Exam 2 Fall 2005 Chemsitry 1211
... Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
... Ca(OH)2 solution, what is the molarity of the Ca(OH)2 solution? a.) b.) c.) d.) e.) ...
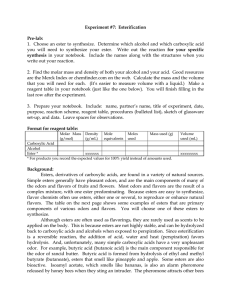
Lab 7_Esterification
... It is important to note that this is a reversible reaction, so the acid and alcohol reactants and ester products are in equilibrium (implied by the double arrow). What this means is that once the reaction reaches equilibrium, there could be a large amount of starting material remaining, resulting in ...
... It is important to note that this is a reversible reaction, so the acid and alcohol reactants and ester products are in equilibrium (implied by the double arrow). What this means is that once the reaction reaches equilibrium, there could be a large amount of starting material remaining, resulting in ...
Test Review
... You should know how to name and draw the structures for the following classes of compounds: alcohols, ethers (both IUPAC and common ways), phenols (see ch. 12), and thiols. ...
... You should know how to name and draw the structures for the following classes of compounds: alcohols, ethers (both IUPAC and common ways), phenols (see ch. 12), and thiols. ...
a. Rank by acidity. The most acidic compound is 1, wh
... Of the following reactions that generate glycols, one reacts with periodic acid as shown above, while the second does not react with the periodic acid. Draw the structures obtained for each of these reactions. Assume proper work-up for each step. (12 points) O ...
... Of the following reactions that generate glycols, one reacts with periodic acid as shown above, while the second does not react with the periodic acid. Draw the structures obtained for each of these reactions. Assume proper work-up for each step. (12 points) O ...
Amines - MCAT Cooperative
... Anomers: isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the anomeric carbon, (carbonyl carbon prior to hemiacetalation or hemiaketalation. ...
... Anomers: isomeric forms of monosaccharides that differ only in their configuration about the anomeric carbon, (carbonyl carbon prior to hemiacetalation or hemiaketalation. ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 25 - Ms. Ose's Chemistry Website
... Branched chain hydrocarbons: hydrocarbon chains with four or more atoms can form branches rather ...
... Branched chain hydrocarbons: hydrocarbon chains with four or more atoms can form branches rather ...
C - sciencegeek
... acids in which the –OH of the carboxyl group has been replaced by an –OR from an alcohol. ...
... acids in which the –OH of the carboxyl group has been replaced by an –OR from an alcohol. ...
Chapter 4 - Warren County Schools
... This leads to formation of large, complex, and diverse molecules ...
... This leads to formation of large, complex, and diverse molecules ...
Presentation
... • Branch of science dealing with the element carbon and its many properties. – It is usually associated with all living organisms. • About 30% of an organism’s dry weight (called Biomass) is Carbon in organic molecules. – Helps to make the organic molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucl ...
... • Branch of science dealing with the element carbon and its many properties. – It is usually associated with all living organisms. • About 30% of an organism’s dry weight (called Biomass) is Carbon in organic molecules. – Helps to make the organic molecules: Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucl ...
Document
... • Green chemistry is the use of environmentally benign methods to synthesize compounds. • Its purpose is to use safer reagents and less solvent, and develop reactions that form fewer by-products and generate less waste. • Since many oxidation methods use toxic reagents (such as OsO4 and O3) and corr ...
... • Green chemistry is the use of environmentally benign methods to synthesize compounds. • Its purpose is to use safer reagents and less solvent, and develop reactions that form fewer by-products and generate less waste. • Since many oxidation methods use toxic reagents (such as OsO4 and O3) and corr ...
Key Concepts PowerPoint
... Predict the crystal field energy-level diagram for a square pyramidal ML5 complex that has two ligands along the +x and +y axes but only one ligand along the z axis. Your diagram should be intermediate between those for an octahedral ML6 complex and a square planar ML4 complex. ...
... Predict the crystal field energy-level diagram for a square pyramidal ML5 complex that has two ligands along the +x and +y axes but only one ligand along the z axis. Your diagram should be intermediate between those for an octahedral ML6 complex and a square planar ML4 complex. ...
