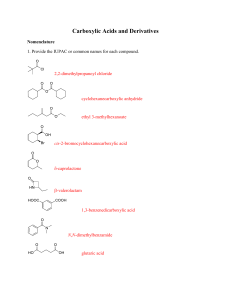
Chapter 18
... Upon application of light, a cis/trans interconversion occurs which is converted into an electrochemical impulse by affecting the concentration of Ca2+ crossing a cell membrane ...
... Upon application of light, a cis/trans interconversion occurs which is converted into an electrochemical impulse by affecting the concentration of Ca2+ crossing a cell membrane ...
Answer keys
... 3. Rank the compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution. ...
... 3. Rank the compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution. ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Asymmetric synthesis: Stoichiometric and catalytic use of reagents Examples of the latter: Sharpless epoxidation, Rh-catalyzed hydrogenation, ketone reductions; Itsuno-Corey reductions, Ru-catalyzed hydrogenations ( for illustration only, details to be covered in next course) Diastereotopic relation ...
... Asymmetric synthesis: Stoichiometric and catalytic use of reagents Examples of the latter: Sharpless epoxidation, Rh-catalyzed hydrogenation, ketone reductions; Itsuno-Corey reductions, Ru-catalyzed hydrogenations ( for illustration only, details to be covered in next course) Diastereotopic relation ...
Slide 1
... can also be written by using the symbol R to represent the alkyl group, CnH2n+1 or the phenyl group, C6H5. (R’ and R’’ represent two alkyl groups. The alkyl groups can be the same or different.) The phenyl group (- C6H5) has the structural formula of: ...
... can also be written by using the symbol R to represent the alkyl group, CnH2n+1 or the phenyl group, C6H5. (R’ and R’’ represent two alkyl groups. The alkyl groups can be the same or different.) The phenyl group (- C6H5) has the structural formula of: ...
Alkane
... α-carbon. This will make the C less open to attack by the OH- in forming the transition state. 2.The effect of solvent. If the solvent is itself Nu, it may participate in the reaction as a reagent. 3.The nature of X. The weaker the C-X bond, the more readily will the sub. take place. Alternatively, ...
... α-carbon. This will make the C less open to attack by the OH- in forming the transition state. 2.The effect of solvent. If the solvent is itself Nu, it may participate in the reaction as a reagent. 3.The nature of X. The weaker the C-X bond, the more readily will the sub. take place. Alternatively, ...
Tris-2,2’-bipyridine Complexes of Iron(II) and Ruthenium (II): Synthesis, Spectroscopy and Electrochemistry
... You will probe the redox behavior of [Ru(bpy)3]2+ and [Fe(bpy)3]2+. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) will be used to make the measurements. Make up 50 mL of acetonitrile/0.1 M TEABF4 (tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate), set up the electrochemical cell and bubble the solution with argon or nitrogen for app ...
... You will probe the redox behavior of [Ru(bpy)3]2+ and [Fe(bpy)3]2+. Cyclic Voltammetry (CV) will be used to make the measurements. Make up 50 mL of acetonitrile/0.1 M TEABF4 (tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroborate), set up the electrochemical cell and bubble the solution with argon or nitrogen for app ...
Chemistry - NTU.edu - Nanyang Technological University
... (a) Reaction of the elements with oxygen, chlorine and water (b) Variation in oxidation number of the oxides (sodium to sulphur only) and of the chlorides (sodium to phosphorus only) (c) Reactions of these oxides and chlorides with water (d) Acid/base behaviour of these oxides and the corresponding ...
... (a) Reaction of the elements with oxygen, chlorine and water (b) Variation in oxidation number of the oxides (sodium to sulphur only) and of the chlorides (sodium to phosphorus only) (c) Reactions of these oxides and chlorides with water (d) Acid/base behaviour of these oxides and the corresponding ...
Chemistry I Final Exam Review Problems 2016
... ____ 77. Solid magnesium reacts with excess hydrochloric acid at STP to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. Write the balanced equation. What volume of hydrogen gas will be produced if 12.0 g of magnesium react? a. 5.53 L c. 11.1 L b. 4.88 L d. 269 L ...
... ____ 77. Solid magnesium reacts with excess hydrochloric acid at STP to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen gas. Write the balanced equation. What volume of hydrogen gas will be produced if 12.0 g of magnesium react? a. 5.53 L c. 11.1 L b. 4.88 L d. 269 L ...
