Organic Chemistry
... • Formula: R-OH (R stands for the “rest” of the molecule) • Examples: 1) Methyl alcohol (methanol) – wood alcohol, used as solvent for waxes, poisonous 2) Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) – alcohol made by fermenting grain, used to make perfume, dyes, rubber ...
... • Formula: R-OH (R stands for the “rest” of the molecule) • Examples: 1) Methyl alcohol (methanol) – wood alcohol, used as solvent for waxes, poisonous 2) Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) – alcohol made by fermenting grain, used to make perfume, dyes, rubber ...
Chemistry Final Exam Test Yourself I
... What reaction is taking place at the anode? (Fe(s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e- ) What reaction is taking place at the cathode? (Ni2+(aq) + 2e- → Ni(s) Where is the nitrate ion going? (to the anode) Where is the K+ ion going? (to the cathode) ...
... What reaction is taking place at the anode? (Fe(s) → Fe2+ (aq) + 2e- ) What reaction is taking place at the cathode? (Ni2+(aq) + 2e- → Ni(s) Where is the nitrate ion going? (to the anode) Where is the K+ ion going? (to the cathode) ...
enantioselective zeolite-catalyzed reactions
... major topic of discussion and research.1 Homogeneous, asymmetry-inducing catalysts have been developed for a wide range of reactions, especially notable are those developed by Knowles, Noyori and Sharpless, for which they jointly received the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.2 Although these reactions ...
... major topic of discussion and research.1 Homogeneous, asymmetry-inducing catalysts have been developed for a wide range of reactions, especially notable are those developed by Knowles, Noyori and Sharpless, for which they jointly received the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.2 Although these reactions ...
Organic Chemistry: Chemistry that involves Carbon
... only a small percentage is separated from crude oil. ...
... only a small percentage is separated from crude oil. ...
inorganic-chemistry-gp-i-alkali-metals
... and all metals reacts with sulphur and may forms polysulphide in presence of excess sulphur like M2Sn where n= 2, 3,4,5,6. M + P M3P the compound are according to the valences of the atom and there for easy to remember while the metal phosphide reacts with water to give phosgene and hydroxide. Rea ...
... and all metals reacts with sulphur and may forms polysulphide in presence of excess sulphur like M2Sn where n= 2, 3,4,5,6. M + P M3P the compound are according to the valences of the atom and there for easy to remember while the metal phosphide reacts with water to give phosgene and hydroxide. Rea ...
Hydrocarbons - OurTeachersPage.com
... •Each functional group gives the molecule distinctive chemical & physical properties. •Molecules with functional groups contain at least one atom that is not C or H. Not hydrocarbons! ...
... •Each functional group gives the molecule distinctive chemical & physical properties. •Molecules with functional groups contain at least one atom that is not C or H. Not hydrocarbons! ...
Regents Unit 15: Hydrocarbon Derivatives
... •Each functional group gives the molecule distinctive chemical & physical properties. •Molecules with functional groups contain at least one atom that is not C or H. Not hydrocarbons! ...
... •Each functional group gives the molecule distinctive chemical & physical properties. •Molecules with functional groups contain at least one atom that is not C or H. Not hydrocarbons! ...
Chapter #4 & 5- PPT - Lawndale High School
... • Mechanism (all natural phenomena are governed by physical & chemical laws) Miller ...
... • Mechanism (all natural phenomena are governed by physical & chemical laws) Miller ...
doc
... Why does this reaction work better for primary and secondary alcohols? These reagents are less acidic and less likely to cause acid catalyzed rearrangements. (Mechanisms are covered in Chapter 11.) ...
... Why does this reaction work better for primary and secondary alcohols? These reagents are less acidic and less likely to cause acid catalyzed rearrangements. (Mechanisms are covered in Chapter 11.) ...
... (8 x 5 = 40) 11. Give a mechanism for the reaction of tert.butyl bromide with aqueous NaOH to form tert.butyl alcohol. 12. Explain Saytzeff rule and Hofmann rule with an example. 13. How is phenol prepared from Cumene. 14. Although both phenol and alcohols contain hydroxyl group, Phenol is acidic wh ...
Reading Guide Organic Chemistry
... What is the fewest number of carbons needed for an alkane to have structural isomers? As the number of carbon atoms increases, what happens to the number of possible structural isomers? ...
... What is the fewest number of carbons needed for an alkane to have structural isomers? As the number of carbon atoms increases, what happens to the number of possible structural isomers? ...
Ch. 16: Solutions - Quynh Nguyen Official Website
... They tend to have similar bps to ethers of the same molar mass They tend to have much lower bps than alcohols, because alcohols are much more polar Aldehydes and ketones of 5 C atoms or less are soluble in water ...
... They tend to have similar bps to ethers of the same molar mass They tend to have much lower bps than alcohols, because alcohols are much more polar Aldehydes and ketones of 5 C atoms or less are soluble in water ...
