Second Semester Review Part 1
... (C) If the compound is in state A, continued reduction of the pressure (at constant temperature) will cause it to melt. (D) None of these statements is correct. 100. A pure substance, above its melting point, is in a high pressure cylinder. Upon opening a valve on the cylinder a gas escapes. A press ...
... (C) If the compound is in state A, continued reduction of the pressure (at constant temperature) will cause it to melt. (D) None of these statements is correct. 100. A pure substance, above its melting point, is in a high pressure cylinder. Upon opening a valve on the cylinder a gas escapes. A press ...
Ch. 09 Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides
... Reaction of Ethers with Strong Acid • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. • HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleo ...
... Reaction of Ethers with Strong Acid • In order for ethers to undergo substitution or elimination reactions, their poor leaving group must first be converted into a good leaving group by reaction with strong acids such as HBr and HI. • HBr and HI are strong acids that are also sources of good nucleo ...
Carbocation Rearrangements
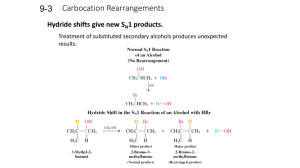
... Other carbocation rearrangements are due to alkyl shifts. Alkyl shifts, rather than hydride shifts, can occur when a carbocation lacks a suitable secondary or tertiary hydrogen next to the positively charged carbon. ...
... Other carbocation rearrangements are due to alkyl shifts. Alkyl shifts, rather than hydride shifts, can occur when a carbocation lacks a suitable secondary or tertiary hydrogen next to the positively charged carbon. ...
PDF aldehydes and ketones
... A carbanion C can form a p–d π bond with an adjacent P or S. The resulting charge delocalization is especially effective if P or S, furnishing the empty d orbital, also has a + charge. Carbanions with these characteristics are called ylides. ...
... A carbanion C can form a p–d π bond with an adjacent P or S. The resulting charge delocalization is especially effective if P or S, furnishing the empty d orbital, also has a + charge. Carbanions with these characteristics are called ylides. ...
Chapter 14
... ethers are used in many organic reactions where alcohols would be impossible to use ...
... ethers are used in many organic reactions where alcohols would be impossible to use ...
Organic Chem Class #2
... (plants and animals) could produce them. Urea was the first organic molecule that scientists synthesized, and they’ve been busy since. The organic molecules we will study are more complex than the simpler molecular and ionic compounds so far, but we get a bunch of tables to help us name them. Some c ...
... (plants and animals) could produce them. Urea was the first organic molecule that scientists synthesized, and they’ve been busy since. The organic molecules we will study are more complex than the simpler molecular and ionic compounds so far, but we get a bunch of tables to help us name them. Some c ...
Complex Ions
... To understand the different reactions that transition elements undergo. How are we going to learn it? Completing tutorial on naming complex ions and then conducting an activity on naming. ...
... To understand the different reactions that transition elements undergo. How are we going to learn it? Completing tutorial on naming complex ions and then conducting an activity on naming. ...
Organic reactions and mechanisms
... The classical structural theory of organic reactions The reactions of organic compounds were explained based on their structural formulae. They are essentially molecular in nature. The classical ‘structural theory’ visualized that the chemical behavior of an organic compound was determined by the fu ...
... The classical structural theory of organic reactions The reactions of organic compounds were explained based on their structural formulae. They are essentially molecular in nature. The classical ‘structural theory’ visualized that the chemical behavior of an organic compound was determined by the fu ...
Ch 10 Haloalkanes n haloarenes
... KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is strong than C-N bond. So alkyl cyanide is the major product but AgCN is covalent so more electronegative N can attach to C and forms isocyanides. Ans 2. Because Cl donates electron to the benzene ring by + R effect and electron density incr ...
... KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is strong than C-N bond. So alkyl cyanide is the major product but AgCN is covalent so more electronegative N can attach to C and forms isocyanides. Ans 2. Because Cl donates electron to the benzene ring by + R effect and electron density incr ...
SN1 vs. SN2 Reactions - Master Organic Chemistry
... Look for halogens (Cl, Br, I) or tosylates/mesylates (OTs, OMs) Alternatively, look for alcohols (OH) if acid is present Once you've identified the leaving group, instpect the carbon it is attached to. How many carbons is that carbon connected to? That will tell you if the carbon is primary, seconda ...
... Look for halogens (Cl, Br, I) or tosylates/mesylates (OTs, OMs) Alternatively, look for alcohols (OH) if acid is present Once you've identified the leaving group, instpect the carbon it is attached to. How many carbons is that carbon connected to? That will tell you if the carbon is primary, seconda ...
the Note
... Alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids when treated with strong oxidizing agents. Alcohol molecules have a non-polar hydrocarbon end and a polar –O-H section. ...
... Alcohols are oxidized to carboxylic acids when treated with strong oxidizing agents. Alcohol molecules have a non-polar hydrocarbon end and a polar –O-H section. ...
