* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
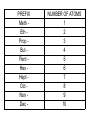
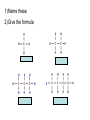
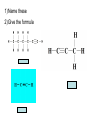
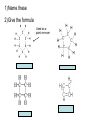
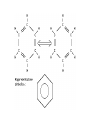
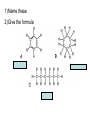
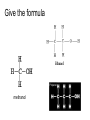
Organic Chemistry Organic Compounds • Compounds that contain carbon • Found in all living things Structure of Carbon • Carbon has 4 valence electrons • Can form bonds with 4 other atoms = wide variety of compounds Hydrocarbons • Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen • Includes: 1) Natural gas – used to heat homes 2) Gasoline – used in cars 3) Kerosene, Butane – used in portable heaters 4) Turpentine – paint thinners Alkanes • Group of hydrocarbons that have only single bonds between carbon atoms • Called “saturated hydrocarbons” because they contain the maximum amount of hydrogen Naming Alkanes • All alkanes end in –ane Ex. methane, ethane, propane • Use prefix to tell how many carbon atoms are present (up to 10) PREFIX Meth Eth Prop But Pent Hex Hept Oct Non Dec - NUMBER OF ATOMS 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1)Name these 2)Give the formula Alkenes • Hydrocarbons that contain one double bond between carbon atoms • Called “unsaturated hydrocarbon” because it does not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms • Alkenes end in – ene • Prefixes are the same as alkanes 1)Name these 2)Give the formula Sprayed on orchards Alkynes • Hydrocarbons that contain one triple bond between carbon atoms • Called “unsaturated hydrocarbon” because it does not have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms • All alkynes end in - yne • Prefixes are the same as alkanes and alkenes 1)Name these 2)Give the formula 1-Hexyne Propyne Ethyne Isomers • Two hydrocarbons with the same molecular formula but with different structural formulas • Have different chemical and physical properties 2-Methyl propane Butane Cyclic Hydrocarbons • Hydrocarbon with a round or ring-type structure • Use same naming rules as regular hydrocarbons but the prefix cyclo- is added Cyclopropane Used as an anesthetic 1)Name these 2)Give the formula Used as a paint remover Cyclohexane Cyclopentane Cyclobutene Cyclobutane Aromatic Hydrocarbons • Molecules that have alternating single and double bonds in six-carbon ring structures • Named because many have a pleasant odor • Found in aspirin, moth balls, explosives, and plastic foam products 1)Name these 2)Give the formula Benzene Cyclohexane Hexane Substituted Hydrocarbons • • Organic compounds with more than just carbon and hydrogen Many practical uses: 1) Freon – used in air conditioners, refrigerators 2) Chloromethane – used in medicines 3) Toluene – used in paint, glue 4) Chlorotoluene – used in dyes, perfume Alcohol • Hydrocarbon in which a hydrogen atom is replaced with a hydroxyl group (OH) • Formula: R-OH (R stands for the “rest” of the molecule) • Examples: 1) Methyl alcohol (methanol) – wood alcohol, used as solvent for waxes, poisonous 2) Ethyl alcohol (ethanol) – alcohol made by fermenting grain, used to make perfume, dyes, rubber Give the formula methanol Organic Acids • Compound formed when one hydrogen of a hydrocarbon is replaced with by a carboxyl group • Carboxyl group consists of 1 carbon, 2 oxygen, and 1 hydrogen • Formula: R-COOH • Example: - Acetic acid (CH3COOH) – present in vinegar Esters • Product of the reaction between an organic acid and an alcohol • Used in making perfumes and flavor of fruits is due to esters Chemistry of Living Things • Organic compounds make up 1/3 of the human body is made up of organic and inorganic compounds • Organic compounds include: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids Carbohydrates • Hydrogen and oxygen atoms are in a 2-1 ratio • Ex: Starches and sugars • Plants use photosynthesis to make sugars • Provides short term energy Lipids • • • • • Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen Provides long-term energy Ex: fats, oils, waxes Animal fats = saturated lipids (bonds?) Vegetable fats (corn oil, peanut oil, olive oil) = unsaturated lipids (bonds?) • Subunit = fatty acid Proteins • Made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen • Most of the muscles, skin, hair, and internal organs are made of protein • Subunit = amino acids • Contain an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) • Different R groups create 20 different amino acids Nucleic Acids • Organic compounds that control the functions of cells • DNA contains info about how to arrange amino acids to make proteins • RNA controls the building of proteins