Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon
... molecules and there is a hydrogen bond between the alcohol molecules. 2- Solubility:Alcohols dissolve in water due to the hydrogen bond. Chemical properties:1- React with metals to produce Alkoxides R-OH + Na ...
... molecules and there is a hydrogen bond between the alcohol molecules. 2- Solubility:Alcohols dissolve in water due to the hydrogen bond. Chemical properties:1- React with metals to produce Alkoxides R-OH + Na ...
Production of synthesis gas
... the manufacture of hydrogen for a growing number of purposes. 2. Methanol not only remains the second largest consumer of syngas but has shown remarkable growth as part of the methyl ethers used as octane enhancers in automotive fuels. 3. The hydroformylation of olefins (the oxo-reaction), a complet ...
... the manufacture of hydrogen for a growing number of purposes. 2. Methanol not only remains the second largest consumer of syngas but has shown remarkable growth as part of the methyl ethers used as octane enhancers in automotive fuels. 3. The hydroformylation of olefins (the oxo-reaction), a complet ...
photooxidative degradation of phenyl
... being a biorecalcitrant compound, its destruction needs a modern technique as a photocatalytic oxidation process (an advanced oxidation process). This method based on photocatalysis using TiO2 is particularly attractive for removing organic pollutants from water because it can destroy toxic and haza ...
... being a biorecalcitrant compound, its destruction needs a modern technique as a photocatalytic oxidation process (an advanced oxidation process). This method based on photocatalysis using TiO2 is particularly attractive for removing organic pollutants from water because it can destroy toxic and haza ...
FINAL EXAM Spring 2012
... 1) The reaction has the rate law, Rate = k[A][B]2. Which will cause the rate to increase the most? A) doubling [A] B) doubling [B] C) tripling [B] D) quadrupling [A] E) doubling both [A] and [B] 2) At a given temperature, a first-order reaction has a rate constant of 2.5 x 10-3 s-1. The time require ...
... 1) The reaction has the rate law, Rate = k[A][B]2. Which will cause the rate to increase the most? A) doubling [A] B) doubling [B] C) tripling [B] D) quadrupling [A] E) doubling both [A] and [B] 2) At a given temperature, a first-order reaction has a rate constant of 2.5 x 10-3 s-1. The time require ...
Page 1 for the analogous molecular reaction, eq 3. Acknowledgment
... Scheme I. In contrast, for molybdenum (and tungsten), C-C bond cleavage is competitive with reductive elimination due to the relative disfavor of the reductive elimination pathway for Mo (and W). The origin of this dramatic difference is the increased u bond strengths in the Mo compounds (- 15 kcal/ ...
... Scheme I. In contrast, for molybdenum (and tungsten), C-C bond cleavage is competitive with reductive elimination due to the relative disfavor of the reductive elimination pathway for Mo (and W). The origin of this dramatic difference is the increased u bond strengths in the Mo compounds (- 15 kcal/ ...
Chemdraw B&W - Pennsylvania State University
... organolithium • 1, 2, 3 alkyl, aryl and alkenyl groups react but not alkynyl groups ...
... organolithium • 1, 2, 3 alkyl, aryl and alkenyl groups react but not alkynyl groups ...
Microsoft Word
... chirotechnologies, which aim to exert the ultimate control over a chemical reaction by directing its enantioselectivity (ee). Asymmetric epoxidation (AE) of unfunctionalized olefins is an important organic transformation since the resulting epoxides are important building blocks for the synthesis of ...
... chirotechnologies, which aim to exert the ultimate control over a chemical reaction by directing its enantioselectivity (ee). Asymmetric epoxidation (AE) of unfunctionalized olefins is an important organic transformation since the resulting epoxides are important building blocks for the synthesis of ...
Exercise 1 (7 points) An Ionic compound: Table Salt Sodium
... usage. Flexible, very hard, non-reactive, easily broken, permeable to water, electric insulator. 4- Ethene undergoes addition reaction with chlorine gas to give a compound (B). - Write the equation of the reaction using the structural formulas and give the name of the compound (B). 5- Based on the a ...
... usage. Flexible, very hard, non-reactive, easily broken, permeable to water, electric insulator. 4- Ethene undergoes addition reaction with chlorine gas to give a compound (B). - Write the equation of the reaction using the structural formulas and give the name of the compound (B). 5- Based on the a ...
