General Chemistry (II) Chapter 1: Chemical Kinetic 1
... 3-10 Cathodic Protection 3-11 Corrosion 3-11-1 Corrosion of Iron 3-11-2 Oxidized Iron 3-12 Faraday’s Law and Silver Coulometer Chapter 4: Coordination Chemistry 4-1 Properties of Transition Metal 4-1-1 Electronic Configuration of Transition Metals ...
... 3-10 Cathodic Protection 3-11 Corrosion 3-11-1 Corrosion of Iron 3-11-2 Oxidized Iron 3-12 Faraday’s Law and Silver Coulometer Chapter 4: Coordination Chemistry 4-1 Properties of Transition Metal 4-1-1 Electronic Configuration of Transition Metals ...
Carbon and Organic Compounds
... Each C can form a maximum of four single bonds, OR two single and one double bond, OR one single and triple bond. The arrangement of C atoms determines the skeleton, so a straight chain and a bent chain represent the same skeleton. Groups joined by single bonds can rotate, so a branch pointing down ...
... Each C can form a maximum of four single bonds, OR two single and one double bond, OR one single and triple bond. The arrangement of C atoms determines the skeleton, so a straight chain and a bent chain represent the same skeleton. Groups joined by single bonds can rotate, so a branch pointing down ...
OrganicCompounds
... • Carbon is usually bonded to H, O or other non-metals • Carbon can bond with itself to form long chains of carbon atoms (polymers; eg: petroleum & plastics) • Organic compounds always have C before H in their formulas (eg: CH4) ...
... • Carbon is usually bonded to H, O or other non-metals • Carbon can bond with itself to form long chains of carbon atoms (polymers; eg: petroleum & plastics) • Organic compounds always have C before H in their formulas (eg: CH4) ...
Chapter 1-
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
... A ketone is formed by the first molar equivalent of Grignard reagent and this immediately reacts with a second equivalent to produce the alcohol The final product contains two identical groups at the alcohol carbon that are both derived from the Grignard reagent ...
Document
... 6. Enthalpies of solution A. are difficult to measure. C. can be positive or negative. E. are always positive. ...
... 6. Enthalpies of solution A. are difficult to measure. C. can be positive or negative. E. are always positive. ...
Practice Problem
... HBr, HI to alkenes to give Markovnikov product • Alkyl dihalide - is synthesized from anti addition of Br2 or Cl2 ...
... HBr, HI to alkenes to give Markovnikov product • Alkyl dihalide - is synthesized from anti addition of Br2 or Cl2 ...
Coordination Chemistry
... on another chemical species to form the new bond. This is different from a covalent bond because both electrons come from one atom or molecule but are shared as in a typical covalent bond. Unlike an ionic bond, a coordinate covalent bond does not rely on formal electrostatic attraction between a cat ...
... on another chemical species to form the new bond. This is different from a covalent bond because both electrons come from one atom or molecule but are shared as in a typical covalent bond. Unlike an ionic bond, a coordinate covalent bond does not rely on formal electrostatic attraction between a cat ...
Week 10 Problem Set (Answers) (4/17, 4/18, 4/19) Reactions and
... intermediate product given that the starting materials are both sources of even-numbered carbons. Additionally, we do not know how to back a carbon-carbon bond between an alkene and a primary carbon, and the alkene can’t have been formed via a reduction of an alkyne since it is disubstituted at one ...
... intermediate product given that the starting materials are both sources of even-numbered carbons. Additionally, we do not know how to back a carbon-carbon bond between an alkene and a primary carbon, and the alkene can’t have been formed via a reduction of an alkyne since it is disubstituted at one ...
CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 OH
... What is a hydrolysis reaction? Using water to break down a compounds into smaller parts. ...
... What is a hydrolysis reaction? Using water to break down a compounds into smaller parts. ...
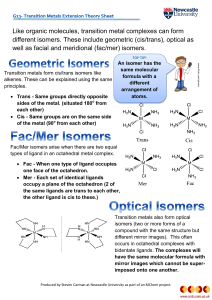
Like organic molecules, transition metal complexes can form
... Fac/Mer isomers arise when there are two equal types of ligand in an octahedral metal complex. Fac - When one type of ligand occupies one face of the octahedron. Mer - Each set of identical ligands occupy a plane of the octahedron (2 of the same ligands are trans to each other, the other ligand ...