Synthesis of Esters
... variety of esters. So what? Well, esters have some unique and valuable properties. Many of the smaller esters have pleasant fragrances that are found in plants and foods. Other esters are a key component in medicinally valuable molecules - such as aspirin. In this lab, you will synthesize aspirin an ...
... variety of esters. So what? Well, esters have some unique and valuable properties. Many of the smaller esters have pleasant fragrances that are found in plants and foods. Other esters are a key component in medicinally valuable molecules - such as aspirin. In this lab, you will synthesize aspirin an ...
Abiotic synthesis of acylglycerols under simulated hydrothermal
... Abiotic formation of aliphatic lipid compounds (i.e., fatty acids, alcohols, and acylglycerols) has been reported to occur at elevated temperatures and pressures under simulated hydrothermal conditions (McCollom et al., 1999; Rushdi and Simoneit, 2001, 2006). Although abiotic chemistry may occur at ...
... Abiotic formation of aliphatic lipid compounds (i.e., fatty acids, alcohols, and acylglycerols) has been reported to occur at elevated temperatures and pressures under simulated hydrothermal conditions (McCollom et al., 1999; Rushdi and Simoneit, 2001, 2006). Although abiotic chemistry may occur at ...
Example
... Table 17.1 Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones from alkenes A number of reactions already studied provide efficient synthetic routes to aldehydes and ketones. ...
... Table 17.1 Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones from alkenes A number of reactions already studied provide efficient synthetic routes to aldehydes and ketones. ...
CHAPTER 11
... points. Second, they ordinarily react with metal ions in a single-step process, whereas with unidentate ligands usually involves two or more intermediate species. ...
... points. Second, they ordinarily react with metal ions in a single-step process, whereas with unidentate ligands usually involves two or more intermediate species. ...
STRUCTURE, INTERMOLECULAR FORCES AND SOLUBILITY
... Some compounds have a H to donate to hydrogen bonding, while others can only accept a H from other compounds to form hydrogen bonds. ...
... Some compounds have a H to donate to hydrogen bonding, while others can only accept a H from other compounds to form hydrogen bonds. ...
5. Functional Groups
... are a characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable way are composed of an atom or group of atoms are groups that replace a H in the corresponding alkane provide a way to classify families of organic compounds ...
... are a characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable way are composed of an atom or group of atoms are groups that replace a H in the corresponding alkane provide a way to classify families of organic compounds ...
oxidation number
... Assign bonding electrons: O is more electronegative than C, so in any bond between C and O, O is assigned or given all of the bonding electrons. For CO2, C shares eight bonding electrons with O. O gets all = 8. C = 0. Assign nonbonding electrons. C has 0, each O = 4. Sum of assigned electrons for C ...
... Assign bonding electrons: O is more electronegative than C, so in any bond between C and O, O is assigned or given all of the bonding electrons. For CO2, C shares eight bonding electrons with O. O gets all = 8. C = 0. Assign nonbonding electrons. C has 0, each O = 4. Sum of assigned electrons for C ...
Metal Complexes
... • Co(en)2Cl2+ – # ligands = 4 (two en’s, two Cl-’s) – C.N. = 6 (not 4!) because each en ligand makes two coordinate covalent bonds to the Co3+ using two different N atoms per ligand TM I-Intro to Complexes 15 ...
... • Co(en)2Cl2+ – # ligands = 4 (two en’s, two Cl-’s) – C.N. = 6 (not 4!) because each en ligand makes two coordinate covalent bonds to the Co3+ using two different N atoms per ligand TM I-Intro to Complexes 15 ...
Organic Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... points: at SATP, C2H6 = gas but CH3OH = liquid. - Solubilities: Compounds with hydrogen bonds are usually soluble in water (a polar molecule): C6H14 = insoluble in water but C5H11OH = soluble in water. Solubility decreases, as the molecule gets longer. (C12H25OH =slightly soluble in water). This is ...
... points: at SATP, C2H6 = gas but CH3OH = liquid. - Solubilities: Compounds with hydrogen bonds are usually soluble in water (a polar molecule): C6H14 = insoluble in water but C5H11OH = soluble in water. Solubility decreases, as the molecule gets longer. (C12H25OH =slightly soluble in water). This is ...
Ni complexes of redox-active pincers with pendant H-bonding sites
... attention, as they have been shown to efficiently effect the electrode-driven reduction of protons to hydrogen, a process of interest in industrial applications [4,5]. The reverse process, oxidation of hydrogen to protons and electrons has also been achieved [6]. The mechanistic understanding gained ...
... attention, as they have been shown to efficiently effect the electrode-driven reduction of protons to hydrogen, a process of interest in industrial applications [4,5]. The reverse process, oxidation of hydrogen to protons and electrons has also been achieved [6]. The mechanistic understanding gained ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.