Alkenes
... In industry, the hydration of ethene is carried out by the direct reaction of ethene and steam. The conditions used are: temperature: 300oC pressure: 65 atmospheres catalyst: phosphoric acid (H3PO4) adsorbed on celite ...
... In industry, the hydration of ethene is carried out by the direct reaction of ethene and steam. The conditions used are: temperature: 300oC pressure: 65 atmospheres catalyst: phosphoric acid (H3PO4) adsorbed on celite ...
ch08 by dr. Dina
... act as a nucleophile to open the halonium ion The product is a halohydrin Halogenations in aqueous solvent Cl2/H2O (HOCl) or Br2/H2O (HOBr) the OH act as nucleophil (Nu+) and halogen as electrophyl Eoverall reaction is: halogen added to less substituted carbon (with more hydrogen) ...
... act as a nucleophile to open the halonium ion The product is a halohydrin Halogenations in aqueous solvent Cl2/H2O (HOCl) or Br2/H2O (HOBr) the OH act as nucleophil (Nu+) and halogen as electrophyl Eoverall reaction is: halogen added to less substituted carbon (with more hydrogen) ...
Biocatalysis Center of Emphasis
... Cathal Healy, John O’Shaughnessy, Éanna Ó Maitiú, Floriana Stomeo, Gillian Whittaker, and John Wong ...
... Cathal Healy, John O’Shaughnessy, Éanna Ó Maitiú, Floriana Stomeo, Gillian Whittaker, and John Wong ...
Warm-Up
... 3. If the pH of a lake is 4.0, what is the hydrogen ion [H+] concentration of the lake? What is the hydroxide [OH-] concentration? ...
... 3. If the pH of a lake is 4.0, what is the hydrogen ion [H+] concentration of the lake? What is the hydroxide [OH-] concentration? ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry (Carbon Chemistry)
... The PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS are generally determined by three factors: a) The carbon skeleton is a very stable, chemically unreactive structure. b) The presence of double or triple bonds increases the reactivity of carbon skeletons. c) “Functional groups" which are other atoms or groups of a ...
... The PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS are generally determined by three factors: a) The carbon skeleton is a very stable, chemically unreactive structure. b) The presence of double or triple bonds increases the reactivity of carbon skeletons. c) “Functional groups" which are other atoms or groups of a ...
PowerPoint **
... α, β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds with a leaving group in the β position are susceptible to addition-elimination reactions. ...
... α, β-Unsaturated carbonyl compounds with a leaving group in the β position are susceptible to addition-elimination reactions. ...
Functional Groups
... Atoms other than hydrogen or carbon covalently bonded to a carbon atom in an organic molecule. Most commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or the halogens. The presence of a functional group drastically changes the chemical properties of a molecule. ...
... Atoms other than hydrogen or carbon covalently bonded to a carbon atom in an organic molecule. Most commonly oxygen, nitrogen, or the halogens. The presence of a functional group drastically changes the chemical properties of a molecule. ...
Instructions for Preparing Manuscript for Bulletin of
... metal and they exhibits octahedral geometry. The catalytic activity of these complexes was studied in olefins using eco-friendly nontoxic molecular oxygen as oxidant. KEYWORDS: Amino acid, Metal complexes, cysteine, Molecular Oxygen ...
... metal and they exhibits octahedral geometry. The catalytic activity of these complexes was studied in olefins using eco-friendly nontoxic molecular oxygen as oxidant. KEYWORDS: Amino acid, Metal complexes, cysteine, Molecular Oxygen ...
Five Slides About: UV-Vis Spectroscopy and Tanabe
... “relatively stable” (meaning relative to its CuII complex under the controlled experimental conditions). 3. Suggest why they are soluble in H2O. 4. It turns out for the reaction: CuI + n L CuILn Kf(CuIMe6Trien) < Kf(CuIBCA2) < Kf(CuIBCS2) Suggest why it is useful to have 3 ligands with 3 differing ...
... “relatively stable” (meaning relative to its CuII complex under the controlled experimental conditions). 3. Suggest why they are soluble in H2O. 4. It turns out for the reaction: CuI + n L CuILn Kf(CuIMe6Trien) < Kf(CuIBCA2) < Kf(CuIBCS2) Suggest why it is useful to have 3 ligands with 3 differing ...