Exam 2-f06 - Clayton State University
... 8.) The equilibrium constant, Kc for the following gas phase reaction is 0.50 at 600°C. A mixture of HCHO, H and CO is introduced into a flask at 600°C. After a short time, analysis of a small amount of the reaction mixture shows the concentration to be [HCHO] = 1.5M, [H2] = 1.2 M and [CO] = 1.0M. W ...
... 8.) The equilibrium constant, Kc for the following gas phase reaction is 0.50 at 600°C. A mixture of HCHO, H and CO is introduced into a flask at 600°C. After a short time, analysis of a small amount of the reaction mixture shows the concentration to be [HCHO] = 1.5M, [H2] = 1.2 M and [CO] = 1.0M. W ...
Aldehydes Ketones
... Direct addition (aka 1,2 addition) occurs when a nucleophile attacks the carbon in the carbonyl directly. Conjugate addition (aka 1,4 addition) occurs when the nucleophile attacks the carbonyl indirectly by attacking the second carbon away from the carbonyl group, called the beta carbon, in an u ...
... Direct addition (aka 1,2 addition) occurs when a nucleophile attacks the carbon in the carbonyl directly. Conjugate addition (aka 1,4 addition) occurs when the nucleophile attacks the carbonyl indirectly by attacking the second carbon away from the carbonyl group, called the beta carbon, in an u ...
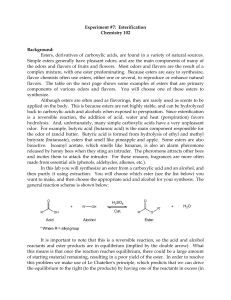
ESTERIFICATION
... effect, putting pressure on the left side). Usually, a threefold molar excess is enough to drive the equilibrium sufficiently to the right in an esterification reaction. Either the alcohol or the acid can be used in excess. The choice can be based on cost, availability and/or ease of purification a ...
... effect, putting pressure on the left side). Usually, a threefold molar excess is enough to drive the equilibrium sufficiently to the right in an esterification reaction. Either the alcohol or the acid can be used in excess. The choice can be based on cost, availability and/or ease of purification a ...
C h e m g u i d e ... HALOGENOALKANES: MAKING
... b) In the bromine and iodine case, you don’t actually start with PBr3 or PI3. Instead, you use a mixture of red phosphorus and either bromine or iodine which first react to make these compounds. Write the equation for the reaction between red phosphorus and bromine to produce PBr3. c) Phosphorus(V) ...
... b) In the bromine and iodine case, you don’t actually start with PBr3 or PI3. Instead, you use a mixture of red phosphorus and either bromine or iodine which first react to make these compounds. Write the equation for the reaction between red phosphorus and bromine to produce PBr3. c) Phosphorus(V) ...
Determining structure of copper complexes with nicotinic
... complexes with aroylhydrazones derived from nicotinic acid hydrazide and salicylaldehide derivatives having different substituents on the benzene ring. Aroylhydrazones can be involved in keto-enol tautomeric interconversion, when the hydrogen atom in keto form moves from amino to carbonyl group, for ...
... complexes with aroylhydrazones derived from nicotinic acid hydrazide and salicylaldehide derivatives having different substituents on the benzene ring. Aroylhydrazones can be involved in keto-enol tautomeric interconversion, when the hydrogen atom in keto form moves from amino to carbonyl group, for ...
Octenes from E1 versus E2 Eliminations
... Group Ltd., London (1966) and Gilow, H. M. Microscale Elimination Reactions, J. Chem. Educ. 1992 69 A265) [Rev 3/16/02] ...
... Group Ltd., London (1966) and Gilow, H. M. Microscale Elimination Reactions, J. Chem. Educ. 1992 69 A265) [Rev 3/16/02] ...
Topic 8 Assessed Homework Task - A
... The structures and names of some of these isomers are given below. Structure ...
... The structures and names of some of these isomers are given below. Structure ...
Absorption Spectra and Colours of Complexes
... "Normal" bonding occurs when a ligand donates electrons to a metal. When a metal ion donates electrons back to the ligand, this is called back-bonding. The combination of normal bonding and back-bonding creates a strong bond between the ligand and the metal. The reason that phosphines, carbon monoxi ...
... "Normal" bonding occurs when a ligand donates electrons to a metal. When a metal ion donates electrons back to the ligand, this is called back-bonding. The combination of normal bonding and back-bonding creates a strong bond between the ligand and the metal. The reason that phosphines, carbon monoxi ...
Chemistry Standards Review
... 37. In the reaction, 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO, if 100.0 g of magnesium reacts with 50.0 g of oxygen, what mass of product is produced? Gases and Their Properties 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 39. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 40. Explain diffusion, use KMT to sup ...
... 37. In the reaction, 2 Mg + O2 2 MgO, if 100.0 g of magnesium reacts with 50.0 g of oxygen, what mass of product is produced? Gases and Their Properties 38. What is the kinetic molecular theory? 39. How do gases create pressure, use KMT to support your answer. 40. Explain diffusion, use KMT to sup ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.