International Arab Baccalaureate
... acid and the appropriate amine, whereas in hydrolysis a molecule is cleaved into two parts by the addition of a molecule of water. Question 2: Amides can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions. Describe the reaction of hydrolysis and give the obtained compounds in acidic medium. ...
... acid and the appropriate amine, whereas in hydrolysis a molecule is cleaved into two parts by the addition of a molecule of water. Question 2: Amides can be hydrolyzed under acidic or basic conditions. Describe the reaction of hydrolysis and give the obtained compounds in acidic medium. ...
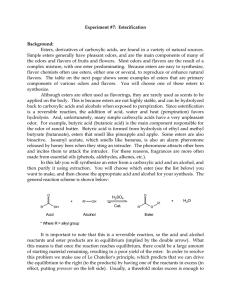
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... drive the equilibrium sufficiently to the right in an esterification reaction. Either the alcohol or the acid can be used in excess. The choice can be based on cost, availability and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric aci ...
... drive the equilibrium sufficiently to the right in an esterification reaction. Either the alcohol or the acid can be used in excess. The choice can be based on cost, availability and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric aci ...
Organic Chemistry
... An ether cannot form hydrogen bonds with other ether molecules since there is no H to be donated (no -OH group) Ethers can be involved in H-bonding with systems able to donate H (e.g. water). The implications of these effects are: o lower melting and boiling points compared to analogous alcohols o s ...
... An ether cannot form hydrogen bonds with other ether molecules since there is no H to be donated (no -OH group) Ethers can be involved in H-bonding with systems able to donate H (e.g. water). The implications of these effects are: o lower melting and boiling points compared to analogous alcohols o s ...
4.5: Bonding in Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... 4.12: Reaction of Primary Alcohols with Hydrogen Halides. The SN2 Mechanism: Methyl and primary carbocations are the least stable, and they are not likely to be intermediates in reaction mechanism RH2C-OH ...
... 4.12: Reaction of Primary Alcohols with Hydrogen Halides. The SN2 Mechanism: Methyl and primary carbocations are the least stable, and they are not likely to be intermediates in reaction mechanism RH2C-OH ...
幻灯片 1
... 15. Examine the following IR spectrum, for substance P (C8H16O). Which oxygen containing functional group is present in P? ...
... 15. Examine the following IR spectrum, for substance P (C8H16O). Which oxygen containing functional group is present in P? ...
synthesis in industry
... Abstract - Organometallic compounds are coming to play a significant role as catalysts and reagents for the synthesis of organic compounds in high technology industry. Some examples involving C-C bond formation include alkylation of chloronaphthoquinones and halobenzenes, a titanium-mediated cycliza ...
... Abstract - Organometallic compounds are coming to play a significant role as catalysts and reagents for the synthesis of organic compounds in high technology industry. Some examples involving C-C bond formation include alkylation of chloronaphthoquinones and halobenzenes, a titanium-mediated cycliza ...
32 . R $ [ ~ % % + l
... 1. When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is released. In this system the release of the hydrogen gas is counteracted by an outside force which results in a smaller volume by the end of the reaction. The work done by the outside force: (a) Is negative on the system (b) Is positive on ...
... 1. When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, hydrogen gas is released. In this system the release of the hydrogen gas is counteracted by an outside force which results in a smaller volume by the end of the reaction. The work done by the outside force: (a) Is negative on the system (b) Is positive on ...
syllabus for entrance examination - NTU.edu
... reactions and of multi-step processes with a rate-determining step, for which n and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is incl ...
... reactions and of multi-step processes with a rate-determining step, for which n and m are both integral and are either 0, 1 or 2. The use of the integrated forms of first- and second-order rate equations is not required but the use of constancy of half-life as a test for first order kinetics is incl ...
questions on the dehydration of alcohols
... 1. a) Ethanol can be converted into ethene by passing the vapour over hot aluminium oxide, and collecting the ethene over water. Write the equation for the reaction. b) Ethanol can also be converted into ethene by heating it at 170°C with excess concentrated sulphuric acid. Before collecting it, the ...
... 1. a) Ethanol can be converted into ethene by passing the vapour over hot aluminium oxide, and collecting the ethene over water. Write the equation for the reaction. b) Ethanol can also be converted into ethene by heating it at 170°C with excess concentrated sulphuric acid. Before collecting it, the ...
Chemistry Honors Study Guide – Organic Chemistry You should be
... Describe cis v. trans isomers ...
... Describe cis v. trans isomers ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.