Review: The preparation of Hydantoins
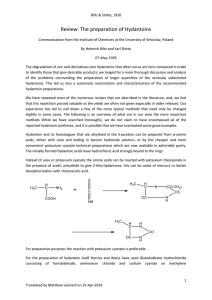
... gave 20 g of pure product, (quantitative yield = 28.9 g). The yield increased to 24 g of pure hydantoin when the mother liquor was evaporated from hydantoic ester and the residue with 50 mL of fuming concentrated hydrochloric acid and 5 g of crude product was thus obtained by recrystallization. Prep ...
... gave 20 g of pure product, (quantitative yield = 28.9 g). The yield increased to 24 g of pure hydantoin when the mother liquor was evaporated from hydantoic ester and the residue with 50 mL of fuming concentrated hydrochloric acid and 5 g of crude product was thus obtained by recrystallization. Prep ...
Chapter 13 Alcohols, Phenols, and Thiols
... • Has a hydroxyl group that ionizes slightly (weak acid). • Is corrosive and irritating to the skin. OH ...
... • Has a hydroxyl group that ionizes slightly (weak acid). • Is corrosive and irritating to the skin. OH ...
Topic 17 notes - A
... This sweet smell can also be used to test for the presence of carboxylic acids and alcohols; a carboxylic acid will give a sweet smell if heated with ethanol and a strong acid, and an alcohol will give a sweet smell if heated with ethanoic acid and a strong acid. Esters are also used as plasticizers ...
... This sweet smell can also be used to test for the presence of carboxylic acids and alcohols; a carboxylic acid will give a sweet smell if heated with ethanol and a strong acid, and an alcohol will give a sweet smell if heated with ethanoic acid and a strong acid. Esters are also used as plasticizers ...
Supporting Information for Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Z52444 © Wiley
... Unless stated otherwise, reactions were performed in oven-dried glassware, under an atmosphere of oxygen, using freshly distilled solvents. Although we have never experienced an accident, all reactions must be performed with appropriate caution in a fume hood due to the flammable nature of mixtures ...
... Unless stated otherwise, reactions were performed in oven-dried glassware, under an atmosphere of oxygen, using freshly distilled solvents. Although we have never experienced an accident, all reactions must be performed with appropriate caution in a fume hood due to the flammable nature of mixtures ...
+ ∂ - CHEM171 – Lecture Series Seven : 2012/05
... CH3CH2COOH + CH3CH2OH CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 + H2O ...
... CH3CH2COOH + CH3CH2OH CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 + H2O ...
Enantioselective Organocatalytic Aminomethylation of Aldehydes: A
... et al. for Mannich reaction of imines, in which an ionic attraction between protonated imine and carboxylate was proposed.9 We tested our hypothesis by conducting the L-proline-catalyzed reaction in the presence of LiCl. If the putative iminium/carboxylate attraction determines the direction of imin ...
... et al. for Mannich reaction of imines, in which an ionic attraction between protonated imine and carboxylate was proposed.9 We tested our hypothesis by conducting the L-proline-catalyzed reaction in the presence of LiCl. If the putative iminium/carboxylate attraction determines the direction of imin ...
Phenol
... Phenol itself is somewhat soluble in water most other Phenols are essentially insoluble in water. Phenols are colorless, but they easily oxidized by atmospheric air and become colored compounds. ...
... Phenol itself is somewhat soluble in water most other Phenols are essentially insoluble in water. Phenols are colorless, but they easily oxidized by atmospheric air and become colored compounds. ...
review-rough
... 16. Which group of these compounds tends to be the most reactive? a. alkanes c. alkynes b. alkenes d. aromatics ...
... 16. Which group of these compounds tends to be the most reactive? a. alkanes c. alkynes b. alkenes d. aromatics ...
Faculteit der Natuurwetenschappen, Wiskunde en Informatica
... General Procedure for the Addition of Grignard Reagents to βaldehyde acetals. A 0.1 M solution of 3 (0.167 g, 0.5 mmol) in toluene was cooled to -78°C. RMgX (2.5 mmol) was added drop wise to the solution. The resulting solution was stirred for one hour and quenched by the addition of NH4Cl and the m ...
... General Procedure for the Addition of Grignard Reagents to βaldehyde acetals. A 0.1 M solution of 3 (0.167 g, 0.5 mmol) in toluene was cooled to -78°C. RMgX (2.5 mmol) was added drop wise to the solution. The resulting solution was stirred for one hour and quenched by the addition of NH4Cl and the m ...
