Industriel katalys
... Catalysis: definition, classification with examples, selectivity issues a) Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis b) Gas phase-, liquid phase-, biphasic catalysis, phase-transfer catalysis c) Metal catalysis, biocatalysis, organocatalysis Safety issues: risk and safety analysis, oxygen balance II. ...
... Catalysis: definition, classification with examples, selectivity issues a) Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis b) Gas phase-, liquid phase-, biphasic catalysis, phase-transfer catalysis c) Metal catalysis, biocatalysis, organocatalysis Safety issues: risk and safety analysis, oxygen balance II. ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
... a) energy is released when an electron jumps to a lower energy level. b) electrons travel in circular paths called orbitals. c) the energy of an electron may have any arbitrary value. d) the spectrum produced by hydrogen atoms should be a continuous spectrum. ...
... a) energy is released when an electron jumps to a lower energy level. b) electrons travel in circular paths called orbitals. c) the energy of an electron may have any arbitrary value. d) the spectrum produced by hydrogen atoms should be a continuous spectrum. ...
Lab 7
... Figure 6. Oxidation Methodology. We determine that the bond that is most easily oxidized is the C-H bond alpha to the carbonyl group in cyclohexanone. When this bond is cleaved, Step 1, we replace the H atom with an –OH group. The generalized methodology is to place –OH groups on open valences where ...
... Figure 6. Oxidation Methodology. We determine that the bond that is most easily oxidized is the C-H bond alpha to the carbonyl group in cyclohexanone. When this bond is cleaved, Step 1, we replace the H atom with an –OH group. The generalized methodology is to place –OH groups on open valences where ...
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic acids
... Sterically, the presence of two bulky (large) groups in ketones will hinder the attack of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon in ketone. Aldehydes have only one bulky group around the carbonyl carbon and it is easier for the nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon as compared to ketones. Electronically ...
... Sterically, the presence of two bulky (large) groups in ketones will hinder the attack of nucleophile to carbonyl carbon in ketone. Aldehydes have only one bulky group around the carbonyl carbon and it is easier for the nucleophile to attack the carbonyl carbon as compared to ketones. Electronically ...
Semester 2 Review
... B. How will an increase in pressure affect the system? ___________________ C. Which direction will the addition of iodine gas shift the system? _________________ What does this do to the concentration of hydrogen gas? _______________________ 64. At 773 K, the reaction: 2 NO(g) + O2 (g) 2NO2 (g) p ...
... B. How will an increase in pressure affect the system? ___________________ C. Which direction will the addition of iodine gas shift the system? _________________ What does this do to the concentration of hydrogen gas? _______________________ 64. At 773 K, the reaction: 2 NO(g) + O2 (g) 2NO2 (g) p ...
Organic Chemistry
... • Halogenation is the replacement of one or more hydrogens in an organic compound by halogen atoms • When methane is reacted with chlorine the products of the reaction depend on whether there is an excess of methane or ...
... • Halogenation is the replacement of one or more hydrogens in an organic compound by halogen atoms • When methane is reacted with chlorine the products of the reaction depend on whether there is an excess of methane or ...
Make Your Own Summary 1. single displacement reaction 2
... neither a single reactant nor a single product, so it can be neither a synthesis reaction nor a decomposition reaction. The reactants are a compound and an element, which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from ...
... neither a single reactant nor a single product, so it can be neither a synthesis reaction nor a decomposition reaction. The reactants are a compound and an element, which prevents the reaction from being a double displacement reaction. The products are two compounds, which prevent the reaction from ...
Preparation and Reaction of Carboxylic Acids - IDC
... nucleophilic group are important for preparing functional derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alcohols provide a usefulreference chemistry against which this class of transformations may be evaluated. In general, the hydroxyl group proved to be a poor leaving group, and virtually all alcohol reacti ...
... nucleophilic group are important for preparing functional derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alcohols provide a usefulreference chemistry against which this class of transformations may be evaluated. In general, the hydroxyl group proved to be a poor leaving group, and virtually all alcohol reacti ...
Organic Chemistry Unit
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) ...
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) ...
Naming carbon compounds - gilmorecollegeyr11chemistry
... • Are hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen • They only have single bonds • CnH2n + 2 • A series of compounds with similar properties in which each member differs from the previous one by –CH2 is known as a homologous series • Structural formulas show the number and location of bonds bu ...
