unit (7) organic compounds: hydrocarbons
... a) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond starts at carbon 2. The name is 2-pentene. The two identical groups (the hydrogen atoms) are on the same side of the double, so we use the prefix “cis”. The full name is cis-2-pentene. b) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond sta ...
... a) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond starts at carbon 2. The name is 2-pentene. The two identical groups (the hydrogen atoms) are on the same side of the double, so we use the prefix “cis”. The full name is cis-2-pentene. b) The longest chain has 5 carbons with the double bond sta ...
Carboxylic acid
... exist primarily of dimers (two molecules held together by H-bonding) • Because of the above properties, carboxylic acids have high boiling points (higher than corresponding alcohols) • Those with less than 5 carbons are soluble in water - those with more than 5 C’s can be soluble when ionized O C ...
... exist primarily of dimers (two molecules held together by H-bonding) • Because of the above properties, carboxylic acids have high boiling points (higher than corresponding alcohols) • Those with less than 5 carbons are soluble in water - those with more than 5 C’s can be soluble when ionized O C ...
Oxoacids of Phosphorus
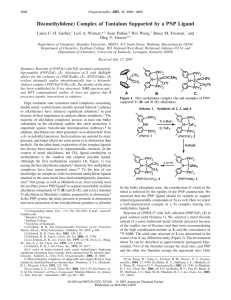
... The reaction of P4 O6 or PCl3 with water yields phosphorous acid, H3 PO3 ; which like hypophosphorous acid is a solid (Mp = 70.1 ◦ C) and very soluble in water. The structure is shown by X-ray crystallography to be comprised of a tetrahedral phosphorus with one hydride and two hydroxides (Figure 1b) ...
... The reaction of P4 O6 or PCl3 with water yields phosphorous acid, H3 PO3 ; which like hypophosphorous acid is a solid (Mp = 70.1 ◦ C) and very soluble in water. The structure is shown by X-ray crystallography to be comprised of a tetrahedral phosphorus with one hydride and two hydroxides (Figure 1b) ...
Metal Complexes
... • Ligands that bind to a metal cation via: – one donor atom are called monodentate ligands • Cl-, NH3, CN-, H2O (donor atoms are, respectively, Cl, N, C (or N!), O ...
... • Ligands that bind to a metal cation via: – one donor atom are called monodentate ligands • Cl-, NH3, CN-, H2O (donor atoms are, respectively, Cl, N, C (or N!), O ...
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 11 Handouts 12 1 2 3 Conversions of
... 3. PBr3 or HBr can convert an alcohol into RBr, capable of normal substitution and elimination reactions. Retrosynthesis Problems (In which you decide what to start from): Design syntheses for the following. Allowed starting materials include: Bromobenzene cyclopentanol any acyclic alcohol or alkene ...
... 3. PBr3 or HBr can convert an alcohol into RBr, capable of normal substitution and elimination reactions. Retrosynthesis Problems (In which you decide what to start from): Design syntheses for the following. Allowed starting materials include: Bromobenzene cyclopentanol any acyclic alcohol or alkene ...
Structural Knowledge Base Development for Metal Complexes
... For a range of metal and ligand types identify factors which influence M-L bond lengths and evaluate their importance. For a defined Metal-Ligand group sub-divide bond length distribution to produce ‘chemically meaningful’ ...
... For a range of metal and ligand types identify factors which influence M-L bond lengths and evaluate their importance. For a defined Metal-Ligand group sub-divide bond length distribution to produce ‘chemically meaningful’ ...
OCR A Level Chemistry B (Salters) Multiple Choice Questions Quiz
... Correct answer: Alkanes have only instantaneous dipole–induced dipole bonds; aldehydes also have permanent dipole– permanent dipole bonds and alcohols can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. Your answer ...
... Correct answer: Alkanes have only instantaneous dipole–induced dipole bonds; aldehydes also have permanent dipole– permanent dipole bonds and alcohols can form hydrogen bonds between molecules. Your answer ...
Lecture Review of Organic Chemistry and Herbicide Chemistry
... the acid form of 2,4-D is only slightly soluble in water and oil so use is limited in commercial formulations the acid can be reacted with bases to form salts: common salt formulations include sodium, potassium, ammonium, lithium, and several amine salts these compounds ionize (dissociate) in water ...
... the acid form of 2,4-D is only slightly soluble in water and oil so use is limited in commercial formulations the acid can be reacted with bases to form salts: common salt formulations include sodium, potassium, ammonium, lithium, and several amine salts these compounds ionize (dissociate) in water ...
Organic Naming Guide
... Alkenes = -ene ending Hydrocarbons that contain multiple bonds are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. If the hydrocarbon has one double bond, its general formula will be CnH2n, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the compound. The alkene family uses the -ene ending. The double bond is stronger t ...
... Alkenes = -ene ending Hydrocarbons that contain multiple bonds are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. If the hydrocarbon has one double bond, its general formula will be CnH2n, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the compound. The alkene family uses the -ene ending. The double bond is stronger t ...