AP Biology Functional Groups of Carbon
... The ester functional group does not look much different next to the carboxylic acid functional group. In fact you might notice the only difference is the hydrogen atom, present in the carboxylic acid absent in the ester. This IS the key difference. Ester have carbon atoms in place of that hydrogen. ...
... The ester functional group does not look much different next to the carboxylic acid functional group. In fact you might notice the only difference is the hydrogen atom, present in the carboxylic acid absent in the ester. This IS the key difference. Ester have carbon atoms in place of that hydrogen. ...
A Guide to Rate of Reactions
... This resource is licensed under a Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 South Africa licence. When using ...
... This resource is licensed under a Attribution-Share Alike 2.5 South Africa licence. When using ...
Click on image to content
... discrimination. He can’t distinguish between good and bad, right or wrong. The consumption of alcohol in large quantities may even cause death by damaging the liver. If methanol is consumed in small quantities, it causes serious poisoning resulting in the loss of eyesight. ...
... discrimination. He can’t distinguish between good and bad, right or wrong. The consumption of alcohol in large quantities may even cause death by damaging the liver. If methanol is consumed in small quantities, it causes serious poisoning resulting in the loss of eyesight. ...
Lecture 2.
... A carborane is a cluster composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms. Like many of the related boranes, these clusters are polyhedral and are similarly classified as closo-, nido-, arachno-, hypho-, etc. based on whether they represent a complete (closo-) polyhedron, or a polyhedron that is missing ...
... A carborane is a cluster composed of boron, carbon and hydrogen atoms. Like many of the related boranes, these clusters are polyhedral and are similarly classified as closo-, nido-, arachno-, hypho-, etc. based on whether they represent a complete (closo-) polyhedron, or a polyhedron that is missing ...
FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
... PROPERTIES OF AMIDES • C-N, N-H, C=O bonds are polar, so molecules are usually polar • Primary and secondary amides experience hydrogen bonding • Soluble in water and other polar solvents, solubility decreases as the number of carbons increases • Primary amides have higher melting and boiling point ...
... PROPERTIES OF AMIDES • C-N, N-H, C=O bonds are polar, so molecules are usually polar • Primary and secondary amides experience hydrogen bonding • Soluble in water and other polar solvents, solubility decreases as the number of carbons increases • Primary amides have higher melting and boiling point ...
Research Biography
... activation, and NOx reduction processes via metal free dual acid catalysis. My previous research projects at CEBC, University of Kansas were focused on gaining an improved understanding of industrially important chemical processes, and involved extensive collaboration with Chemical Engineering group ...
... activation, and NOx reduction processes via metal free dual acid catalysis. My previous research projects at CEBC, University of Kansas were focused on gaining an improved understanding of industrially important chemical processes, and involved extensive collaboration with Chemical Engineering group ...
01 Chemical bases of life
... Each hydrogen atom has one electron. As the two hydrogen atoms get closer together, the positively charged nucleus of each atom begins to attract the electron of the other atom. At an optimal distance, the two nuclei mutually attract the two electrons, and each electron is shared by both nuclei. The ...
... Each hydrogen atom has one electron. As the two hydrogen atoms get closer together, the positively charged nucleus of each atom begins to attract the electron of the other atom. At an optimal distance, the two nuclei mutually attract the two electrons, and each electron is shared by both nuclei. The ...
Chapter 10 for 301
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
... There cannot be any acidic protons in the solvent, as the Grignard is such a strong base. There cannot be any pi bonds in the solvent as those are sites of reactivity that the Grignard will attack. From here on, I will use Grignard to refer to both Grignard reagents and organolithiums, as they ...
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... B. fermentation: breaking down of sugar without oxygen; products are ethanol and carbon dioxide; enzymes provided by yeast or bacteria example: glucose ethanol + carbon dioxide C. oxidation: combustion or burning of hydrocarbons with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water; supplies our society wi ...
... B. fermentation: breaking down of sugar without oxygen; products are ethanol and carbon dioxide; enzymes provided by yeast or bacteria example: glucose ethanol + carbon dioxide C. oxidation: combustion or burning of hydrocarbons with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water; supplies our society wi ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.