Double Bond
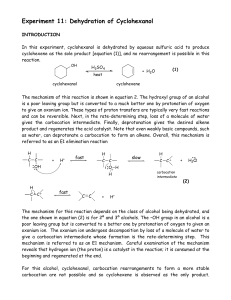
... Secondary and tertiary alcohols dehydrate by an E1 mechanism. The protonated hydroxy forms an alkyloxonium ion providing a good leaving group: water. Loss of water forms a secondary or tertiary carbocation. Deprotonation forms the alkene. ...
... Secondary and tertiary alcohols dehydrate by an E1 mechanism. The protonated hydroxy forms an alkyloxonium ion providing a good leaving group: water. Loss of water forms a secondary or tertiary carbocation. Deprotonation forms the alkene. ...
1 Big-Picture Exam Topics
... In addition to the standard naming schemes covered in lecture & in your book, these are the common names that you need to know for the test next week. You should be able to (i) write the names of these molecules if given structures OR (ii) draw structures of these molecules if given names. ...
... In addition to the standard naming schemes covered in lecture & in your book, these are the common names that you need to know for the test next week. You should be able to (i) write the names of these molecules if given structures OR (ii) draw structures of these molecules if given names. ...
Problem Set Chapter 13 Solutions February 28, 2013 13.27 Draw
... 13.48 Acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2,2-dimethylcyclohexanol yields a mixture of 1,2dimethylcyclohexene and isopropylidene cyclopentane. Propose a mechanism to account for the formation of both products. OH H+ ...
... 13.48 Acid-catalyzed dehydration of 2,2-dimethylcyclohexanol yields a mixture of 1,2dimethylcyclohexene and isopropylidene cyclopentane. Propose a mechanism to account for the formation of both products. OH H+ ...
Organic Chemistry Powerpoint
... The diversity of organic compounds results from the uniqueness of carbon’s structure and bonding. Carbon atoms are unique in their ability to form long chains and rings of covalently bonded atoms. ...
... The diversity of organic compounds results from the uniqueness of carbon’s structure and bonding. Carbon atoms are unique in their ability to form long chains and rings of covalently bonded atoms. ...
Alkene/Alkyne Addition Reactions
... H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” ...
... H-OH to an alkene or alkyne is the one obtained when the H atom of the reagent is added to the C atom of the multiple bond that already has the greater number of H atoms. “The rich get richer” ...
Organic Halides
... 2. All living systems have a way of getting rid of toxic compounds. Unfortunately most of the mrthods O disposal cannot handle waterinsoluble compounds that contain halogens. Some living systems solve this problem by replacing the halogen atoms by an –OH group. This increases the water solubitity of ...
... 2. All living systems have a way of getting rid of toxic compounds. Unfortunately most of the mrthods O disposal cannot handle waterinsoluble compounds that contain halogens. Some living systems solve this problem by replacing the halogen atoms by an –OH group. This increases the water solubitity of ...
Chemistry 21 A - El Camino College
... f) Cr2O72-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 3Mn2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3MnO2(s) + H2O(l) 14. Consider all of the following compounds to be water soluble and write the formulas of the ions that would be formed if the compoundes were disolved in water. ...
... f) Cr2O72-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 3Mn2+(aq) → 2Cr3+(aq) + 3MnO2(s) + H2O(l) 14. Consider all of the following compounds to be water soluble and write the formulas of the ions that would be formed if the compoundes were disolved in water. ...
Final-01 - Yale Department of Chemistry
... 1. Structure : (25 pts.) Compound A (C7H12) reacts with HBr/ROOR (Kharasch Reaction) to give stereoisomeric compounds B and C. When compound B is treated with aqueous KOH, compound D (C7H12) is formed. Under the same conditions compound C forms both A (major) and D (minor). Ozonolysis and dimethyl s ...
... 1. Structure : (25 pts.) Compound A (C7H12) reacts with HBr/ROOR (Kharasch Reaction) to give stereoisomeric compounds B and C. When compound B is treated with aqueous KOH, compound D (C7H12) is formed. Under the same conditions compound C forms both A (major) and D (minor). Ozonolysis and dimethyl s ...
A-level Paper 2 Practice Paper 1 - A
... In a similar three-step mechanism, one molecule of X reacts further with one molecule of ethanal. The product is a trimer containing six carbon atoms. Deduce the structure of this trimer. ...
... In a similar three-step mechanism, one molecule of X reacts further with one molecule of ethanal. The product is a trimer containing six carbon atoms. Deduce the structure of this trimer. ...
1995
... In the volumetric determination of chloride ions with silver nitrate(V) in neutral solutions, potassium chromate(VI) can be used as an indicator. (i) Explain the action of this indicator. (ii) Why is this titration not carried out in strongly acidic or strongly basic conditions? (3 marks) ...
