* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
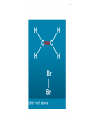
Organic Chemistry 10 Chemistry Quiz Alkanes • General Formula • Description • Combustion • Reactivity • Chemical test • Uses • CnH2n+2 • Saturated • Burns in Oxygen to form CO2 + H20 (CO with low O2) • Low • None • Fuels The chlorination of methane • Halogenation is the replacement of one or more hydrogens in an organic compound by halogen atoms • When methane is reacted with chlorine the products of the reaction depend on whether there is an excess of methane or chlorine • If there is an excess of methane it form chloromethane and hydrogen chloride To do • Write down a word equation for the chlorination of methane • Can you write a chemical equation? • How about a full balanced chemical equation? Movie Halogenation methane chlorine chloromethane hydrogen chloride CH 4 Cl2 CH3Cl HCl CH 4 ( g ) Cl2 ( g ) CH3Cl ( g ) HCl ( g ) With an excess of chlorine a mixture of products is formed. Chlorine can obviously replace up to 4 of the hydrogen atoms. Why halogenation? • These products are generally used as intermediate compound for further synthesis Natural Gas and Oil Separating the fractions Fractional distillation • Preheated crude oil is pumped into the column (340 C) • The vapour in the crude oil rises due to differences in density with different fractions condensing in different regions • The liquid part of the crude oil sinks in the column • The low density fractions are thin and light coloured, the high density fractions are ‘viscous’ and dark How does it work? • Components separate due to different boiling points • Crude oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons • Molecules are chemically bonded with strong covalent bonds but contain different numbers of carbon atoms Go on… • The weak attractive forces between the molecules have to be broken if the hydrocarbon is to boil • The longer the hydrocarbon molecule is, the stronger the intermolecular forces are • The shorter chains are more volatile – they form a vapour Boiling Volatility • We can smell petrol (gasoline) much easier than we can smell engine oil • This is because petrol has 5-10 carbon atoms and engine oil has 14-20 carbons atoms Combustion combustion Viscosity Viscosity Homework • Go to: http://www.rscoilstrike.org/preloader.swf • Play the game • Take a screen shot (print screen) or use the snipping tool to take an A4 image • Print this out and stick it in • Winner (most money) gets a ‘get out of homework free’ card Incomplete Combustion Alkanes The end of year test • Can contain ANYTHING we have covered over the course of this year (see specific learning objectives) • May contain anything from the Organic Chemistry too Origami time Youtube Homologous series • A family of hydrocarbons is a homologous series • This means they have the same functional groups • You can have alcohols (ROH), alkanes (RH), Haloalkanes (RX) and MANY OTHERS Roger Frost Isomerism • Hydrocarbons are based upon the number of carbon atoms • The carbon atoms can be rearranged in different ways: these are called isomers Alkenes Alkenes • • • • • Formed from cracking One or more double carbon bond Hence unsaturated Reactivity due to double bond Tested with bromine water Alkenes Alkenes • General Formula • Description • Combustion • Reactivity • Chemical test • Uses • CnH2n • unsaturated • Burns in Oxygen to form CO2 + H20 (CO with low O 2) • High (double bond), undergo addition reactions • Turns bromine water from brown to colourless • Making polymers Isomers of Alkenes Questions • Q1 (a) Draw displayed formulae for hexene • (b) Describe a test to distinguish between hexane and hexene • Q2 Draw two isomers of pentene • Homework: revise Next lesson • Oil spill clean up