Chapter 2 - U of L Class Index
... Electrons in the lower energy d orbitals can absorb photons and be excited into the higher energy d orbitals. Since ∆o corresponds to the energy of light in the visible region (and there is more than one way to absorb a photon), some wavelengths of visible light are absorbed. The wavelengths that a ...
... Electrons in the lower energy d orbitals can absorb photons and be excited into the higher energy d orbitals. Since ∆o corresponds to the energy of light in the visible region (and there is more than one way to absorb a photon), some wavelengths of visible light are absorbed. The wavelengths that a ...
Exam 2
... Chern 24 2 (w 2016) exam #2B 1. (10 pts) Circle what is true about Substitution and elimination reactions. ...
... Chern 24 2 (w 2016) exam #2B 1. (10 pts) Circle what is true about Substitution and elimination reactions. ...
Exam 2 Study Guide
... Exam 2, on Tuesday May 8th, will cover chapters 13 and 14.1 to 14.3. The exam is an open lecture and lab note but closed textbook exam. You will be provided a copy of the periodic table, electronegativity values and trends and a table of the functional groups that we study in this course, and thus y ...
... Exam 2, on Tuesday May 8th, will cover chapters 13 and 14.1 to 14.3. The exam is an open lecture and lab note but closed textbook exam. You will be provided a copy of the periodic table, electronegativity values and trends and a table of the functional groups that we study in this course, and thus y ...
Section 5b and c: crude oil and synthetic polymers Fractional
... Examples of monomers are ethane, glucose, amino acids, … There are two types of polymerization reactions: addition and condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization This type of polymerization can only be carried out by using unsaturated monomers, i.e. alkenes, as during this reaction the dou ...
... Examples of monomers are ethane, glucose, amino acids, … There are two types of polymerization reactions: addition and condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization This type of polymerization can only be carried out by using unsaturated monomers, i.e. alkenes, as during this reaction the dou ...
Chem 216 H W13 Notes - Dr. Masato Koreeda Thin
... adsorbent layer. When illuminated with an ultraviolet (UV) lamp, the absorbent then glows the pale green or blue colored fluorescent light. However, dark spots show up at the places where UVabsorbing organic compounds are located on the TLC plate because they quench the fluorescence. To be detectabl ...
... adsorbent layer. When illuminated with an ultraviolet (UV) lamp, the absorbent then glows the pale green or blue colored fluorescent light. However, dark spots show up at the places where UVabsorbing organic compounds are located on the TLC plate because they quench the fluorescence. To be detectabl ...
Intro to Transition Metal Complexes(CH 21) Valence Bond Theory
... factors, metal ligand complexes are often quite labile. That is, ligands are added/removed/replaced relatively easily ...
... factors, metal ligand complexes are often quite labile. That is, ligands are added/removed/replaced relatively easily ...
File
... Body odour often begins with secretions from glands called apocrine glands, which are most numerous in the armpits. Bacteria, which live in the armpits, use these secretions to produce energy and many different waste products. Scientists have isolated one of these waste products, compound E, which i ...
... Body odour often begins with secretions from glands called apocrine glands, which are most numerous in the armpits. Bacteria, which live in the armpits, use these secretions to produce energy and many different waste products. Scientists have isolated one of these waste products, compound E, which i ...
Chapter 22 - U of L Class Index
... Electrons in the lower energy d orbitals can absorb photons and be excited into the higher energy d orbitals. Since ∆o corresponds to the energy of light in the visible region (and there is more than one way to absorb a photon), some wavelengths of visible light are absorbed. The wavelengths that a ...
... Electrons in the lower energy d orbitals can absorb photons and be excited into the higher energy d orbitals. Since ∆o corresponds to the energy of light in the visible region (and there is more than one way to absorb a photon), some wavelengths of visible light are absorbed. The wavelengths that a ...
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
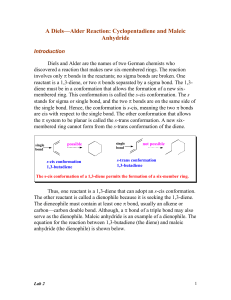
... We saw in previous lessons that some groups are electron donating (EDG) and some are electron withdrawing (EWG). The manner of substitution of electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups in the reactants governs how easily the reactants produce a Diels-Alder product. When you give someone dir ...