... In the volumetric determination of chloride ions with silver nitrate(V) in neutral solutions, potassium chromate(VI) can be used as an indicator. (i) Explain the action of this indicator. (ii) Why is this titration not carried out in strongly acidic or strongly basic conditions? (3 marks) ...
excess
... 5. From the Ka values in the table, calculate the pKa for each compound. Using these data, arrange the compounds in order of increasing acidity and explain the trend. (Hint: be sure to identify the hydrogen to which the Ka applies.) Ka Ka pKa pKa ...
... 5. From the Ka values in the table, calculate the pKa for each compound. Using these data, arrange the compounds in order of increasing acidity and explain the trend. (Hint: be sure to identify the hydrogen to which the Ka applies.) Ka Ka pKa pKa ...
Write the symbols and electronic configurations for each of the first
... E.g. Iron in the Haber Process (ammonia being made from hydrogen and nitrogen) E.g. Rh, Pd & Pt in catalytic converters in automobiles (used to convert CO, nitrogen oxides and unburnt hydrocarbons into CO2, N2 and H2O. Homogeneous: the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants and product ...
... E.g. Iron in the Haber Process (ammonia being made from hydrogen and nitrogen) E.g. Rh, Pd & Pt in catalytic converters in automobiles (used to convert CO, nitrogen oxides and unburnt hydrocarbons into CO2, N2 and H2O. Homogeneous: the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants and product ...
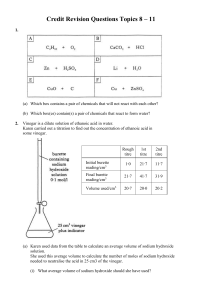
Credit Revision Questions Topics 8 – 11 1. (a) Which box contains a
... It reacts with cold water. ...
... It reacts with cold water. ...
CHEMISTRY MCQ
... a) chelates are more stable than ordinary complexes b) ordinary complexes are more stable than chelates c) monodentate ligand form chelate d) chelates have no ring structure 6) in contact process the catalyst used for conversion of SO2 to SO3 is a) magnesium oxide b) Aluminium oxide c) silicon dioxi ...
... a) chelates are more stable than ordinary complexes b) ordinary complexes are more stable than chelates c) monodentate ligand form chelate d) chelates have no ring structure 6) in contact process the catalyst used for conversion of SO2 to SO3 is a) magnesium oxide b) Aluminium oxide c) silicon dioxi ...
8th Grade Ch. 7 Chemical Reactions Study guide
... ____ 21. Substances formed during chemical reactions are ____. A. catalysts B. oxides C. reactants D. products ____ 22. A ____ is a process in which new substances are formed. A. chemical reaction B. catalyst C. reactant D. subscript ____ 23. The melting of ice is an example of a(n) ____. A. chemica ...
... ____ 21. Substances formed during chemical reactions are ____. A. catalysts B. oxides C. reactants D. products ____ 22. A ____ is a process in which new substances are formed. A. chemical reaction B. catalyst C. reactant D. subscript ____ 23. The melting of ice is an example of a(n) ____. A. chemica ...
CH 3 Br + Nu
... 10. Which statement(s) is/are true of an E1 elimination? A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation t ...
... 10. Which statement(s) is/are true of an E1 elimination? A) it is a two-step process and has the same first step as a SN1 mechanism B) it involves the formation of the carbocation from elimination of a good leaving group C) a common competing reaction is rearrangement of a less stable carbocation t ...
Aldehydes and Ketones
... Generally, the hemiacetals and acetals are only a minor component of an equilibrium mixture. In order to favor formation of acetals the carbonyl compound and alcohol is reacted with acid in the absence of water. Dry HCl) The acetals or hemiacetals maybe converted back to the carbonyl compound by tre ...
... Generally, the hemiacetals and acetals are only a minor component of an equilibrium mixture. In order to favor formation of acetals the carbonyl compound and alcohol is reacted with acid in the absence of water. Dry HCl) The acetals or hemiacetals maybe converted back to the carbonyl compound by tre ...
Extra Unit 3 Problems for the Web Site (Honors
... [Note that the questions marked (R) on the Unit 2 web page are relevant to Honors students in this unit) 1. Balance the following equations: (a) Ag2O ---> Ag + O2 (b) Zn + HCl ---> ZnCl2 + H2 (c) NaOH + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + H2O 2. Upon the addition of heat to an unknown amount of potassium chlorate, ...
... [Note that the questions marked (R) on the Unit 2 web page are relevant to Honors students in this unit) 1. Balance the following equations: (a) Ag2O ---> Ag + O2 (b) Zn + HCl ---> ZnCl2 + H2 (c) NaOH + H2SO4 ---> Na2SO4 + H2O 2. Upon the addition of heat to an unknown amount of potassium chlorate, ...
Organic Chemistry
... 1. Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. 2. Hydrocarbons are compounds of C and H. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, CH4, which is used for heating and in gas stoves for cooking. 3. Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds. (Saturated means “full.” Saturated hydrocar ...
... 1. Organic chemistry is the study of compounds containing carbon. 2. Hydrocarbons are compounds of C and H. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, CH4, which is used for heating and in gas stoves for cooking. 3. Saturated hydrocarbons have only single bonds. (Saturated means “full.” Saturated hydrocar ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.