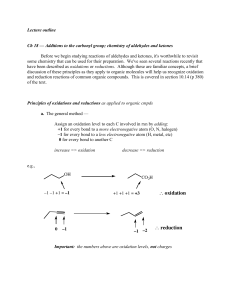
Aldehydes and Ketones
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
... 2. Cleavage of Carbon–Carbon double bond by Ozone: Oxidative cleavage of an alkene breaks both the σ and π bonds of the double bond to form two carbonyl groups. Depending on the number of R groups bonded to the double bond, oxidative cleavage yields either ketones or aldehydes. ...
Chemical Equations
... (aka Oxidation Number) Hypothetical charge use to indicate the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) Rules in assigning oxidation states: 1) The oxidation state of a free element is zero (0). ex. O2 (g), Ag (s) 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its ionic charge. (ex. Na+, Cl-3) ...
... (aka Oxidation Number) Hypothetical charge use to indicate the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) Rules in assigning oxidation states: 1) The oxidation state of a free element is zero (0). ex. O2 (g), Ag (s) 2) The oxidation state of a monatomic ion is equal to its ionic charge. (ex. Na+, Cl-3) ...
Slide 1
... 3) p-MO’s of cyclic conjugated ligands For qualitative analysis of bonding between transition metals and p-electron donors such as organic compounds with C=C bonds it is necessary to know how the ligand p-MO’s look like. Frost diagrams allow establish the shape, degeneracy and the energy sequence o ...
... 3) p-MO’s of cyclic conjugated ligands For qualitative analysis of bonding between transition metals and p-electron donors such as organic compounds with C=C bonds it is necessary to know how the ligand p-MO’s look like. Frost diagrams allow establish the shape, degeneracy and the energy sequence o ...
NOTES CHEMICAL REACTIONS:
... • 6. Insoluble: All salts containing carbonate, chromates, hydroxides, oxides, phosphates, and sulfides • Exceptions: • Group IIA chromates, except barium chromate are solulbe • Group IIA hydroxides, except magnesium hydroxide, are soluble ...
... • 6. Insoluble: All salts containing carbonate, chromates, hydroxides, oxides, phosphates, and sulfides • Exceptions: • Group IIA chromates, except barium chromate are solulbe • Group IIA hydroxides, except magnesium hydroxide, are soluble ...
File
... 18. Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration constant and average life period. How much time will it take for 90% decay? 19. (a) Describe the structure and magnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2– ion on the basis of valence bond theory. (Atomic No. of Ni = 28) ...
... 18. Half-life period of a radioactive element is 100 seconds. Calculate the disintegration constant and average life period. How much time will it take for 90% decay? 19. (a) Describe the structure and magnetic behaviour of [Ni(CN)4]2– ion on the basis of valence bond theory. (Atomic No. of Ni = 28) ...
Chemical Reactions
... indicate relative, not absolute, amounts of reactants and products. 2. The relative masses of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction can be determined from the reaction’s coefficients. 3. The reverse reaction for a chemical equation has the same relative amounts of substances as the forwa ...
... indicate relative, not absolute, amounts of reactants and products. 2. The relative masses of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction can be determined from the reaction’s coefficients. 3. The reverse reaction for a chemical equation has the same relative amounts of substances as the forwa ...
chemistry (paper 2)
... Chemical change ................................................................................................................................................................................. 3 Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions ................................................................... ...
... Chemical change ................................................................................................................................................................................. 3 Endothermic and Exothermic Reactions ................................................................... ...
Organic Reactions
... Organic Reactions Why? Many organic reactions lead to products we use everyday. Organic reactions can be categorized by looking at the reactants used and the products formed. Soap, alcohol, fragrances, flavors and flames in your barbeque are all products of organic reactions. ...
... Organic Reactions Why? Many organic reactions lead to products we use everyday. Organic reactions can be categorized by looking at the reactants used and the products formed. Soap, alcohol, fragrances, flavors and flames in your barbeque are all products of organic reactions. ...
Question paper - Unit A173/02 - Module C7 - Higher tier
... Fill in the boxes to complete the balanced symbol equation for burning propane. ...
... Fill in the boxes to complete the balanced symbol equation for burning propane. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.