5-Lipids
... • Animal fats, such as butter and lard, which are naturally saturated, can also be used in baking, but unlike the vegetable oils, they come with cholesterol, which is undesirable for health reasons. ...
... • Animal fats, such as butter and lard, which are naturally saturated, can also be used in baking, but unlike the vegetable oils, they come with cholesterol, which is undesirable for health reasons. ...
Unit-5-LipidsClick copy
... • Animal fats, such as butter and lard, which are naturally saturated, can also be used in baking, but unlike the vegetable oils, they come with cholesterol, which is undesirable for health reasons. ...
... • Animal fats, such as butter and lard, which are naturally saturated, can also be used in baking, but unlike the vegetable oils, they come with cholesterol, which is undesirable for health reasons. ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.