... • Are hydrocarbons that contain only carbon and hydrogen • They only have single bonds • CnH2n + 2 • A series of compounds with similar properties in which each member differs from the previous one by –CH2 is known as a homologous series • Structural formulas show the number and location of bonds bu ...
aminoalkanes (or amines)
... E.g.: CH3CH2NH2 Ethylamine – amine –common name Aminoethane – aminoalkane – systematic name Ethanamine – alkanamine – systematic name Mines all contain a nitrogen atom in the organic molecule. They occur widely in nature and are used to manufacture local anaesthetics, sulfur drugs and many oth ...
... E.g.: CH3CH2NH2 Ethylamine – amine –common name Aminoethane – aminoalkane – systematic name Ethanamine – alkanamine – systematic name Mines all contain a nitrogen atom in the organic molecule. They occur widely in nature and are used to manufacture local anaesthetics, sulfur drugs and many oth ...
الشريحة 1
... A pi bond is one in which the electrons in the p orbitals are held above and below the plane of the molecule. The sigma bond is stronger than the pi bond. A double bond is formed from a sigma bond and a pi bond, and so it is stronger than a single bond. ...
... A pi bond is one in which the electrons in the p orbitals are held above and below the plane of the molecule. The sigma bond is stronger than the pi bond. A double bond is formed from a sigma bond and a pi bond, and so it is stronger than a single bond. ...
CH 3
... • Boiling Points: Compounds with hydrogen bonding have higher than expected boiling points: at SATP, C2H6 = gas but CH3OH = liquid. • Solubilities: Compounds with hydrogen bonds are usually soluble in water (a polar molecule): C6H14 = insoluble in water but C5H11OH = soluble in water. • Solubility d ...
... • Boiling Points: Compounds with hydrogen bonding have higher than expected boiling points: at SATP, C2H6 = gas but CH3OH = liquid. • Solubilities: Compounds with hydrogen bonds are usually soluble in water (a polar molecule): C6H14 = insoluble in water but C5H11OH = soluble in water. • Solubility d ...
Name
... 5. In the reaction 2Al2O3 → 4Al + 3O2, what is the mole ratio of aluminum to oxygen? a. 10:6 b. 3:4 c. 2:3 d. 4:3 6. In the reaction Ca + Cl2 → CaCl2, what is the mole ratio of chlorine to calcium chloride? a. 2:3 b. 2:1 c. 1:2 d. 1:1 ...
... 5. In the reaction 2Al2O3 → 4Al + 3O2, what is the mole ratio of aluminum to oxygen? a. 10:6 b. 3:4 c. 2:3 d. 4:3 6. In the reaction Ca + Cl2 → CaCl2, what is the mole ratio of chlorine to calcium chloride? a. 2:3 b. 2:1 c. 1:2 d. 1:1 ...
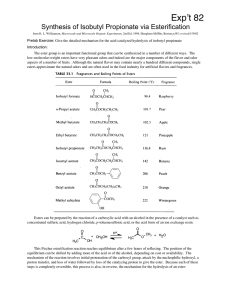
Synthesis of Isobutyl Propionate via Esterification
... Assemble a microscale chromatography column (see Lab Guide for review), being sure it is clamped in a vertical position. Close the valve, and fill the column with dichloromethane to the bottom of the funnel. Prepare a slurry of 1 g of silica gel in 4 mL of dichloromethane in a small beaker. Stir the ...
... Assemble a microscale chromatography column (see Lab Guide for review), being sure it is clamped in a vertical position. Close the valve, and fill the column with dichloromethane to the bottom of the funnel. Prepare a slurry of 1 g of silica gel in 4 mL of dichloromethane in a small beaker. Stir the ...
19-3 Esters and Anhydrides (PPT)
... zero, Go will be close to zero and the equilibrium constant for the reaction will be close to 1. The equilibrium can be shifted in the direction of the products by using an excess of one of the starting materials, or by removing either water or the ester from the reaction mixture. ...
... zero, Go will be close to zero and the equilibrium constant for the reaction will be close to 1. The equilibrium can be shifted in the direction of the products by using an excess of one of the starting materials, or by removing either water or the ester from the reaction mixture. ...
Organic Chemistry Unit Test! /50
... 1. Thalidomide has caused enormous grief, yet now it is a source of hope. Explain, using key terms and knowledge of organic chemistry, how thalidomide has gone from “zero to hero”. (4 marks) ...
... 1. Thalidomide has caused enormous grief, yet now it is a source of hope. Explain, using key terms and knowledge of organic chemistry, how thalidomide has gone from “zero to hero”. (4 marks) ...
Unit 1: Building Blocks Homework
... elements in the Periodic Table. Copy and complete the table by circling a word in each box to give correct information about each group. (Two pieces of correct information have already been circled.) ...
... elements in the Periodic Table. Copy and complete the table by circling a word in each box to give correct information about each group. (Two pieces of correct information have already been circled.) ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.