Organometallics - X-Ray - University of Kentucky
... and DFT computational studies. It does not appear that 4 possesses agostic interactions in solution. High oxidation state transition metal complexes containing double metal-carbon bonds (usually termed Schrock1 carbenes or alkylidenes) have attracted significant attention,2 in part because of their ...
... and DFT computational studies. It does not appear that 4 possesses agostic interactions in solution. High oxidation state transition metal complexes containing double metal-carbon bonds (usually termed Schrock1 carbenes or alkylidenes) have attracted significant attention,2 in part because of their ...
Transition Metals & Complex ions
... and cobalt(II) ions have four chloride ions bonded to them rather than six, because the chloride ions are too big to fit any more around the central metal ion. ...
... and cobalt(II) ions have four chloride ions bonded to them rather than six, because the chloride ions are too big to fit any more around the central metal ion. ...
2.277 October 2005 Mid-Term Test
... An enzyme-catalyzed reaction was carried out with the substrate concentration initially a thousand times greater than the Km for that substrate. After 9 minutes, 1% of the substrate had been converted to product, and the amount of product formed in the reaction mixture was 12 µmol. If, in a separate ...
... An enzyme-catalyzed reaction was carried out with the substrate concentration initially a thousand times greater than the Km for that substrate. After 9 minutes, 1% of the substrate had been converted to product, and the amount of product formed in the reaction mixture was 12 µmol. If, in a separate ...
Final Study Questions - Porterville College Home
... benzene, C6H6 cyclohexatriene, C6H12 cyclohexene, C6H10 cyclohexatriene, C6H9 cyclohexane, C6H12 ...
... benzene, C6H6 cyclohexatriene, C6H12 cyclohexene, C6H10 cyclohexatriene, C6H9 cyclohexane, C6H12 ...
IMPORTANT CONCEPTS IN ALKYNE CHEMISTRY
... Carbon nucleophiles are widely used in organic synthesis to create new carbon-carbon bonds when they react with electrophiles, and therefore exapand a carbon chain. To be nucleophilic, the carbon atom must be bonded to a less electronegative atom to create a dipole favoring higher electron density o ...
... Carbon nucleophiles are widely used in organic synthesis to create new carbon-carbon bonds when they react with electrophiles, and therefore exapand a carbon chain. To be nucleophilic, the carbon atom must be bonded to a less electronegative atom to create a dipole favoring higher electron density o ...
assignment 4-2
... Hydrogen bonding in organic compounds influences their characteristic properties, such as boiling point, solubility, etc. Alcohols show hydrogen bonding due to the presence of an oxygen atom. Which of the compounds shown below shows the greatest hydrogen-bonding effect? a. CH3 – CH2 – OH c. CH3 – OH ...
... Hydrogen bonding in organic compounds influences their characteristic properties, such as boiling point, solubility, etc. Alcohols show hydrogen bonding due to the presence of an oxygen atom. Which of the compounds shown below shows the greatest hydrogen-bonding effect? a. CH3 – CH2 – OH c. CH3 – OH ...
Year 12 Unit 1b - Moulsham High School
... aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids. 2o alcohols are oxidised to ketones. results of testing oxidation products with Benedict’s solution – Aldehydes give a brick red precipitate with Benedict’s. Ketones do not react at all. Dehydration to alkene – Water is lost from the alcohol to make the alkene ...
... aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids. 2o alcohols are oxidised to ketones. results of testing oxidation products with Benedict’s solution – Aldehydes give a brick red precipitate with Benedict’s. Ketones do not react at all. Dehydration to alkene – Water is lost from the alcohol to make the alkene ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
NCEA Level 1 Chemistry (90932) 2015
... Process 1: Fractional distillation Process 2: Cracking Process 3: Polymerisation ...
... Process 1: Fractional distillation Process 2: Cracking Process 3: Polymerisation ...
106KB - NZQA
... Process 1: Fractional distillation Process 2: Cracking Process 3: Polymerisation ...
... Process 1: Fractional distillation Process 2: Cracking Process 3: Polymerisation ...
Unit 1: Learning Outcomes
... An ultra-violet / visible spectrometer measures the intensity of radiation transmitted through the sample and compares this with the intensity of incident radiation. Transition metals or their compounds act as catalysts in many chemical reactions It is believed that the presence of unpaired d electr ...
... An ultra-violet / visible spectrometer measures the intensity of radiation transmitted through the sample and compares this with the intensity of incident radiation. Transition metals or their compounds act as catalysts in many chemical reactions It is believed that the presence of unpaired d electr ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
8.2-Organic Nomenclature packet
... Alkenes = -ene ending Hydrocarbons that contain multiple bonds are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. If the hydrocarbon has one double bond, its general formula will be CnH2n, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the compound. The alkene family uses the -ene ending. The double bond is stronger th ...
... Alkenes = -ene ending Hydrocarbons that contain multiple bonds are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. If the hydrocarbon has one double bond, its general formula will be CnH2n, where n is the number of carbon atoms in the compound. The alkene family uses the -ene ending. The double bond is stronger th ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.