... Fac/Mer isomers arise when there are two equal types of ligand in an octahedral metal complex. Fac - When one type of ligand occupies one face of the octahedron. Mer - Each set of identical ligands occupy a plane of the octahedron (2 of the same ligands are trans to each other, the other ligand ...
Chapter 13 – Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, and Thioethers
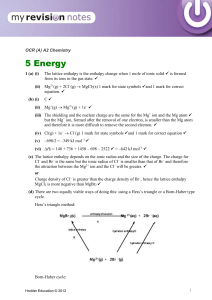
... forgotten it.) Le Châtelier’s principle reminds us that when a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will adjust so as restore the equilibrium. Although the temperatures at which these reactions ...
... forgotten it.) Le Châtelier’s principle reminds us that when a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will adjust so as restore the equilibrium. Although the temperatures at which these reactions ...
Exam practice answers 5
... (f) Add silver nitrate to each and observe the colour of the precipitate. MgCl2 would give a white solid and MgBr2 would give a cream solid. If dilute ammonia, NH3, is added the white precipitate dissolves. The cream precipitate will only dissolve in concentrated NH3. There are other ways of d ...
... (f) Add silver nitrate to each and observe the colour of the precipitate. MgCl2 would give a white solid and MgBr2 would give a cream solid. If dilute ammonia, NH3, is added the white precipitate dissolves. The cream precipitate will only dissolve in concentrated NH3. There are other ways of d ...
Introduction (HL)
... A halogenoalkane reacts with a hot solution of NaOH dissolved in ethanol to produce an alkene. ...
... A halogenoalkane reacts with a hot solution of NaOH dissolved in ethanol to produce an alkene. ...
CH 301 Practice Test Questions
... at 298 K and 1 atm pressure? The number below each substance is the absolute entropy of the substance at 298 K, 1 atm, in units of J/(mol•K). 19. What is the molarity of a HCl solution if 2.50 L is needed to react with 12.7 g of Al according to the reaction 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3H2 ? 20. Conside ...
... at 298 K and 1 atm pressure? The number below each substance is the absolute entropy of the substance at 298 K, 1 atm, in units of J/(mol•K). 19. What is the molarity of a HCl solution if 2.50 L is needed to react with 12.7 g of Al according to the reaction 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3H2 ? 20. Conside ...
Carboxylic Acids
... Electron withdrawing groups can increase acid strength by weakening the OH bond and stabilizing the acid anion. The positive inductive effect of E-groups is very small through more than two or three carbon-carbon bonds. Electron donating groups reduce the partially positive charge of carboxyl carbon ...
... Electron withdrawing groups can increase acid strength by weakening the OH bond and stabilizing the acid anion. The positive inductive effect of E-groups is very small through more than two or three carbon-carbon bonds. Electron donating groups reduce the partially positive charge of carboxyl carbon ...
NACOS with Nitroxy Radicals as Cocatalysts: An Efficient, Green
... with bulk electron withdrawing group. AZADO and 1Me-AZADO were reported to have higher catalytic efficiency than TEMPO due to less steric hindrance.29 However, they have not yet been employed in aerobic alcohol oxidations. As expected, the two displayed enhanced activities than TEMPO under our condi ...
... with bulk electron withdrawing group. AZADO and 1Me-AZADO were reported to have higher catalytic efficiency than TEMPO due to less steric hindrance.29 However, they have not yet been employed in aerobic alcohol oxidations. As expected, the two displayed enhanced activities than TEMPO under our condi ...
Direct production of hydrogen peroxide from CO, O2, and H2O over
... for highly selectively converting organic compounds into value-added products, as well as for industrial or municipal wastewater treatment and water disinfection.1 Currently, the commercial production of H2O2 is mainly based on a multistep process involving cyclic hydrogenation and oxidation of an a ...
... for highly selectively converting organic compounds into value-added products, as well as for industrial or municipal wastewater treatment and water disinfection.1 Currently, the commercial production of H2O2 is mainly based on a multistep process involving cyclic hydrogenation and oxidation of an a ...
Alcohols
... In case of acidic medium, nucleophile goes to more steric carbon i.e. carbon containing less number of hydrogen. In case of basic medium, nucleophile goes to less steric carbon i.e. carbon containing great number of hydrogen. ...
... In case of acidic medium, nucleophile goes to more steric carbon i.e. carbon containing less number of hydrogen. In case of basic medium, nucleophile goes to less steric carbon i.e. carbon containing great number of hydrogen. ...
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? __________________________________________ ...
... 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? __________________________________________ ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.