CHAPTER 8 Structures and nomenclature of organic
... of two —CH2 units gives propane, CH3CH2CH3 or C3H8. Alkanes with carbon atoms in long chains are known as straight-chain hydrocarbons. Alkanes have the structural formula CnH2n + 2, where n is an integer. A family of carbon compounds that are structurally related and where members of the family can ...
... of two —CH2 units gives propane, CH3CH2CH3 or C3H8. Alkanes with carbon atoms in long chains are known as straight-chain hydrocarbons. Alkanes have the structural formula CnH2n + 2, where n is an integer. A family of carbon compounds that are structurally related and where members of the family can ...
Oxidative reactions ppt - Senior Chemistry
... •This is not a practical laboratory method -- it is better suited to industrial processes. •The reaction stops at the aldehyde stage -- no more removal of hydrogen can take place. WWU -- Chemistry ...
... •This is not a practical laboratory method -- it is better suited to industrial processes. •The reaction stops at the aldehyde stage -- no more removal of hydrogen can take place. WWU -- Chemistry ...
Chap 1 - Notes - StrucandPropOrganicComp
... o Example: fossil fuels such as natural gas and gasoline ...
... o Example: fossil fuels such as natural gas and gasoline ...
Organic Chemistry III
... substituted onto the N atom in place of H atoms. Therefore more electron density is pushed onto the N atom (as the inductive effect of alkyl groups is greater than that of H atoms). One might expect using the same trend that tertiary amine would be the strongest amine base but the trend does not hol ...
... substituted onto the N atom in place of H atoms. Therefore more electron density is pushed onto the N atom (as the inductive effect of alkyl groups is greater than that of H atoms). One might expect using the same trend that tertiary amine would be the strongest amine base but the trend does not hol ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
... groups More electrophilic carbonyl groups are more reactive to addition (acyl halides are most reactive, amides are least) The intermediate with the best leaving group decomposes fastest Based on McMurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 21, 6th edition, (c) 2003 ...
... groups More electrophilic carbonyl groups are more reactive to addition (acyl halides are most reactive, amides are least) The intermediate with the best leaving group decomposes fastest Based on McMurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 21, 6th edition, (c) 2003 ...
ppt file
... groups More electrophilic carbonyl groups are more reactive to addition (acyl halides are most reactive, amides are least) The intermediate with the best leaving group decomposes fastest Based on McMurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 21, 6th edition, (c) 2003 ...
... groups More electrophilic carbonyl groups are more reactive to addition (acyl halides are most reactive, amides are least) The intermediate with the best leaving group decomposes fastest Based on McMurry, Organic Chemistry, Chapter 21, 6th edition, (c) 2003 ...
Producing Olefins for Use in Gasoline, Jet and Diesel Fuels from
... tubular flow reactors and an inter-stage separator in a single catalytic system. The chemical transformation proceeds via conversion of GVL to an n-butene, which is then introduced into a second reactor where the butene is converted via acid catalyzed oligomerization to higher molecular weight olefi ...
... tubular flow reactors and an inter-stage separator in a single catalytic system. The chemical transformation proceeds via conversion of GVL to an n-butene, which is then introduced into a second reactor where the butene is converted via acid catalyzed oligomerization to higher molecular weight olefi ...
New Phenylglycine-Derived Primary Amine Organocatalysts for the
... anticipated by us that introducing sterically more demanding side chains through cyclohexylglycine or tert-leucine (amino alcohols 16–17) would enhance the enantioselectivity even further, a hypothesis obviously invalidated by experiment. Clearly, the presence of an aromatic moiety is crucial. Among ...
... anticipated by us that introducing sterically more demanding side chains through cyclohexylglycine or tert-leucine (amino alcohols 16–17) would enhance the enantioselectivity even further, a hypothesis obviously invalidated by experiment. Clearly, the presence of an aromatic moiety is crucial. Among ...
Alcohol

In chemistry, an alcohol is any organic compound in which the hydroxyl functional group (–OH) is bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term alcohol originally referred to the primary alcohol ethyl alcohol (ethanol), the predominant alcohol in alcoholic beverages.The suffix -ol appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority; in substances where a higher priority group is present the prefix hydroxy- will appear in the IUPAC name. The suffix -ol in non-systematic names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance includes a hydroxyl functional group and, so, can be termed an alcohol. But many substances, particularly sugars (examples glucose and sucrose) contain hydroxyl functional groups without using the suffix. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest members is the saturated straight chain alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH.