... We saw in previous lessons that some groups are electron donating (EDG) and some are electron withdrawing (EWG). The manner of substitution of electron-donating and electron-withdrawing groups in the reactants governs how easily the reactants produce a Diels-Alder product. When you give someone dir ...
Cell Molecules
... Macromolecules are organic molecules that weigh more than 100,000 daltons (ATOMIC MASS UNIT). ...
... Macromolecules are organic molecules that weigh more than 100,000 daltons (ATOMIC MASS UNIT). ...
alcohols - A-Level Chemistry
... Give the names and structures of all eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. State in each case whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols. Identify the three isomers which can give two different alkenes when dehydrated and identify the possible alkene products in each case. Identify t ...
... Give the names and structures of all eight alcohols with the formula C5H12O. State in each case whether they are primary, secondary or tertiary alcohols. Identify the three isomers which can give two different alkenes when dehydrated and identify the possible alkene products in each case. Identify t ...
2B - ligands 2
... a minimum of 3 donor atoms (usually O, N, S) - 4-6 donor atoms are the most common ligand structure type The “curvy bits” in the schematic diagram on the right are usually carbon-based chains. ...
... a minimum of 3 donor atoms (usually O, N, S) - 4-6 donor atoms are the most common ligand structure type The “curvy bits” in the schematic diagram on the right are usually carbon-based chains. ...
OS-FGI Lecture2
... The trick to achieving selective substitution (i.e. allylic bromination) is to know that the addition of Br• to the alkene is reversible whereas the allylic H-abstraction is effectively irreversible. A high concentration of Br2 favours the addition product by trapping out the intermediate radical A. ...
... The trick to achieving selective substitution (i.e. allylic bromination) is to know that the addition of Br• to the alkene is reversible whereas the allylic H-abstraction is effectively irreversible. A high concentration of Br2 favours the addition product by trapping out the intermediate radical A. ...
Document
... experiment to test the statement and fill out the chart. Write the statement and chart. Statement: Plants grow best in blue light. ...
... experiment to test the statement and fill out the chart. Write the statement and chart. Statement: Plants grow best in blue light. ...
1044771584 - Papacambridge
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
- cK-12
... 1. What happens to the oxidation number of an element that is oxidized in a reaction? a) Its oxidation number increases. b) Its oxidation number decreases. c) Its oxidation number changes from positive to negative. d) Its oxidation number may increase or decrease. ...
... 1. What happens to the oxidation number of an element that is oxidized in a reaction? a) Its oxidation number increases. b) Its oxidation number decreases. c) Its oxidation number changes from positive to negative. d) Its oxidation number may increase or decrease. ...
Reactivity of Transition Metal Complexes
... • insensitive to nature of incoming ligand L’ • more common for high coordination number complexes and those containing very bulky ligands L ...
... • insensitive to nature of incoming ligand L’ • more common for high coordination number complexes and those containing very bulky ligands L ...
Topic 12: Organic Chemistry
... below, pay attention to how the products of each reaction is formed from the given reactants. You are often asked to predict a reactant or a product of ...
... below, pay attention to how the products of each reaction is formed from the given reactants. You are often asked to predict a reactant or a product of ...
Document
... • Fuels (e.g. the RM1.92 RM2.10 Ron95) are made up mostly of alkanes. In excess oxygen • CnH2n+2 + (1.5n+½)O2 nCO2 + (n+1)H2O ...
... • Fuels (e.g. the RM1.92 RM2.10 Ron95) are made up mostly of alkanes. In excess oxygen • CnH2n+2 + (1.5n+½)O2 nCO2 + (n+1)H2O ...
National 5 Unit 1 Homework Booklet
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
... (c) Name the two pollutant gases changed by the catalyst and describe what they are changed into. 4. Explain why solid citric acid does not conduct electricity yet when it dissolves in water it does conduct. 5. Electrolysis of acids can be used to confirm the presence of hydrogen ions. (a) At which ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.