Ketones - WordPress.com
... Both aldehydes and ketones form an orange precipitate with 2,4-DNPH. To differentiate, we may react the solution with Tollens’ reagent – a solution of silver nitrate in excess ammonia. ...
... Both aldehydes and ketones form an orange precipitate with 2,4-DNPH. To differentiate, we may react the solution with Tollens’ reagent – a solution of silver nitrate in excess ammonia. ...
Contents
... 3 Organocobalt Syntheses via Cobalt (I) Reagents, 250 4 Organocobalt Syntheses via Cobalt(II) Reagents, 271 5 Organocobalt Syntheses via Cobalt(III) Reagents, 277 ...
... 3 Organocobalt Syntheses via Cobalt (I) Reagents, 250 4 Organocobalt Syntheses via Cobalt(II) Reagents, 271 5 Organocobalt Syntheses via Cobalt(III) Reagents, 277 ...
WS Unit Review File
... True or False – If the statement is true, write “true.” If it is false, write “false” and then change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 11. Acids are often defined a proton donors. 12. Strong acids are poor electrolytes. 13. Weak bases produce small numbers of ions when disso ...
... True or False – If the statement is true, write “true.” If it is false, write “false” and then change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 11. Acids are often defined a proton donors. 12. Strong acids are poor electrolytes. 13. Weak bases produce small numbers of ions when disso ...
New MOF materials: structure-properties
... materials show catalytic activity in the oxidation of methyl phenyl sulfide. Among all them, those belonging to the LRH family, with a 2D structure with cationic inorganic layers, are very active and selective catalysts in sulfides oxidation. Those belonging to the RPF families are also good catalys ...
... materials show catalytic activity in the oxidation of methyl phenyl sulfide. Among all them, those belonging to the LRH family, with a 2D structure with cationic inorganic layers, are very active and selective catalysts in sulfides oxidation. Those belonging to the RPF families are also good catalys ...
Regular Evening08-11-2013Tuition
... boiling point of 80.31℃. Determine the molar mass of this compound (B.P of purebenzene = 80.10℃ and Kb for benzene = 2.53℃ Kg/mol) 9. Define the terms Osmosis and Osmotic pressure what is the advantage of using osmotic pressure as compared to other colligative properties for the determination of mol ...
... boiling point of 80.31℃. Determine the molar mass of this compound (B.P of purebenzene = 80.10℃ and Kb for benzene = 2.53℃ Kg/mol) 9. Define the terms Osmosis and Osmotic pressure what is the advantage of using osmotic pressure as compared to other colligative properties for the determination of mol ...
Final exam review - Iowa State University
... 29. Without doing a calculation, predict whether the entropy change will be positive or negative when each of the following reactions occurs in the direction it is written. a. CH3OH(l) + 3/2 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) b. Na(s) + 1/2 F2(g) NaF(s) ...
... 29. Without doing a calculation, predict whether the entropy change will be positive or negative when each of the following reactions occurs in the direction it is written. a. CH3OH(l) + 3/2 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) b. Na(s) + 1/2 F2(g) NaF(s) ...
1) In the reaction H2O + CH3COOH H3O+ + CH3COO
... Numerical Problems. You must show all your work for complete credit. 6) (20 points) Consider an aqueous solution which contains 0.010 M acetic acid (CH3COOH), 0.010 M sodium acetate (Na+ CH3COO-) and 0.010 M sodium chloride (Na+ Cl-). The pKA of acetic acid is 4.75. a) Assuming that all activity co ...
... Numerical Problems. You must show all your work for complete credit. 6) (20 points) Consider an aqueous solution which contains 0.010 M acetic acid (CH3COOH), 0.010 M sodium acetate (Na+ CH3COO-) and 0.010 M sodium chloride (Na+ Cl-). The pKA of acetic acid is 4.75. a) Assuming that all activity co ...
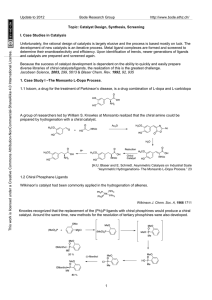
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.